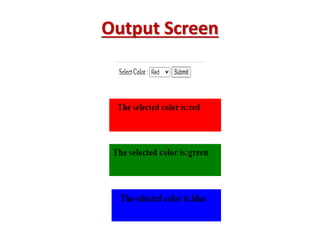
Cookies are small text files created by web servers that are stored in web browsers. They allow servers to maintain state between HTTP requests from a browser. There are two types of cookies - permanent/persistent cookies that are stored on a user's computer and not deleted when the browser closes, and session/transient cookies that are stored in memory only during a user's browsing session and deleted when the browser closes. Cookies are commonly used to track website activity, for online shopping carts, and to provide personalized web pages. They work by the server adding a cookie to the response which gets stored in the browser cache, and the browser then sends that cookie back with subsequent requests so the server can recognize the user.

![Cookies
• Hyper Text Transfer Protocol [HTTP]
does not maintain a persistent connection.
Each request made by a Web browser is
made using a new connection. Hence this
protocol does not maintain state across
HTTP requests, so cookies are used.
• Cookies are small text files that are
created by a server side program such as
a Servlet run at the Web server.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enterprisejavaunit-2chapter-2-210914080401/85/Enterprise-java-unit-2_chapter-2-2-320.jpg)





![Session / Transient Cookies
Session or Transient cookies are those cookies that are
stored in the computer’s memory only during a user’s
browsing session and are automatically deleted from the
user’s computer when the Web browser is closed.
Those cookies usually store a session ID that is not
permanently bound to the user, allowing the user to move
from page to page without having to login repeatedly. They
are widely used by commercial websites [for example, to
keep track of items that a consumer has added to a
shopping cart].
Session cookies are never written on the hard drive and
they do not collect any information from the user’s
computer. Session cookies expire at the end of the user’s
browser session.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enterprisejavaunit-2chapter-2-210914080401/85/Enterprise-java-unit-2_chapter-2-8-320.jpg)



![SecondServlet.java
public class SecondServlet extends HttpServlet
{
protected void processRequest(HttpServletRequest
request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8");
try (PrintWriter out = response.getWriter())
{
Cookie ck[]=request.getCookies();
out.print("Hello" +ck[0].getValue());
out.close();
} }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enterprisejavaunit-2chapter-2-210914080401/85/Enterprise-java-unit-2_chapter-2-12-320.jpg)