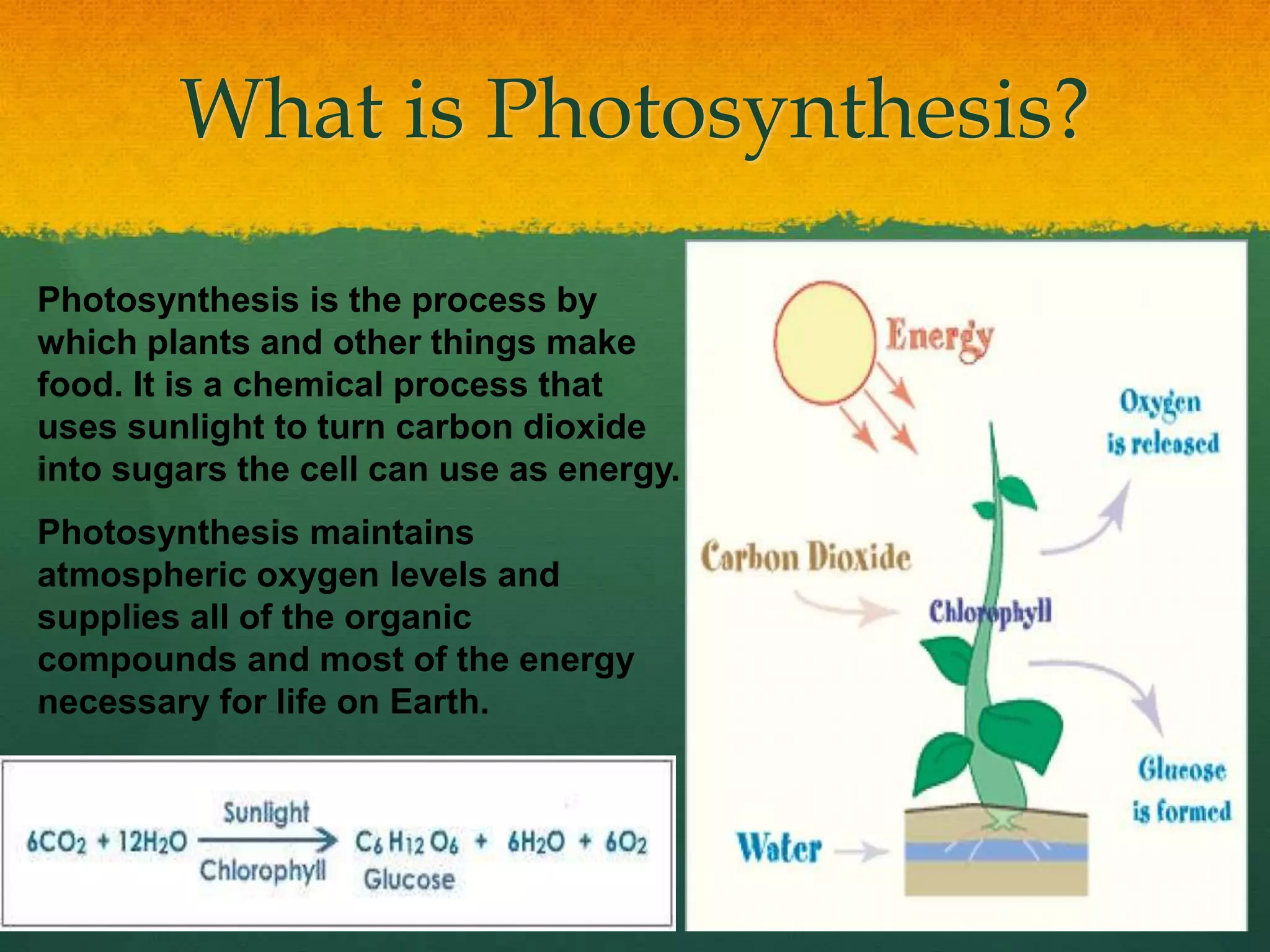
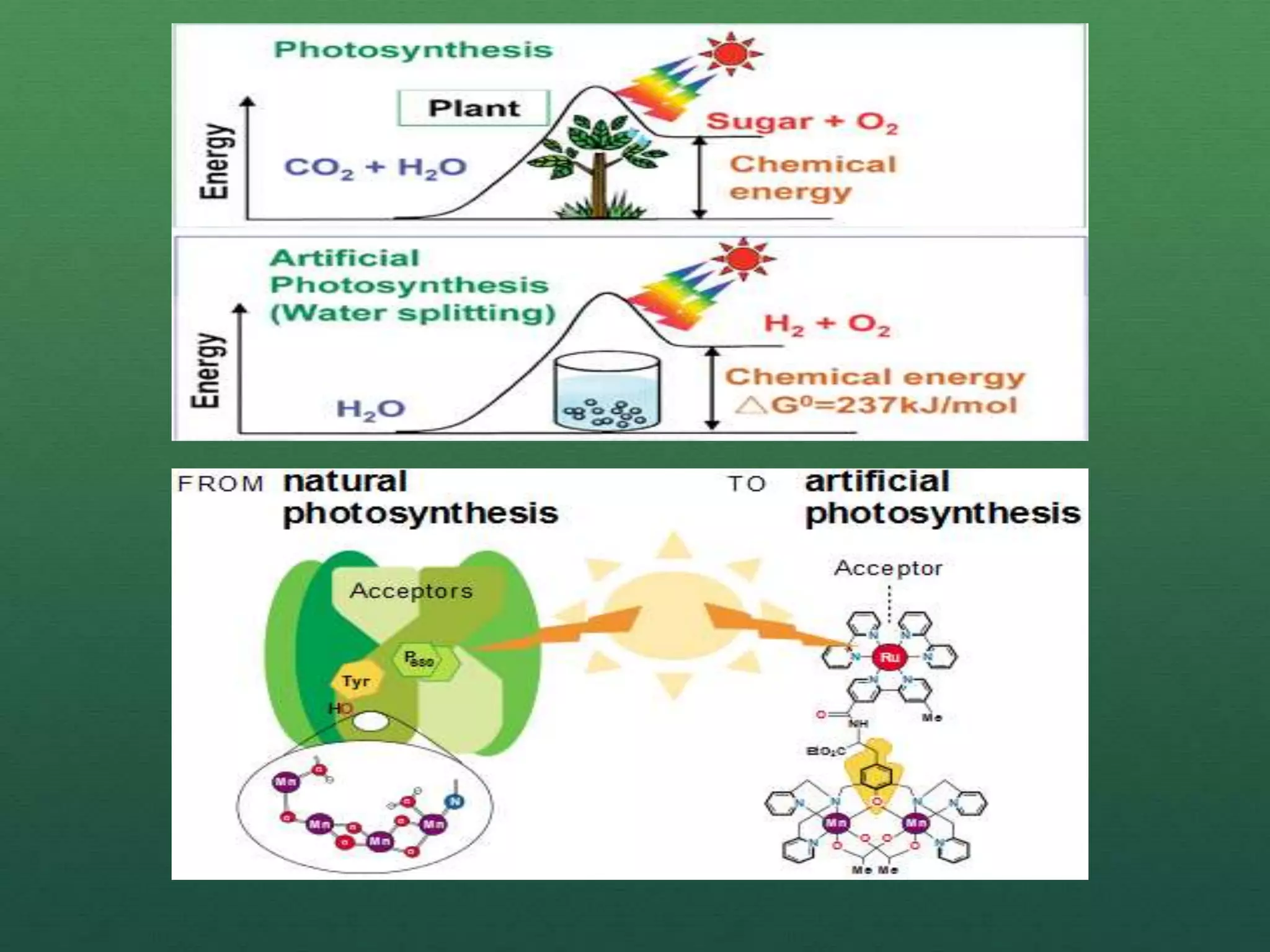
Photosynthesis is a natural process that enables plants to convert sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into food and oxygen, while artificial photosynthesis mimics this process to produce solar fuels like hydrogen. Key components include catalysts, such as manganese and cobalt oxide, which facilitate the water-splitting reaction necessary for energy conversion. Despite challenges like catalyst instability and material degradation, artificial photosynthesis offers a promising, eco-friendly alternative to fossil fuels.