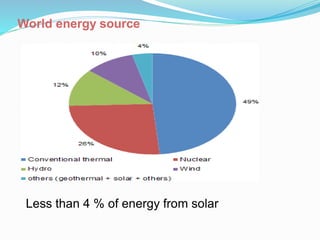
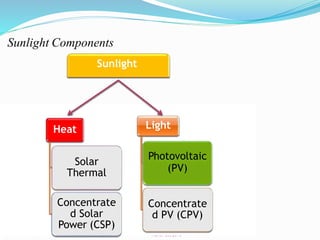
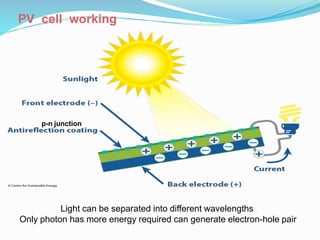
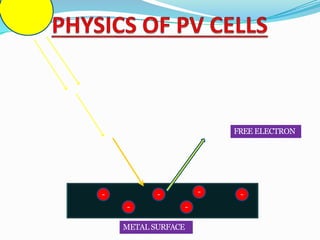
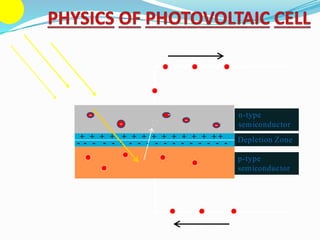
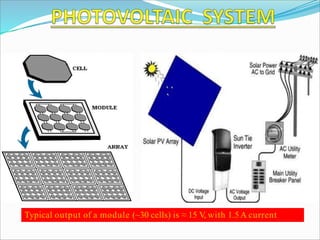
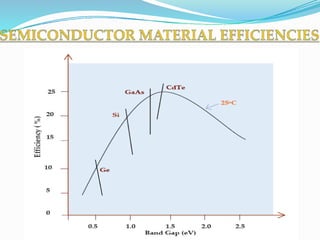
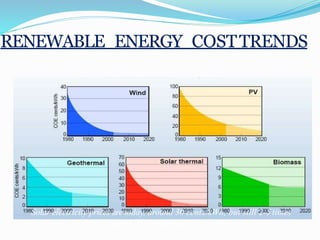
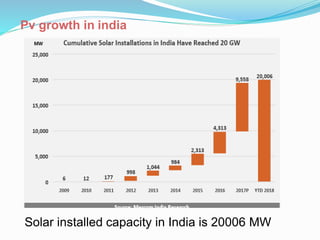
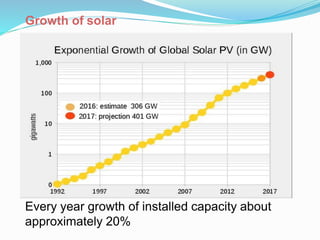
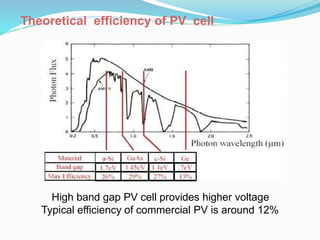
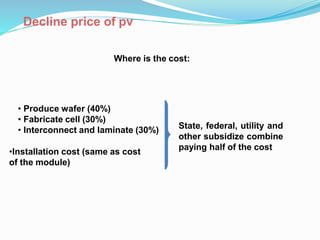
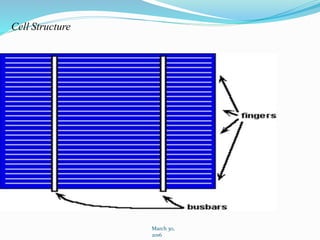
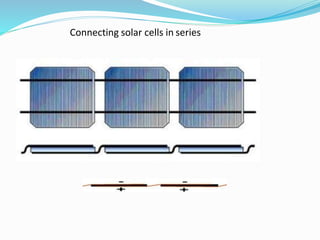
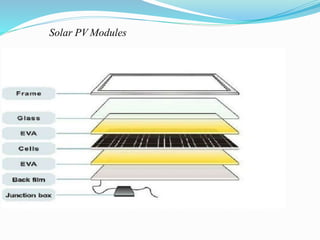
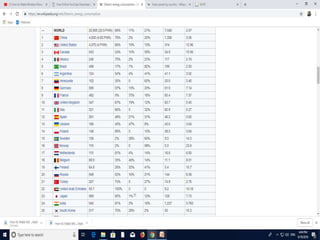
This document discusses recent developments and future trends in electrical engineering, with a focus on solar photovoltaics. It describes several recent research areas in electrical engineering and then provides details on solar cell technology, including how different types of solar cells work and their efficiencies. It discusses India's growing solar capacity and declining costs of solar electricity. The document predicts that if solar continues growing at 20% annually, it could provide over half of the world's energy within 50 years.