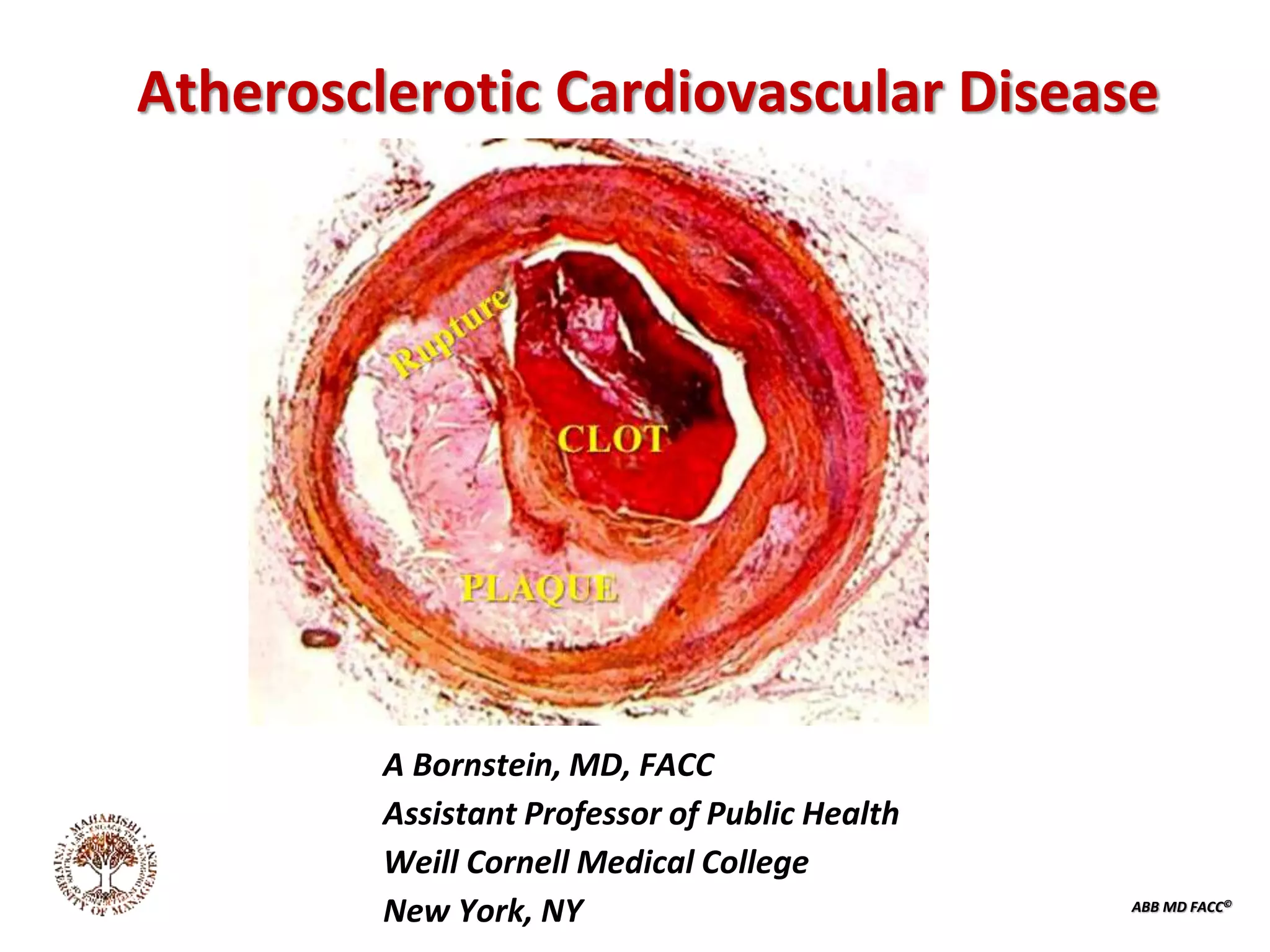
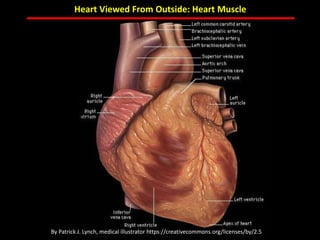
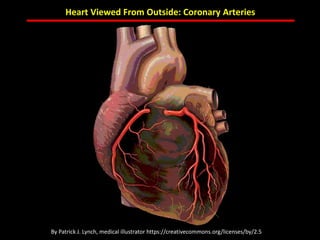
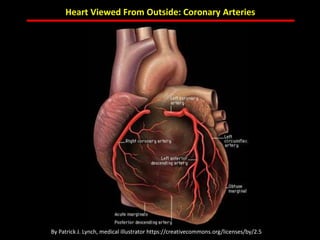
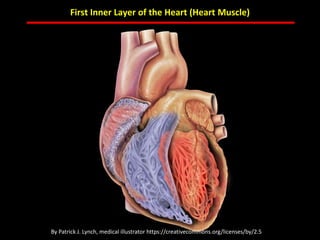
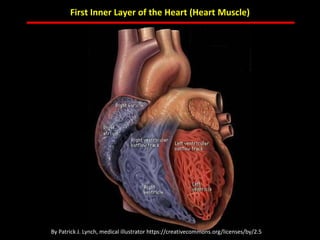
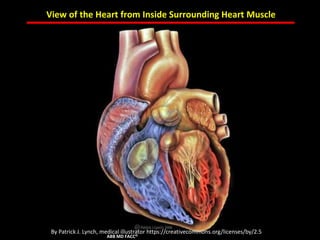
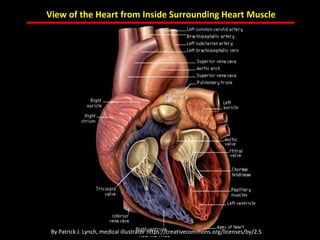
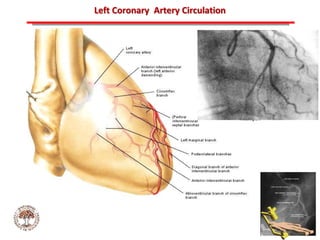
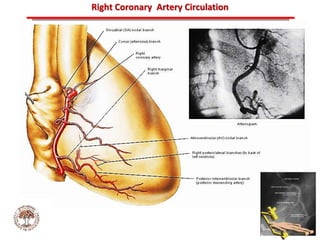
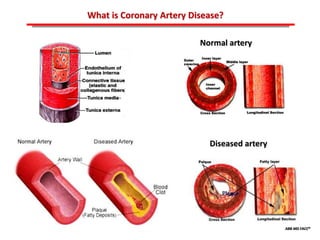
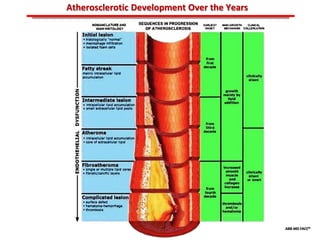
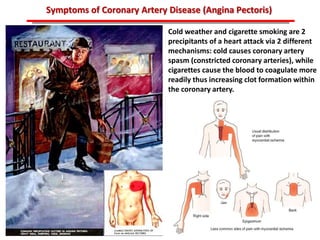
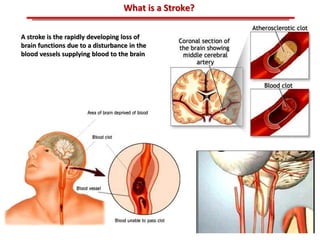
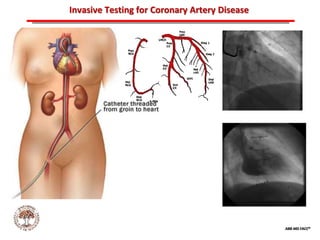
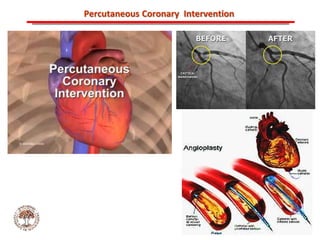
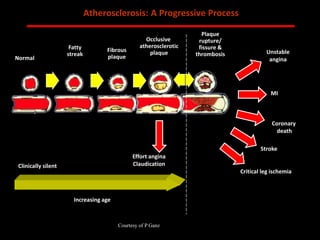
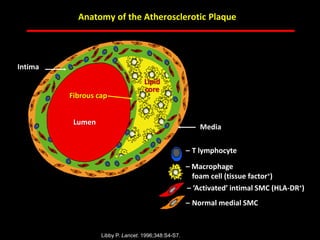
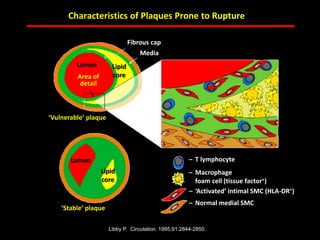
The document discusses atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease and coronary artery disease. It provides illustrations and descriptions of the heart anatomy, including the coronary arteries and heart muscle. Risk factors for coronary artery disease and heart attack are outlined, along with descriptions of atherosclerosis, angina, heart attack, and diagnostic tests like cardiac catheterization. Invasive treatments for coronary artery disease like percutaneous coronary intervention are also mentioned.