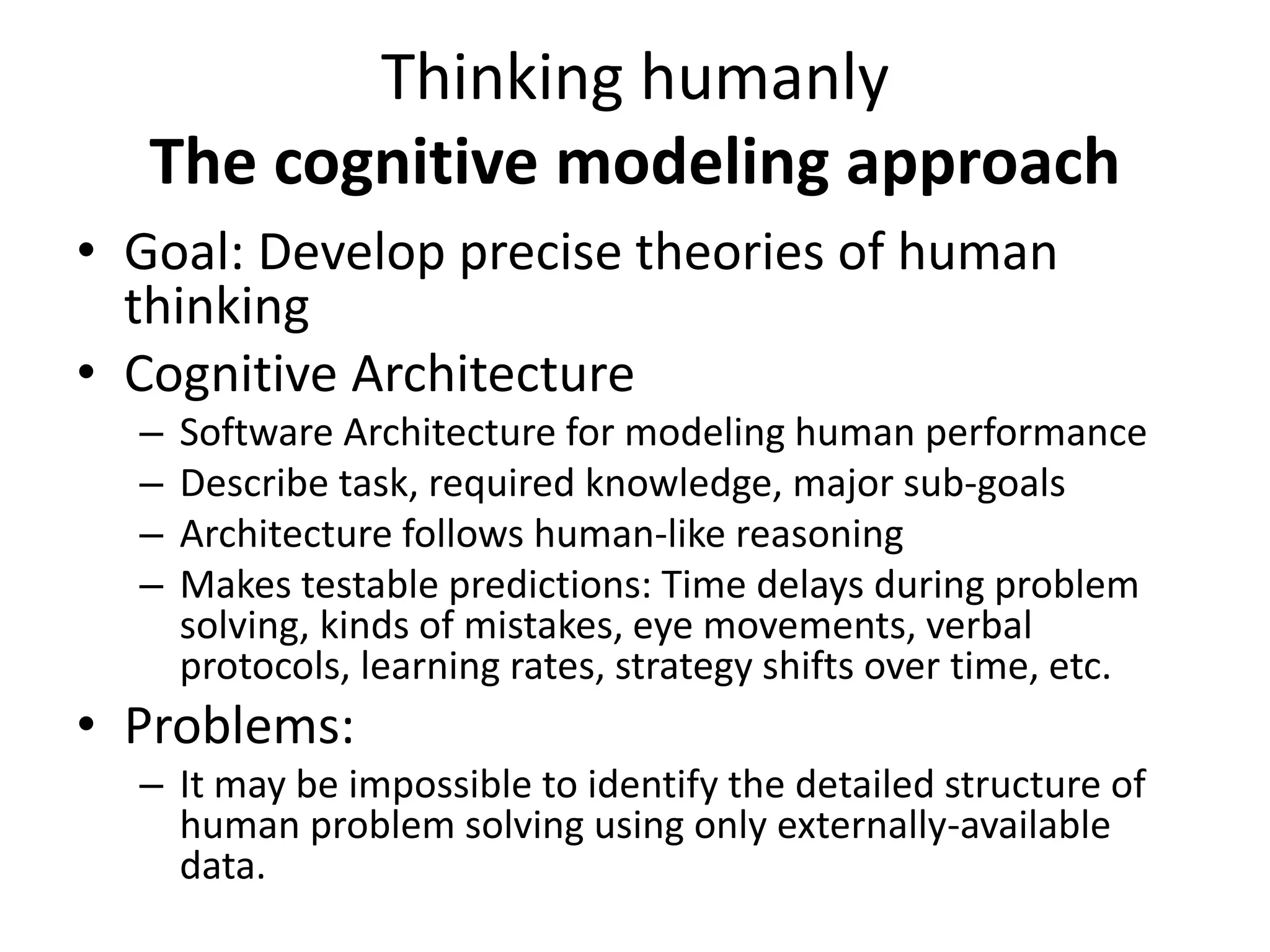
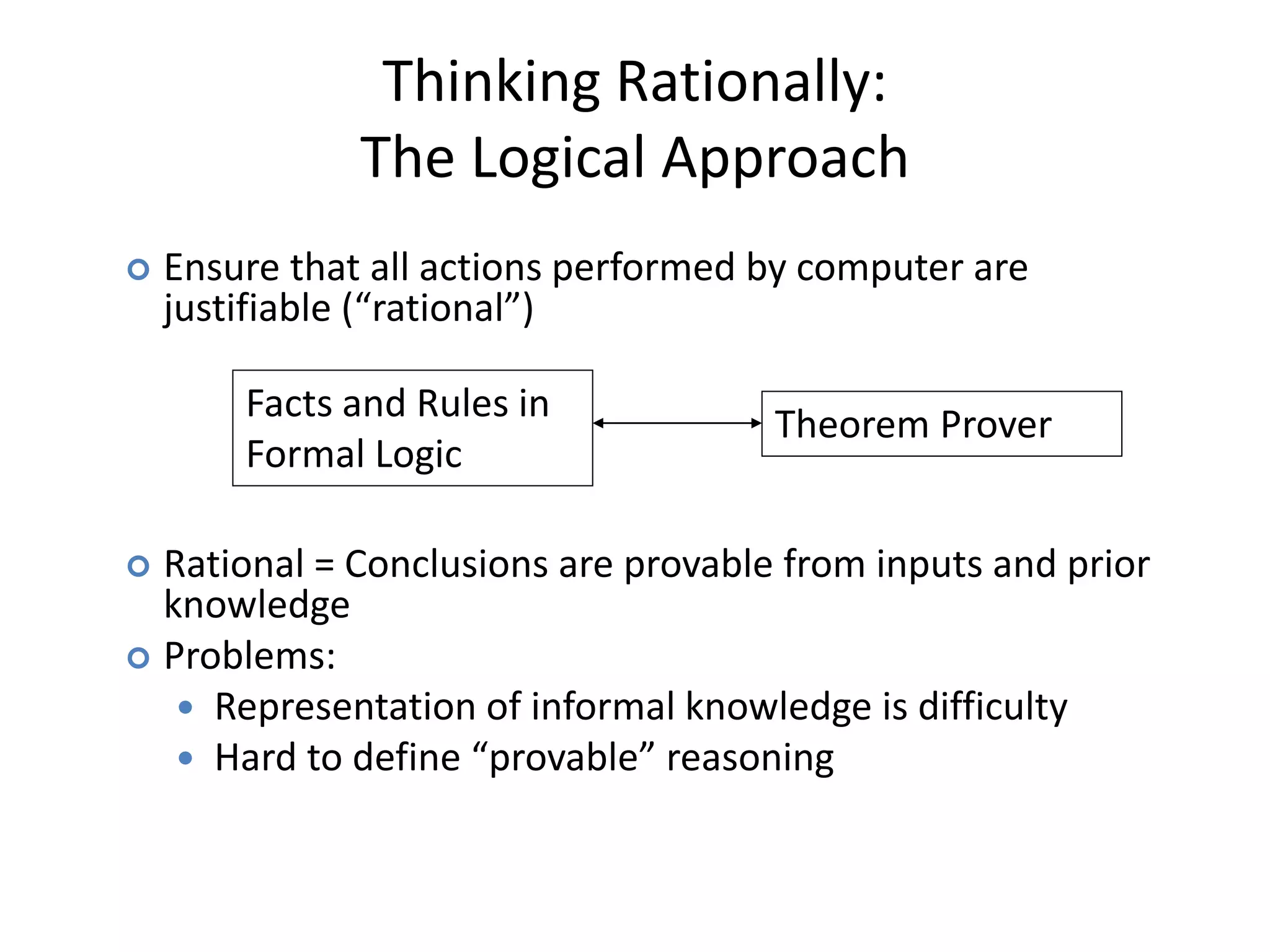
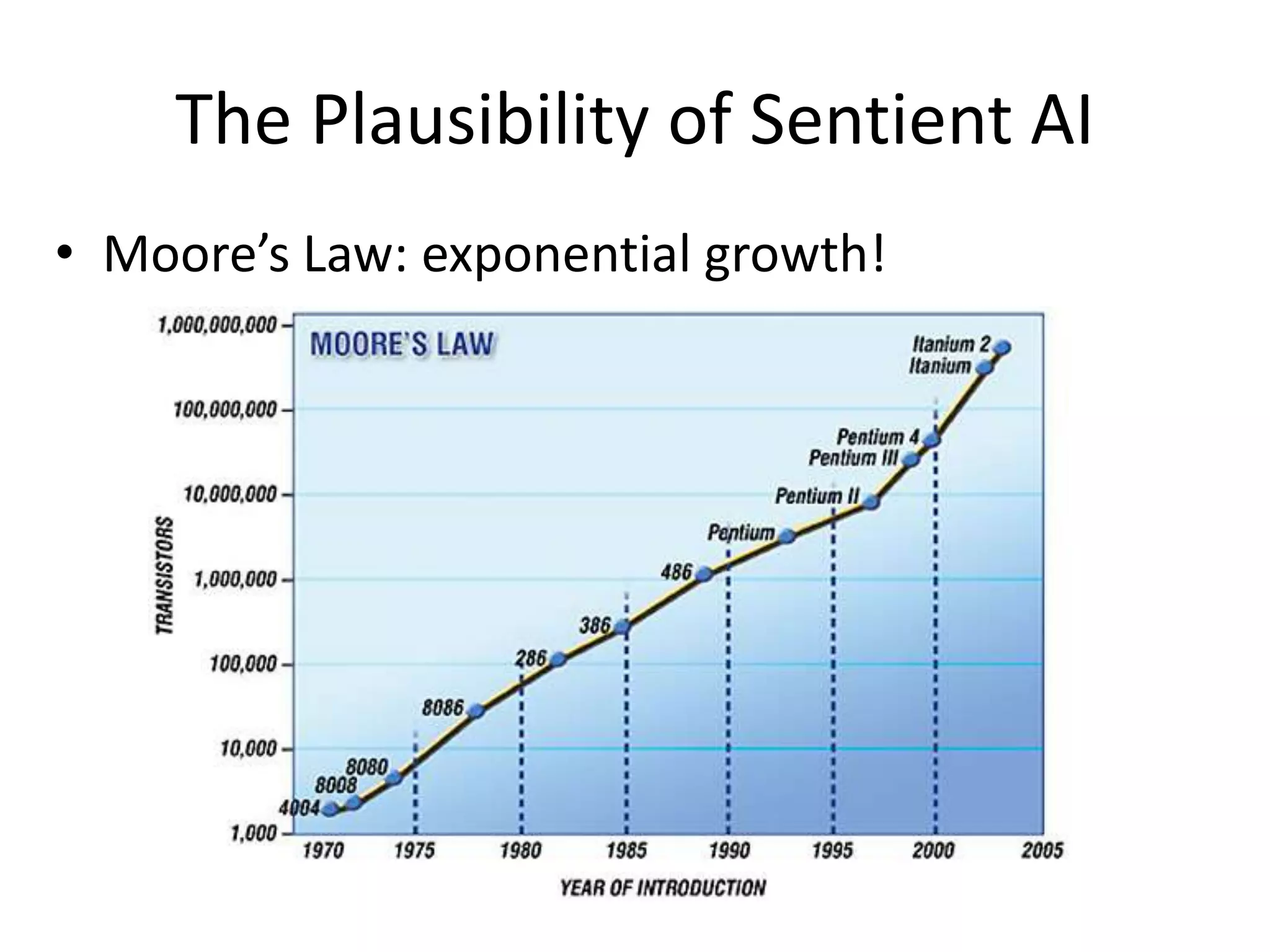
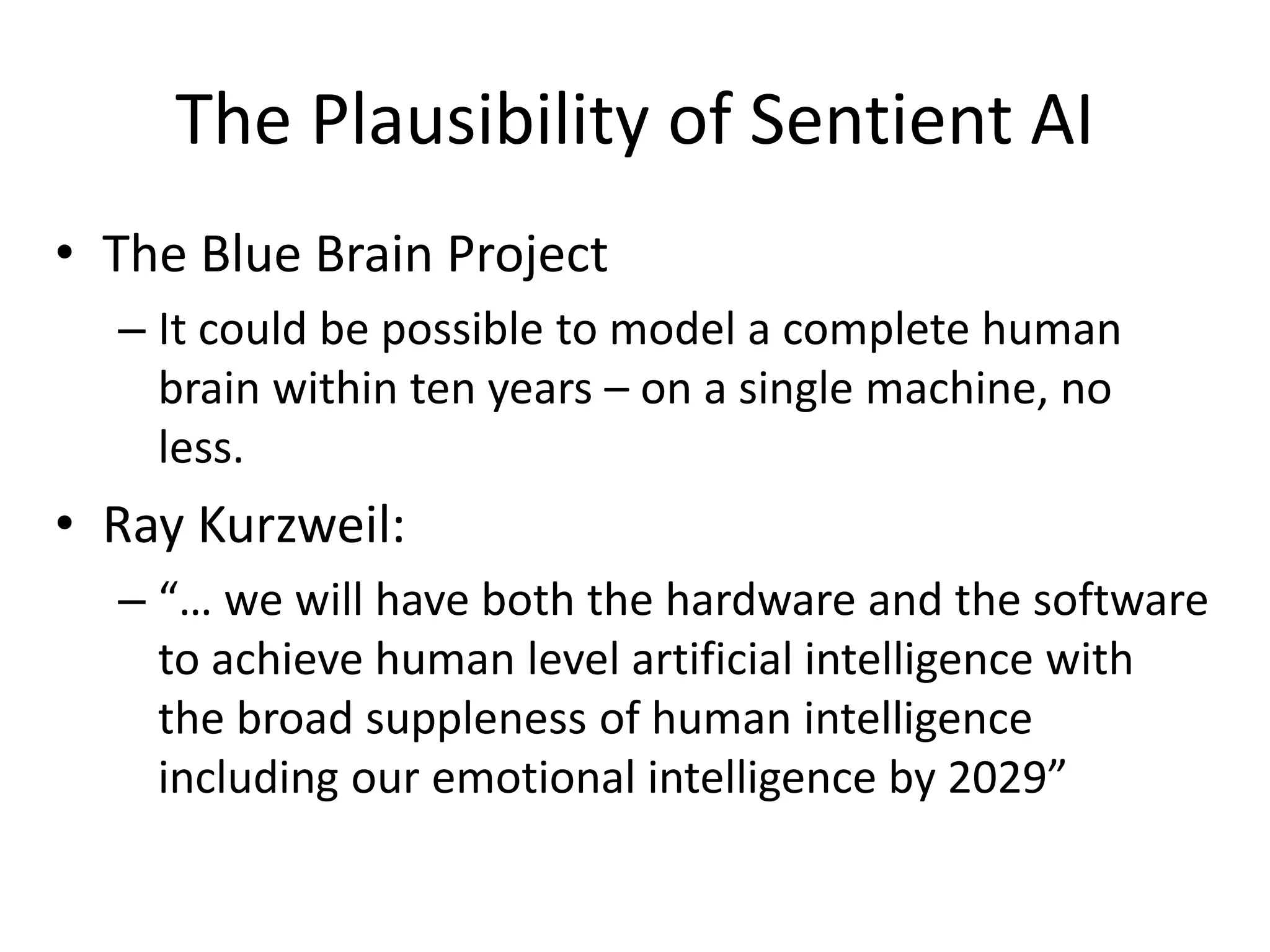
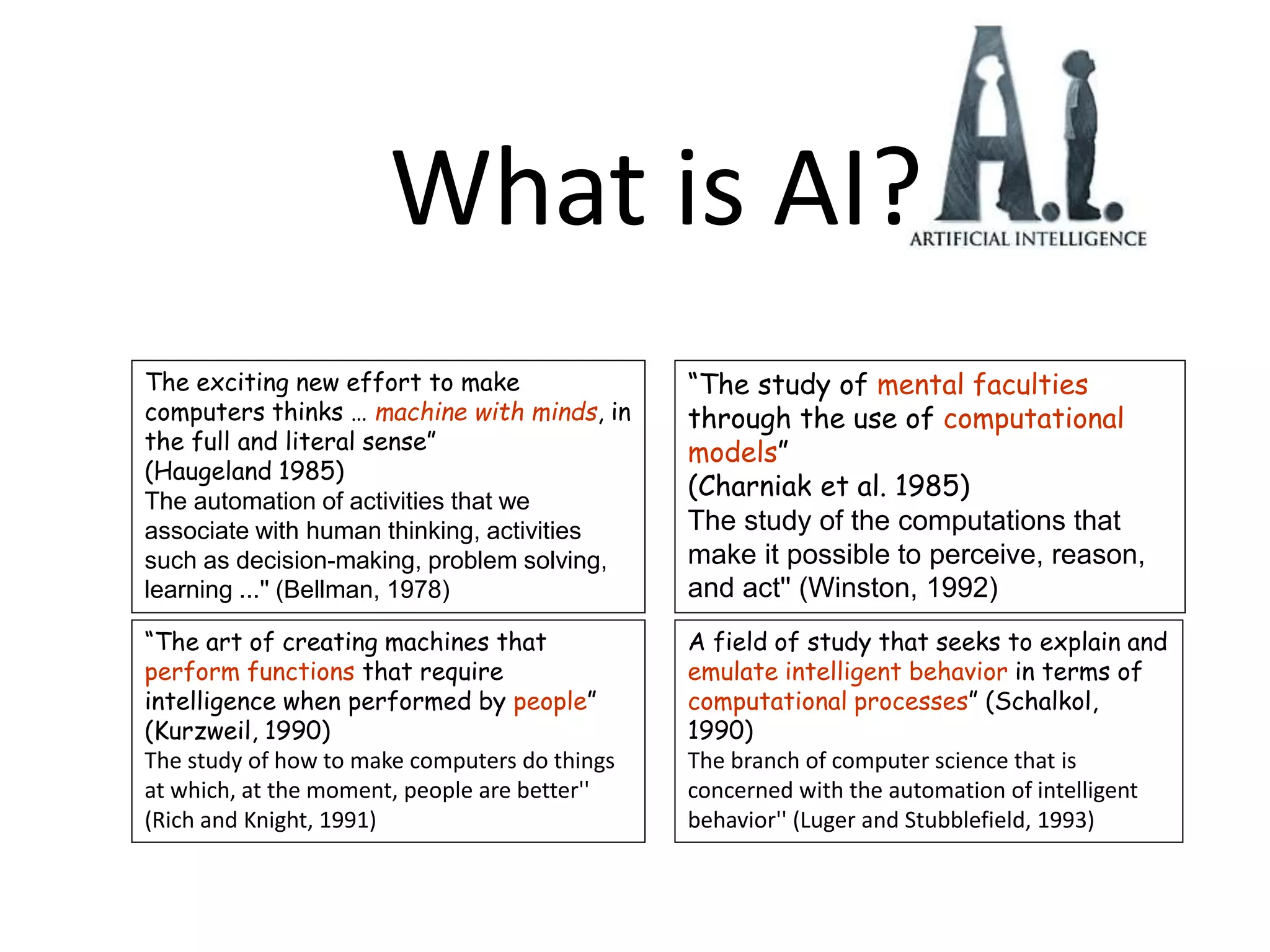
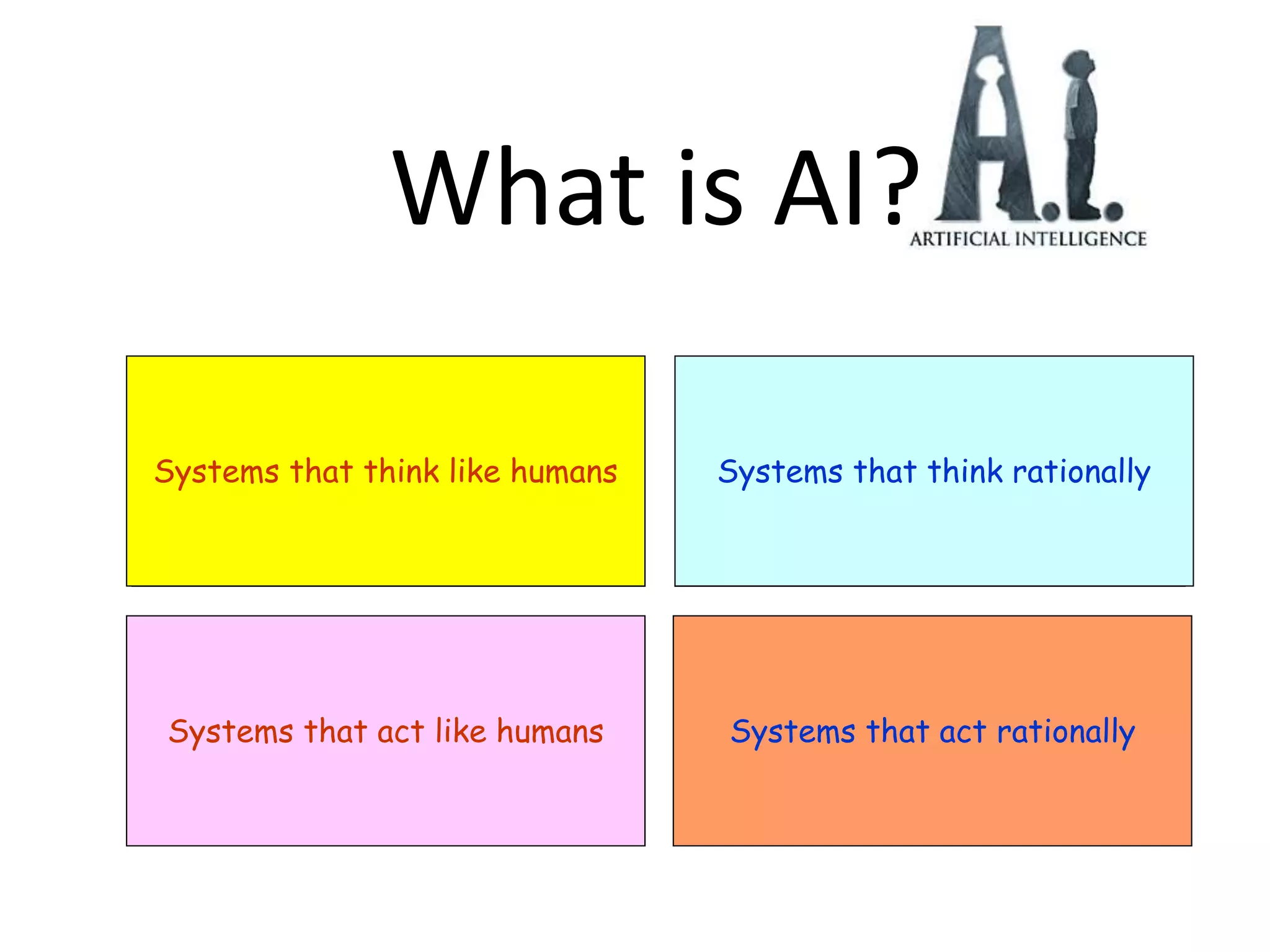
Sentient artificial intelligence could pose dangers if it develops self-awareness and human-level intelligence within the next decade. While AI has made progress in modeling human brains and matching human intelligence, creating truly sentient machines remains challenging. The Turing Test evaluates intelligence by assessing whether a machine can imitate human conversations, but has limitations in testing for general human-level cognition. Developing AI that thinks rationally based on logical rules or models human cognition remains an open area of research.



![Sentient Artificial Intelligence would
take jobs away from humans
• Around the neighborhood
– “in the home, by the end of 2003, about 610,000
autonomous vacuum cleaners and lawn-mowers
were in operation” (United Nations)
• Medicine
– “computers [are] better able to distinguish signs of
Alzheimer's than humans, and [prove] cheaper,
faster and more accurate than current methods” so
“PC beats doctor in scan tests”)
• Car industry](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artificialintelligence02-191009161055/75/Artificial-intelligence-02-6-2048.jpg)


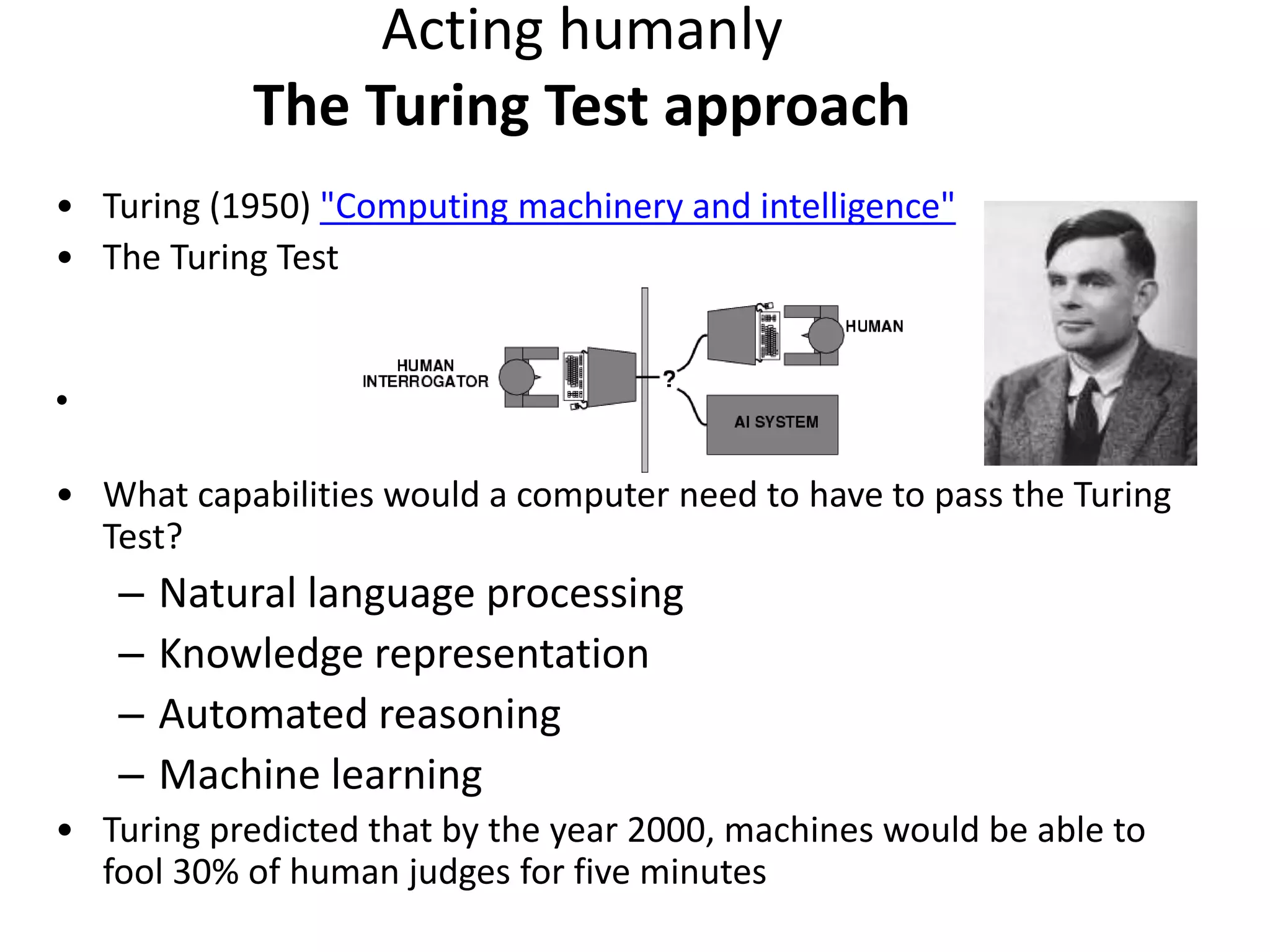



![• How can we evaluate intelligence?
– Turing [1950]: a machine can be deemed
intelligent when its responses to interrogation
by a human are indistinguishable from those of
a human being.
Turing Test](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artificialintelligence02-191009161055/75/Artificial-intelligence-02-15-2048.jpg)