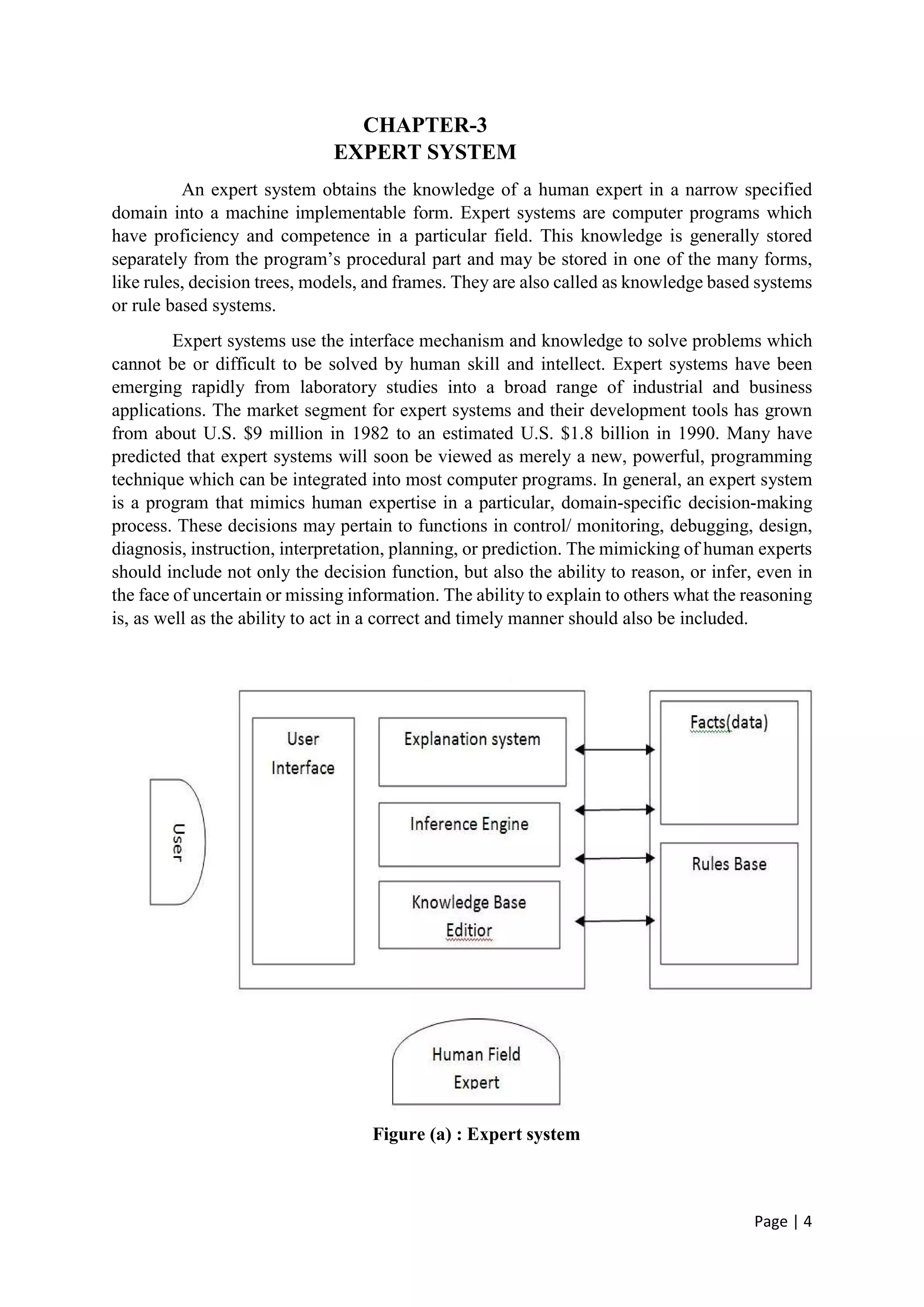
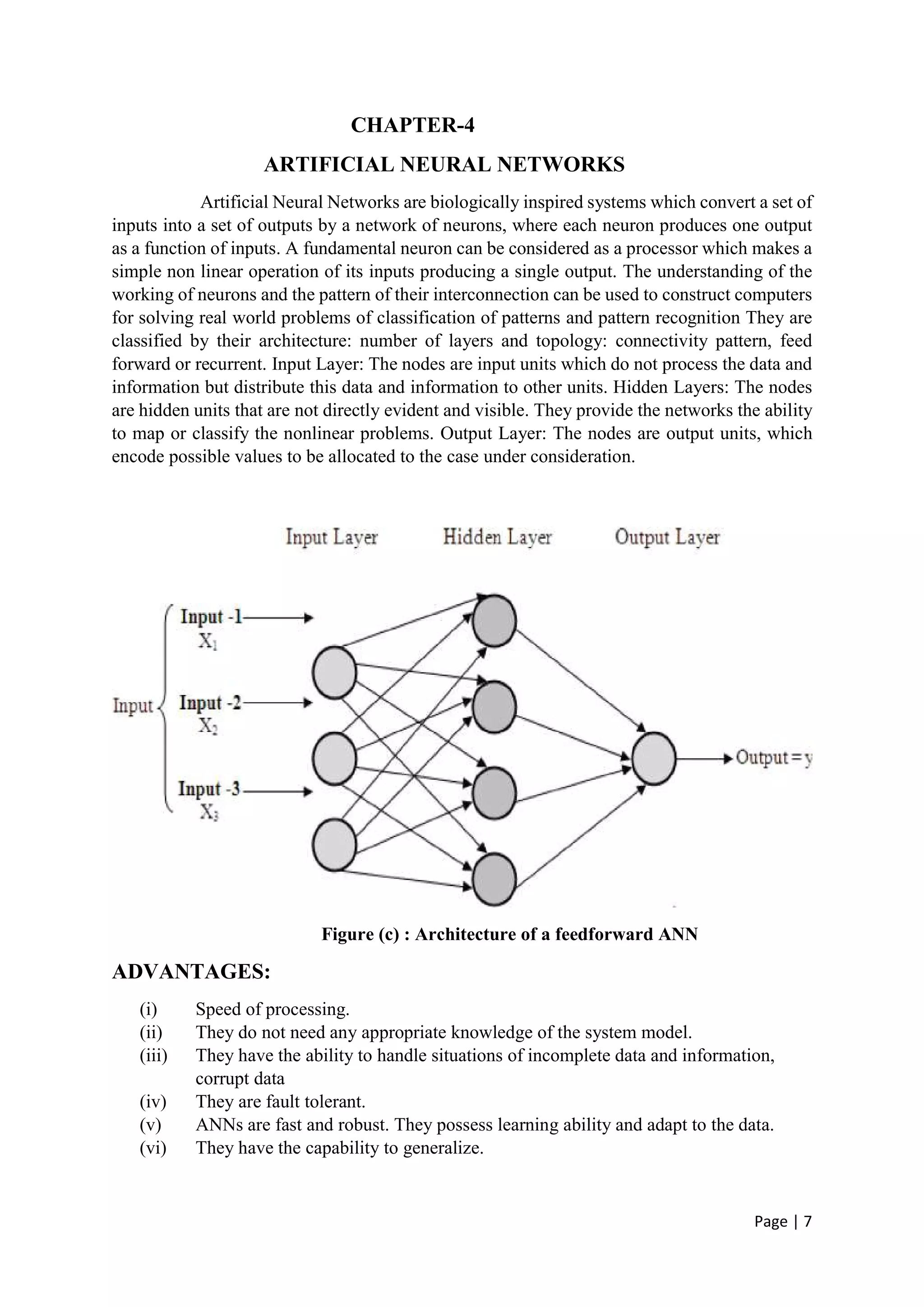
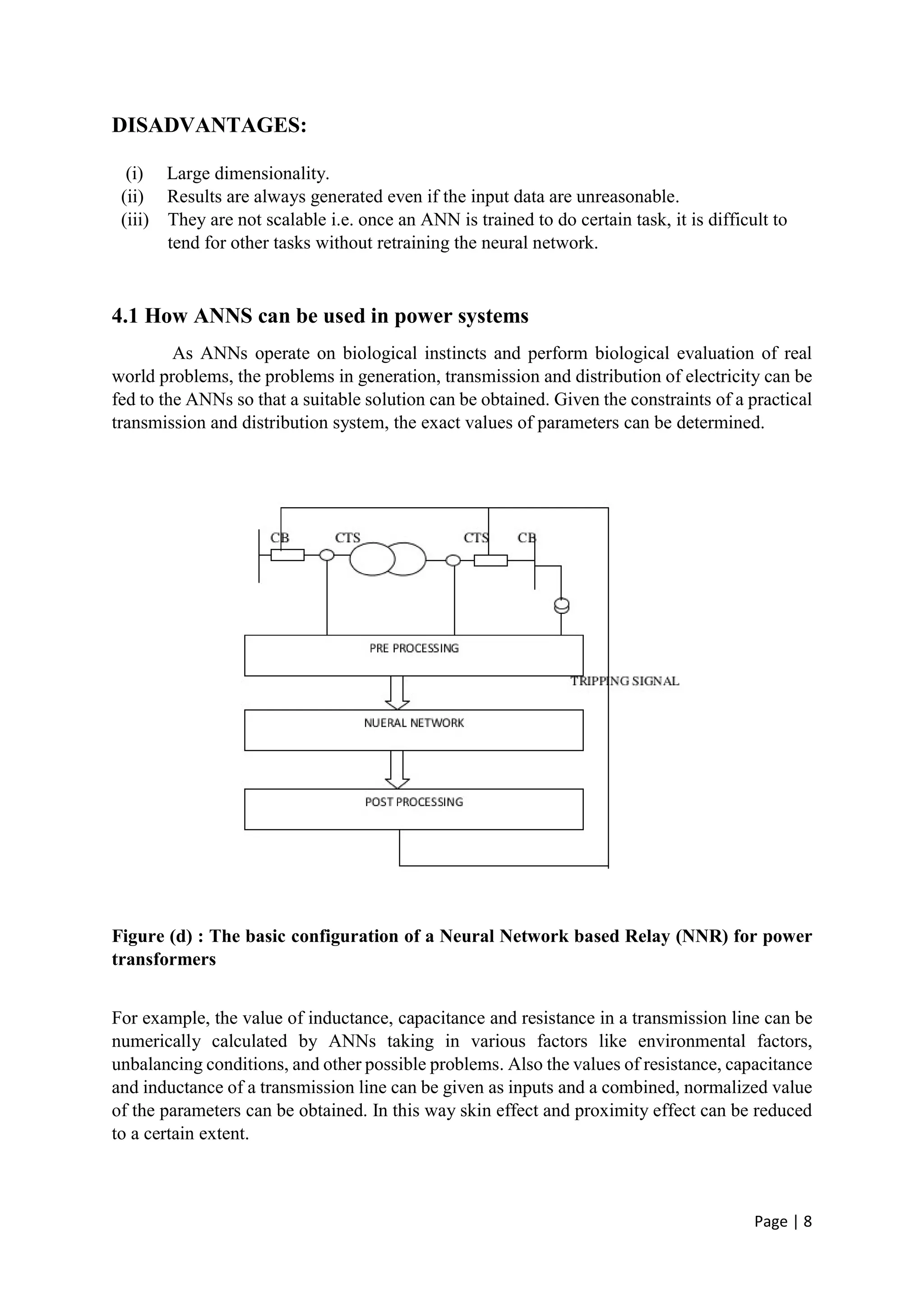
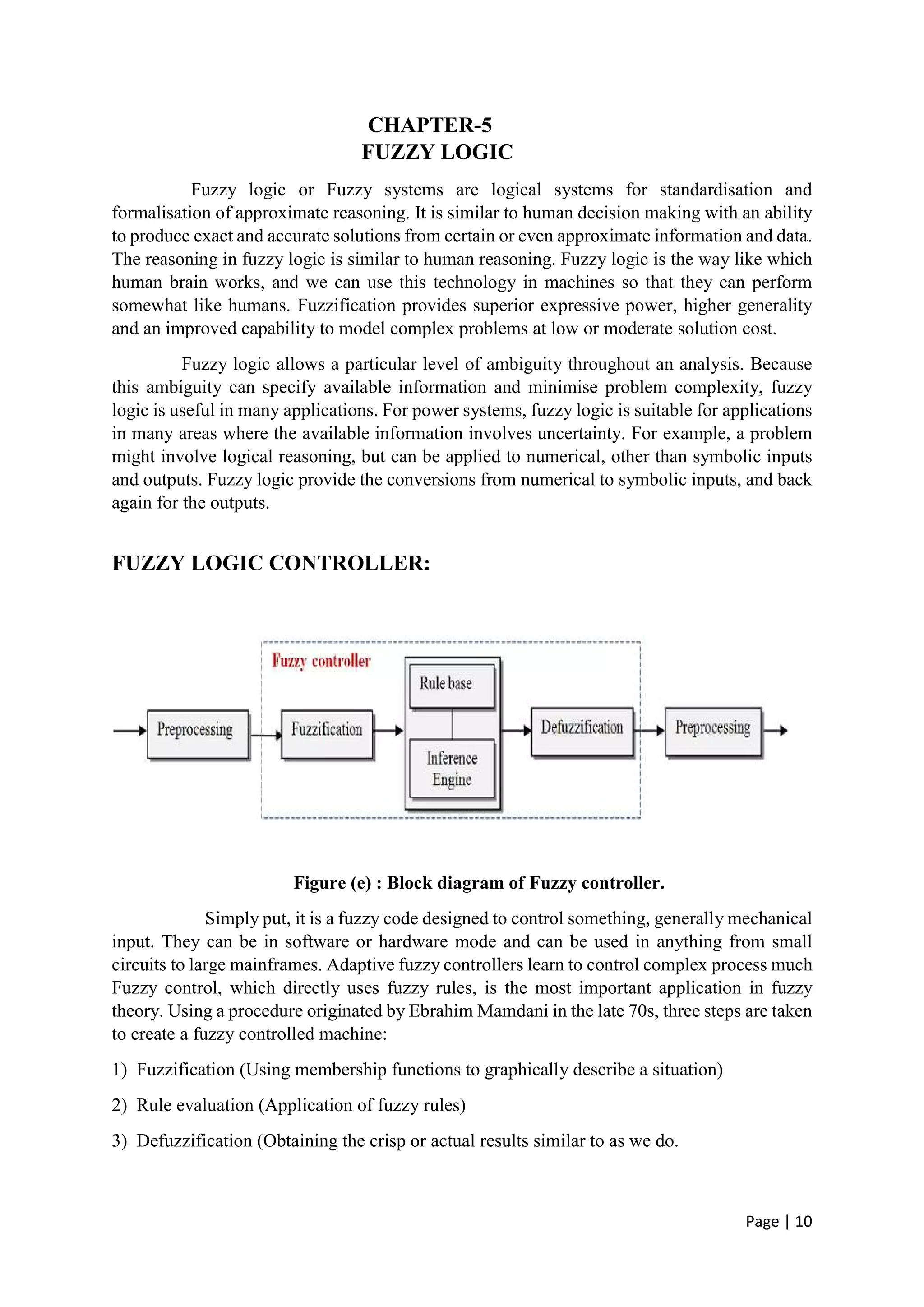
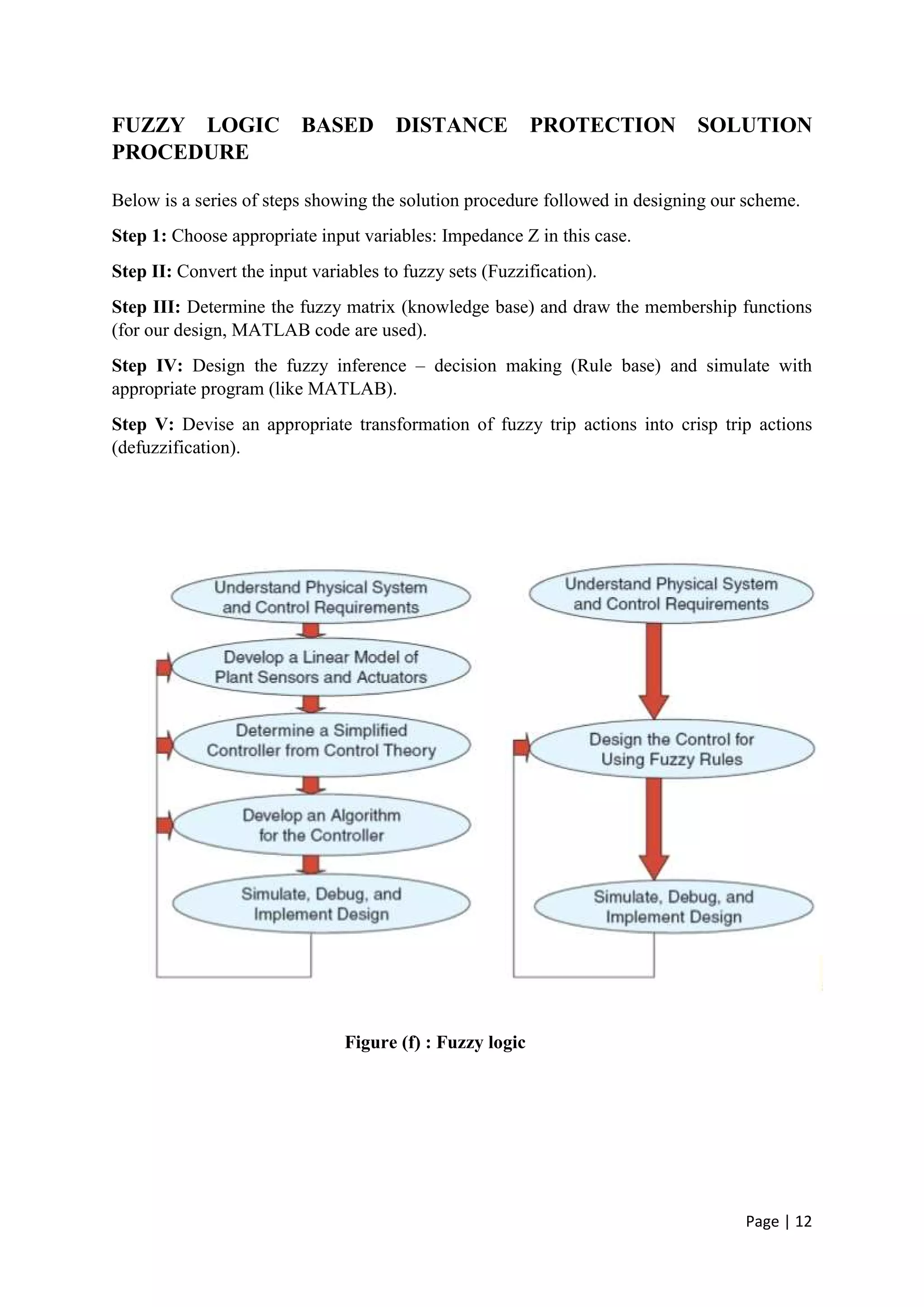
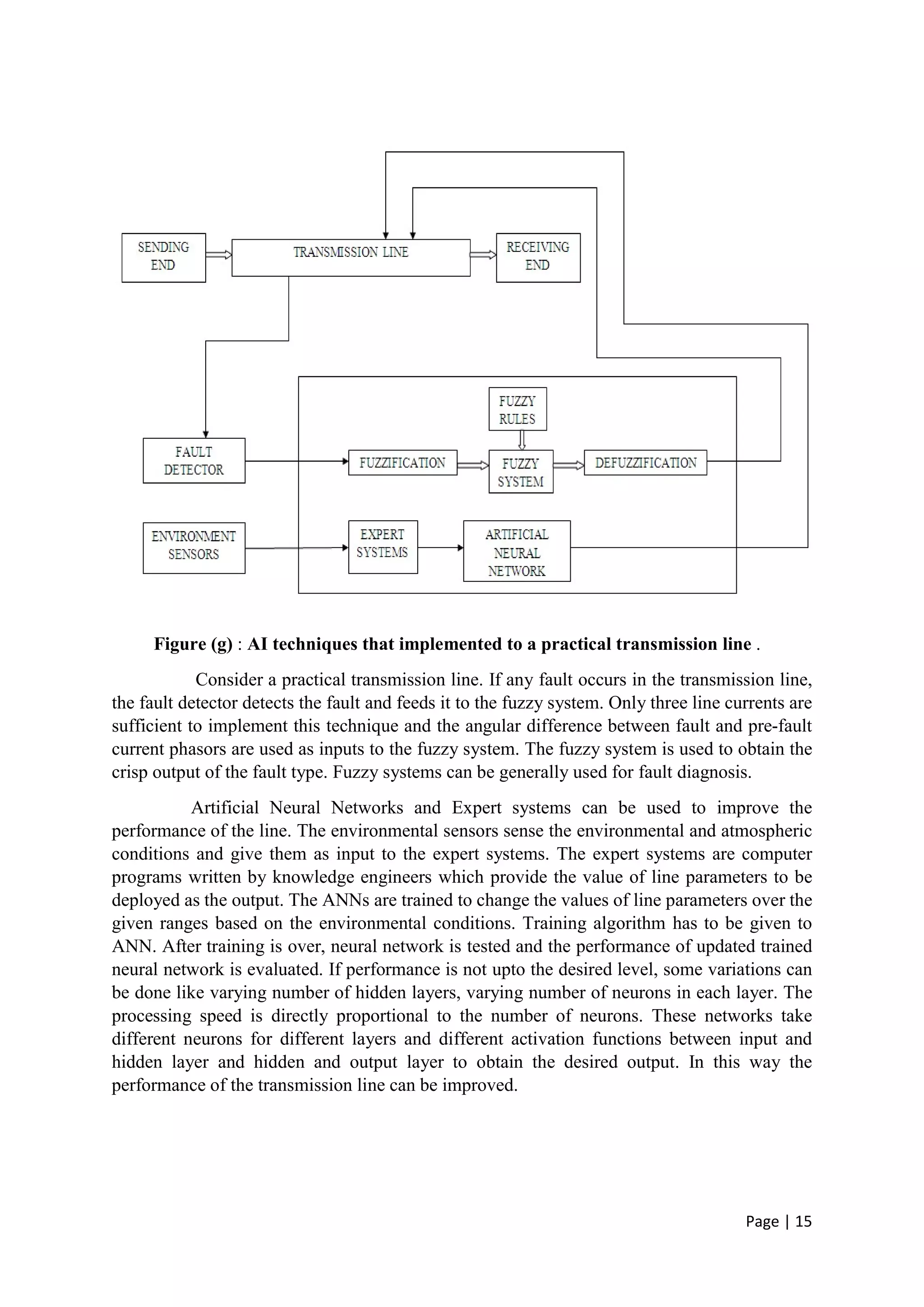
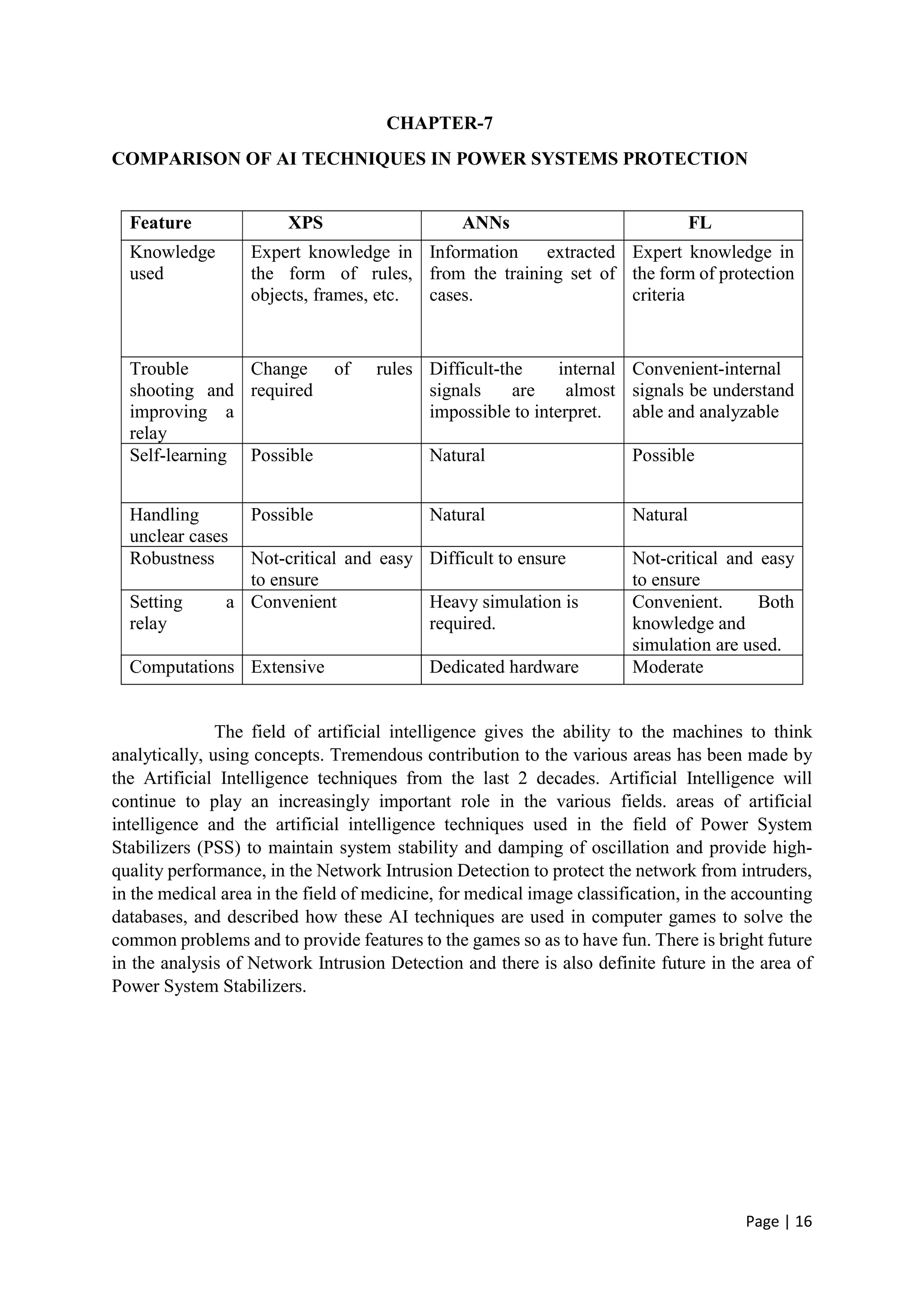
The document discusses the increasing role of artificial intelligence (AI) in power systems, detailing various AI techniques such as expert systems, artificial neural networks (ANNs), and fuzzy logic, which are used to address complex challenges in electricity generation, transmission, and distribution. It emphasizes the need for these technologies to improve decision-making, fault detection, and system operations due to the evolving complexity of power systems. The content also highlights the practical applications of AI in enhancing system reliability and efficiency, particularly in fault protection and operational management.