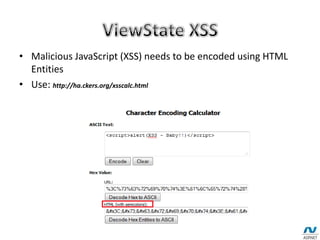
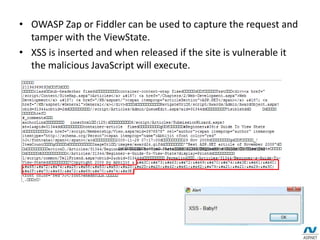
Stateless means there is no persistent connection between the server and client - the server responds to each client request independently without remembering previous requests. Stateless sites require clients to provide credentials for every request, while stateful sites maintain session state through techniques like cookies and viewstate. Viewstate stores page and control state to allow ASP.NET to repopulate form fields on postbacks, but it is only base64-encoded by default, not encrypted, so its contents may be readable or tamperable by attackers through tools like Fiddler. Developers should avoid storing sensitive data in viewstate and use encryption and signing to prevent viewstate tampering attacks.