1) Effective language teaching involves motivating students through a combination of intrinsic and extrinsic factors like enjoyment, satisfaction, and social interaction.
2) While immersion programs provide extensive exposure, they require at least a year abroad and are very expensive. Quality teaching from knowledgeable teachers is important for any language program to be successful.
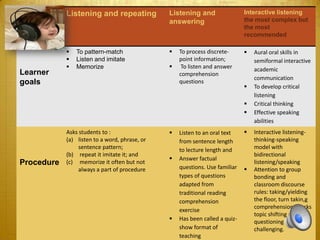
3) Successful early language learning focuses on listening, speaking, reading and writing skills through frequent practice, attention to individual needs, and encouraging cultural understanding and collaboration between students.