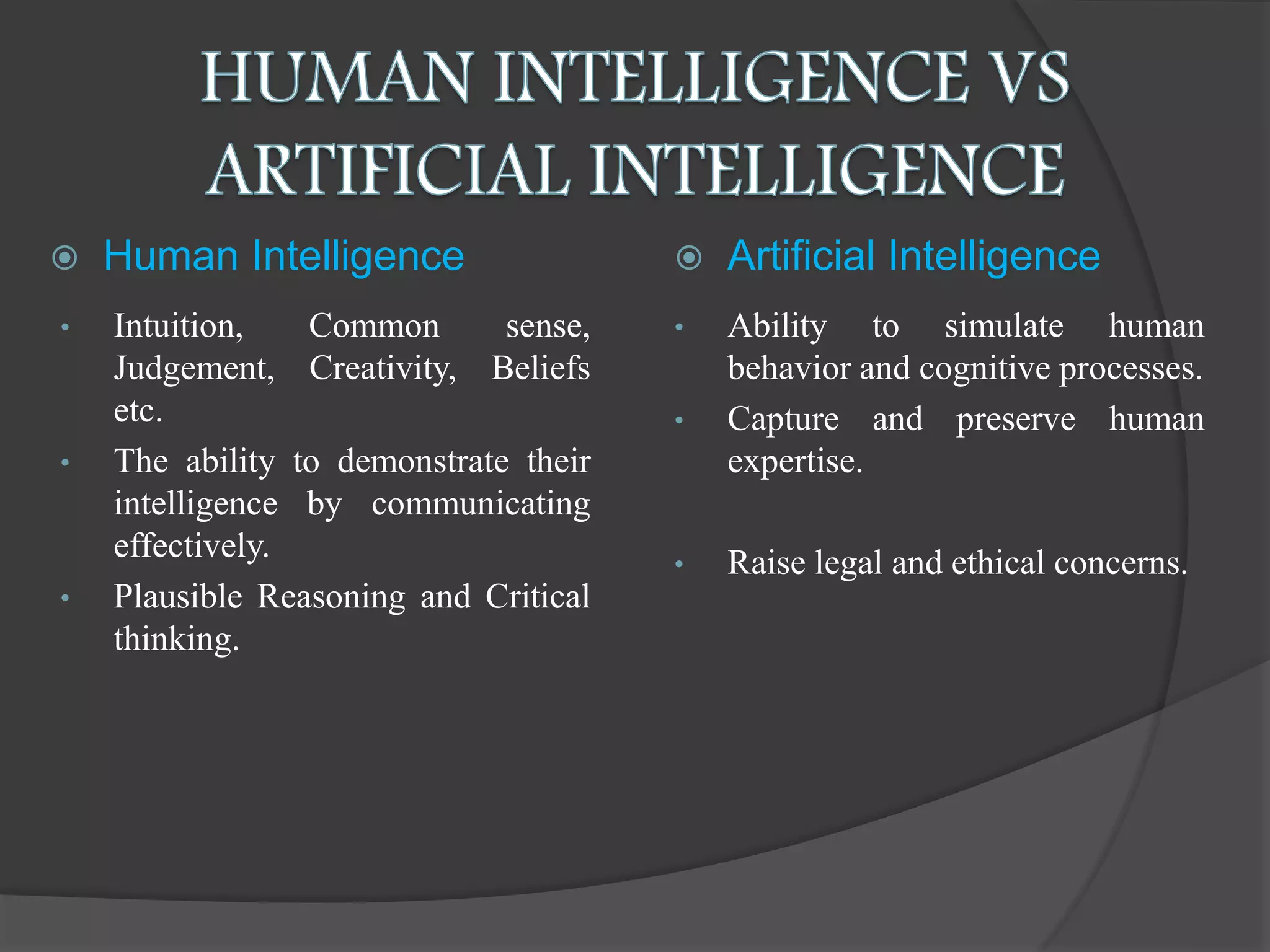
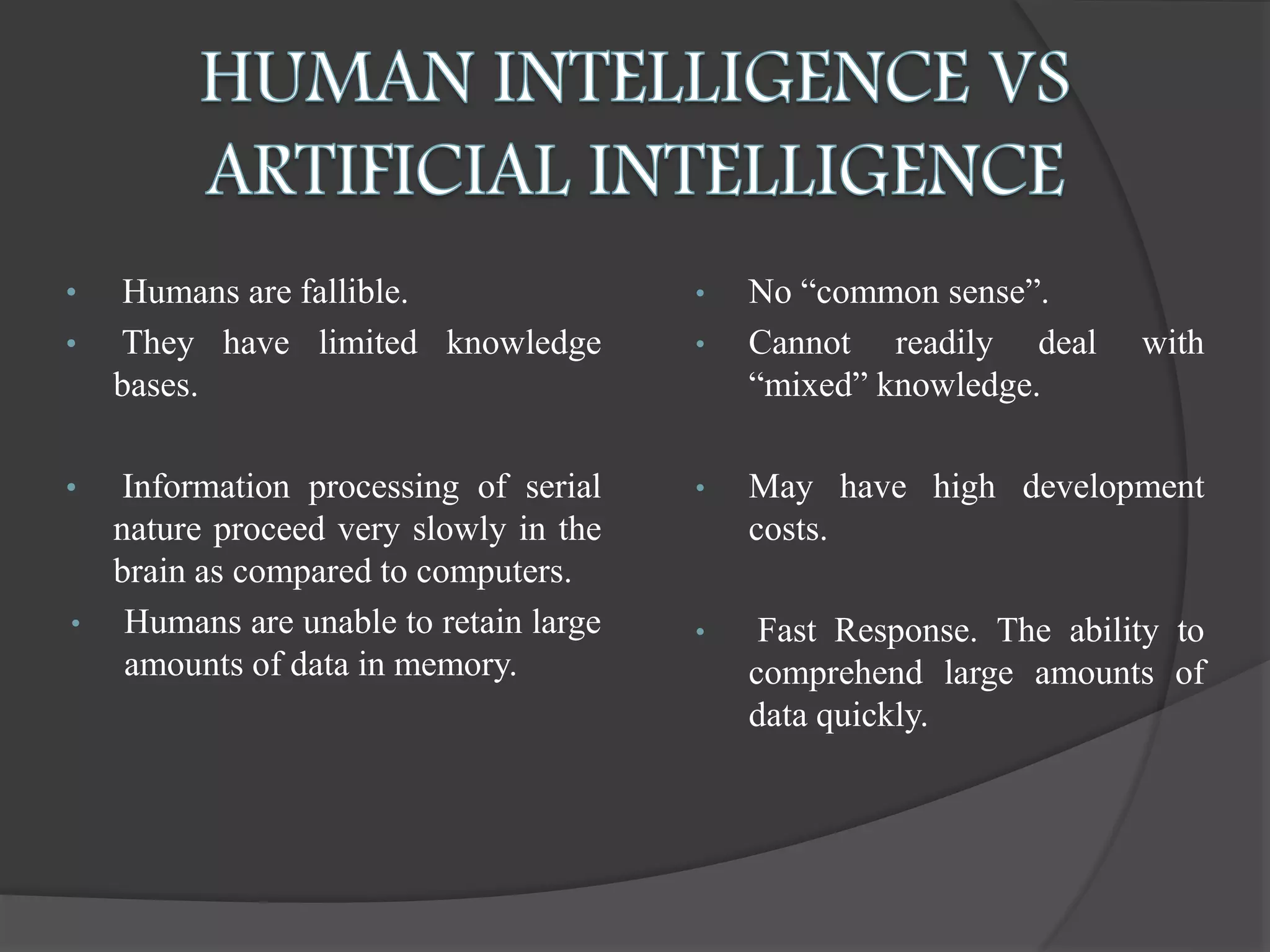
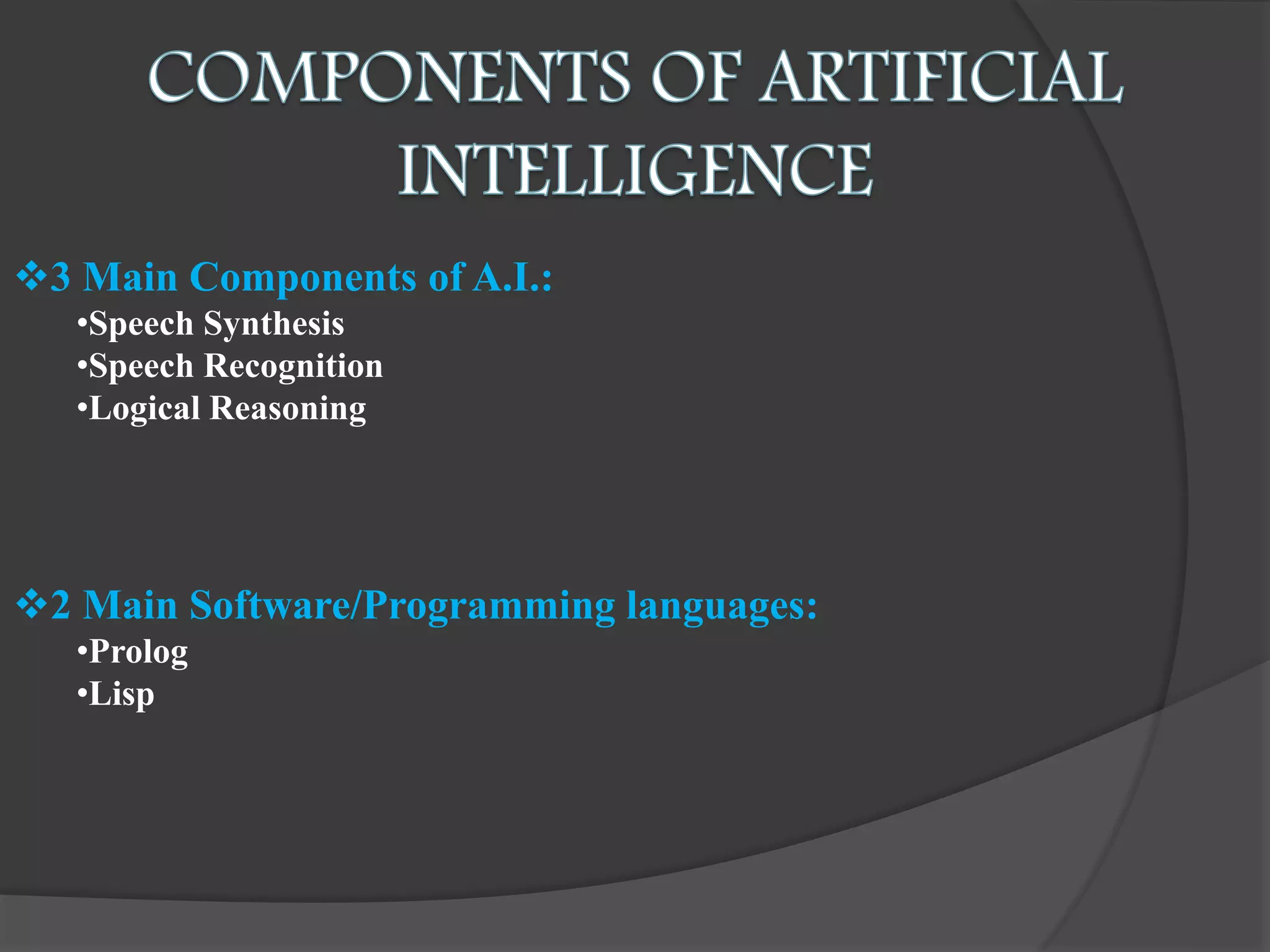
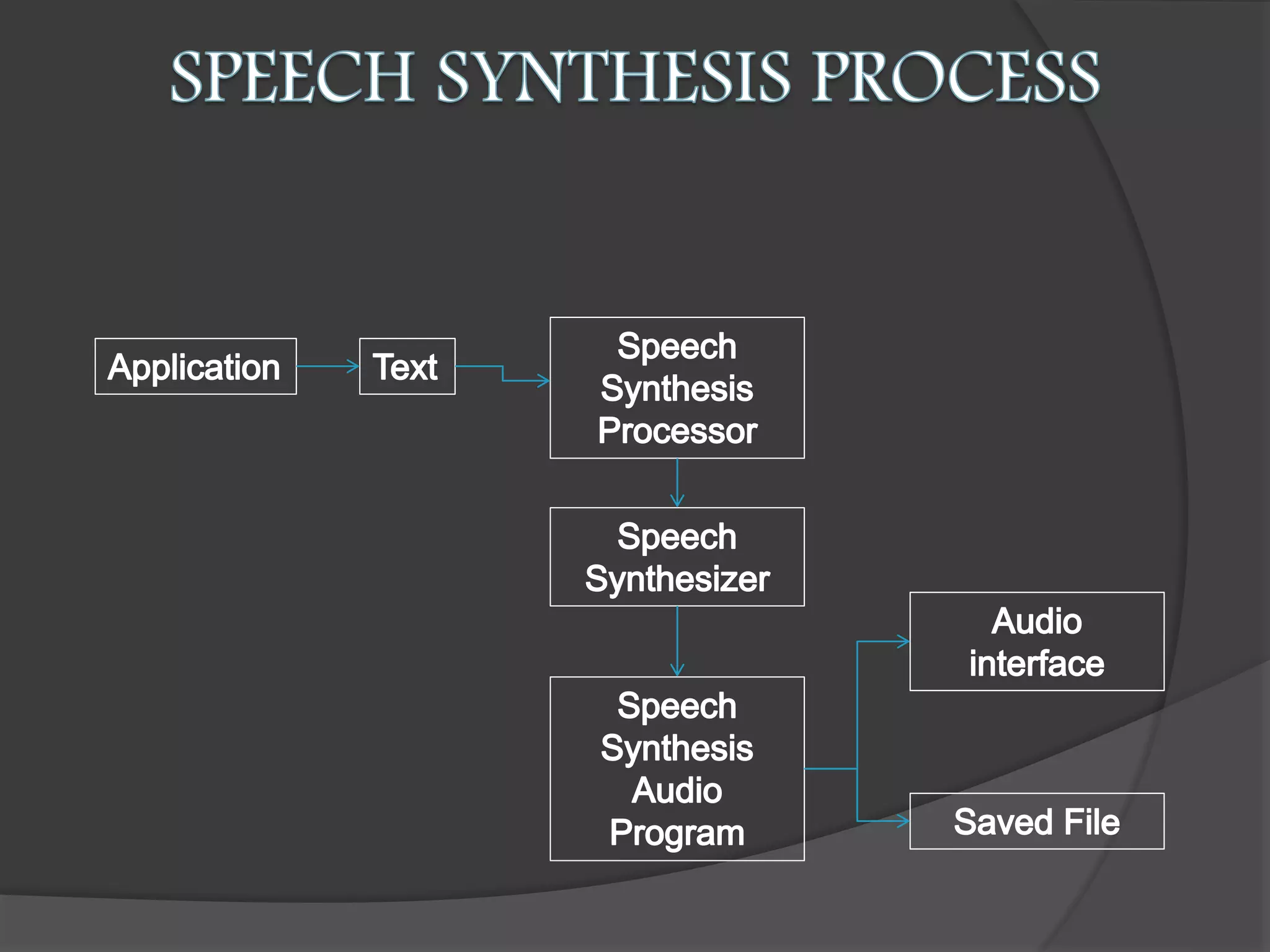
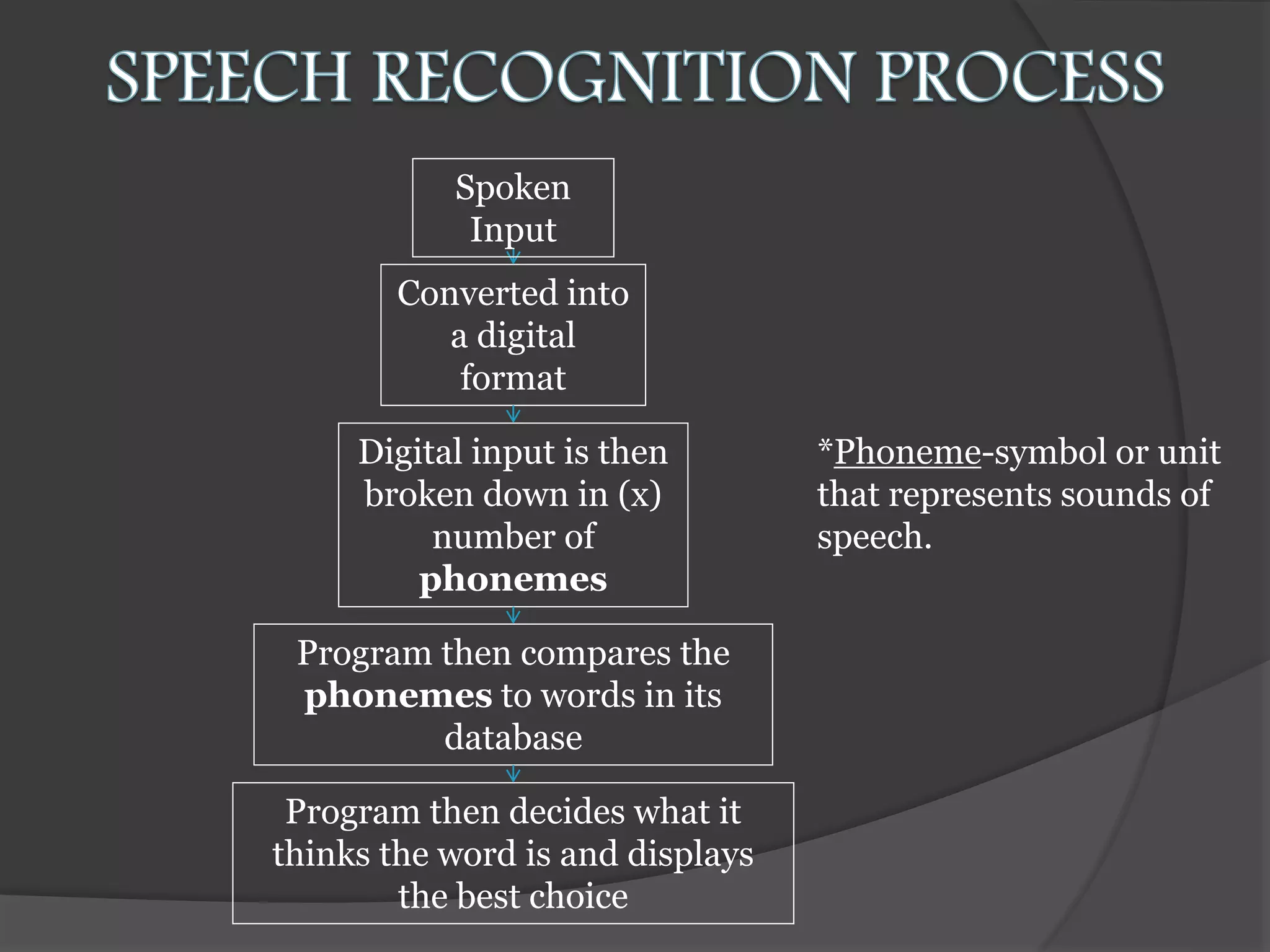
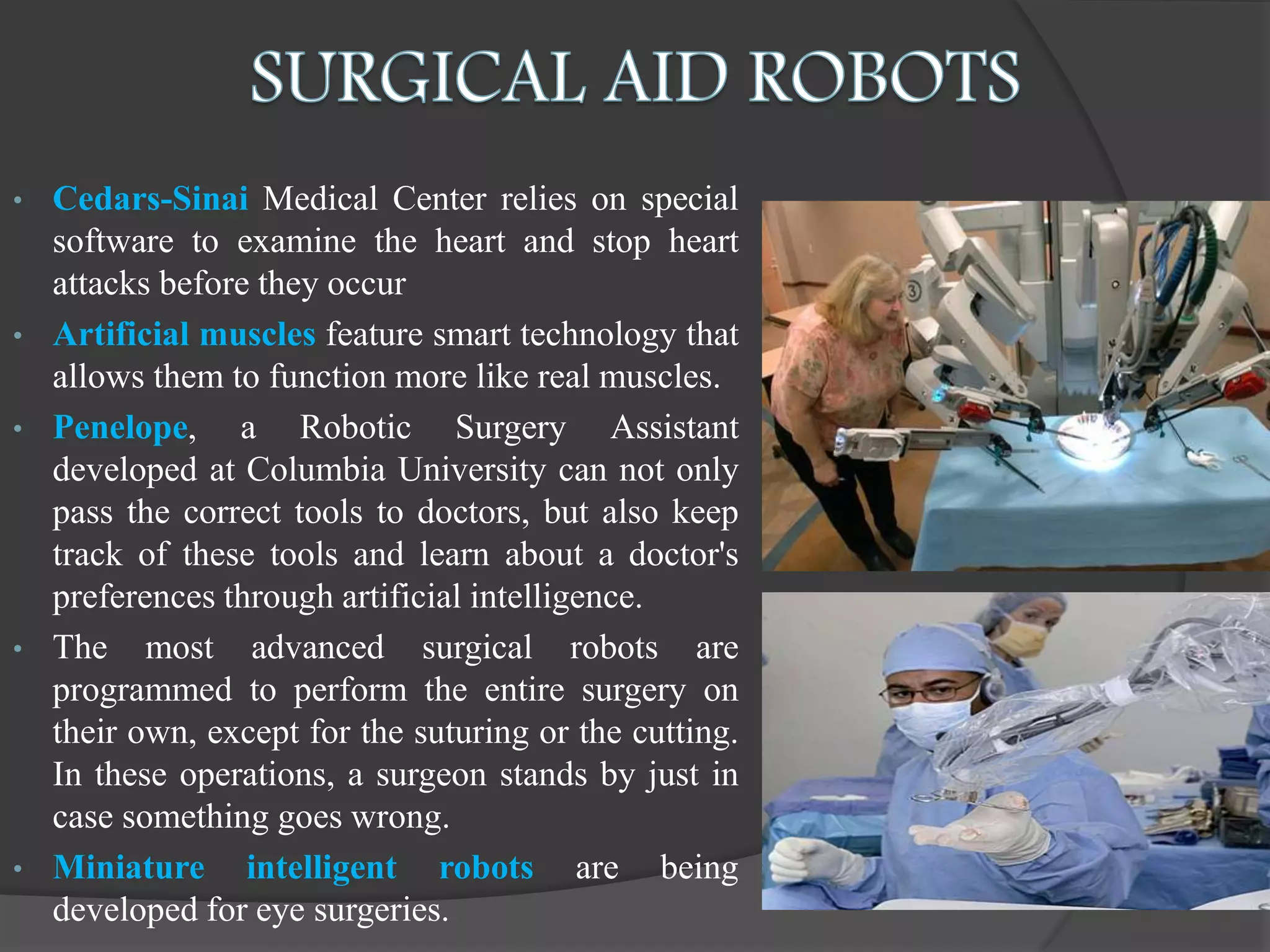
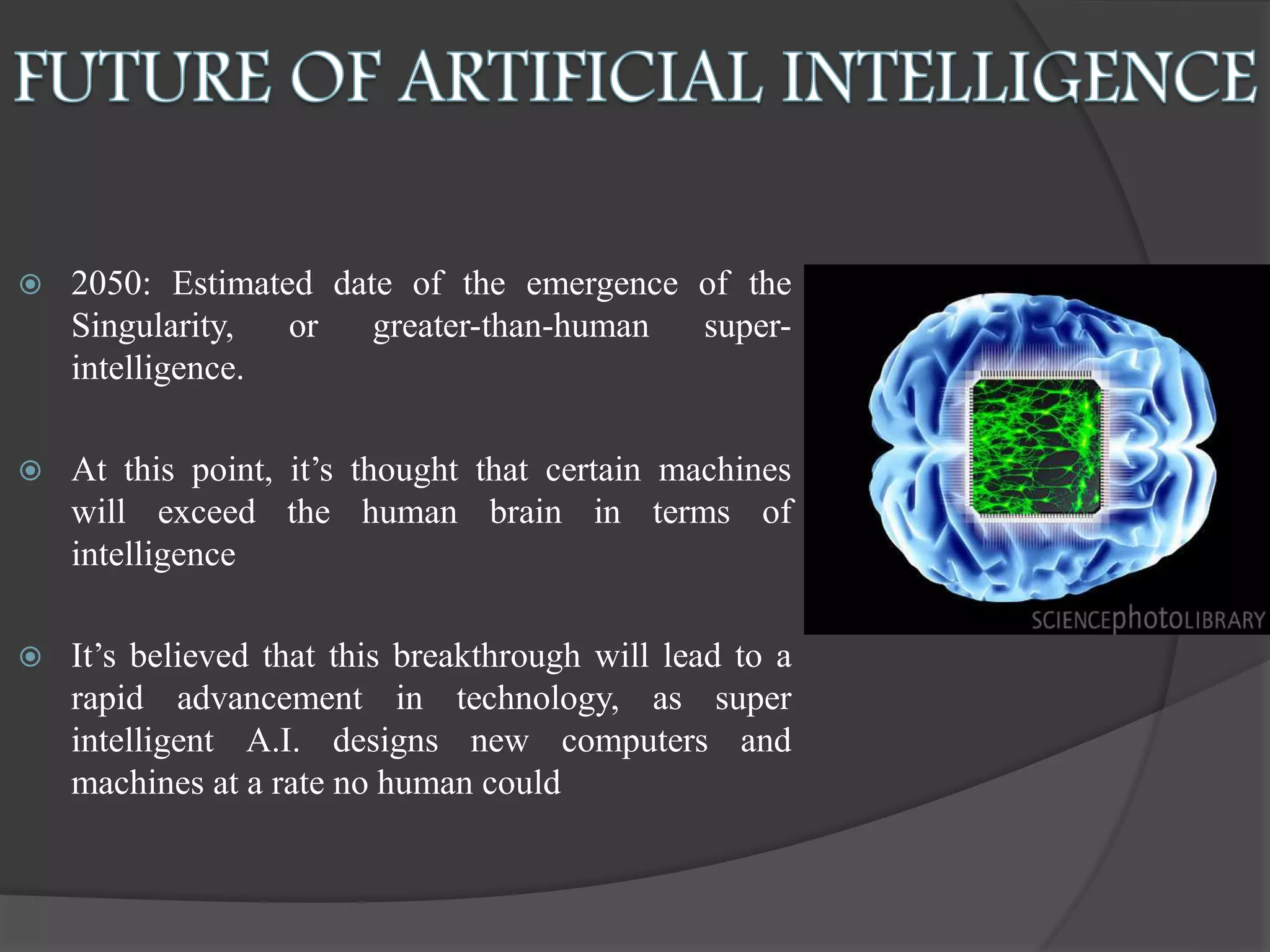
The document presents an overview of artificial intelligence (AI), defining it as the science of enabling computers to perform tasks that require human-like intelligence. It covers the historical emergence of AI, key pioneers, programming languages, and applications ranging from autonomous vehicles to medical robotics. Additionally, it touches on the concept of virtual reality, its types, and components, highlighting its potential for user interaction and real-time simulation.