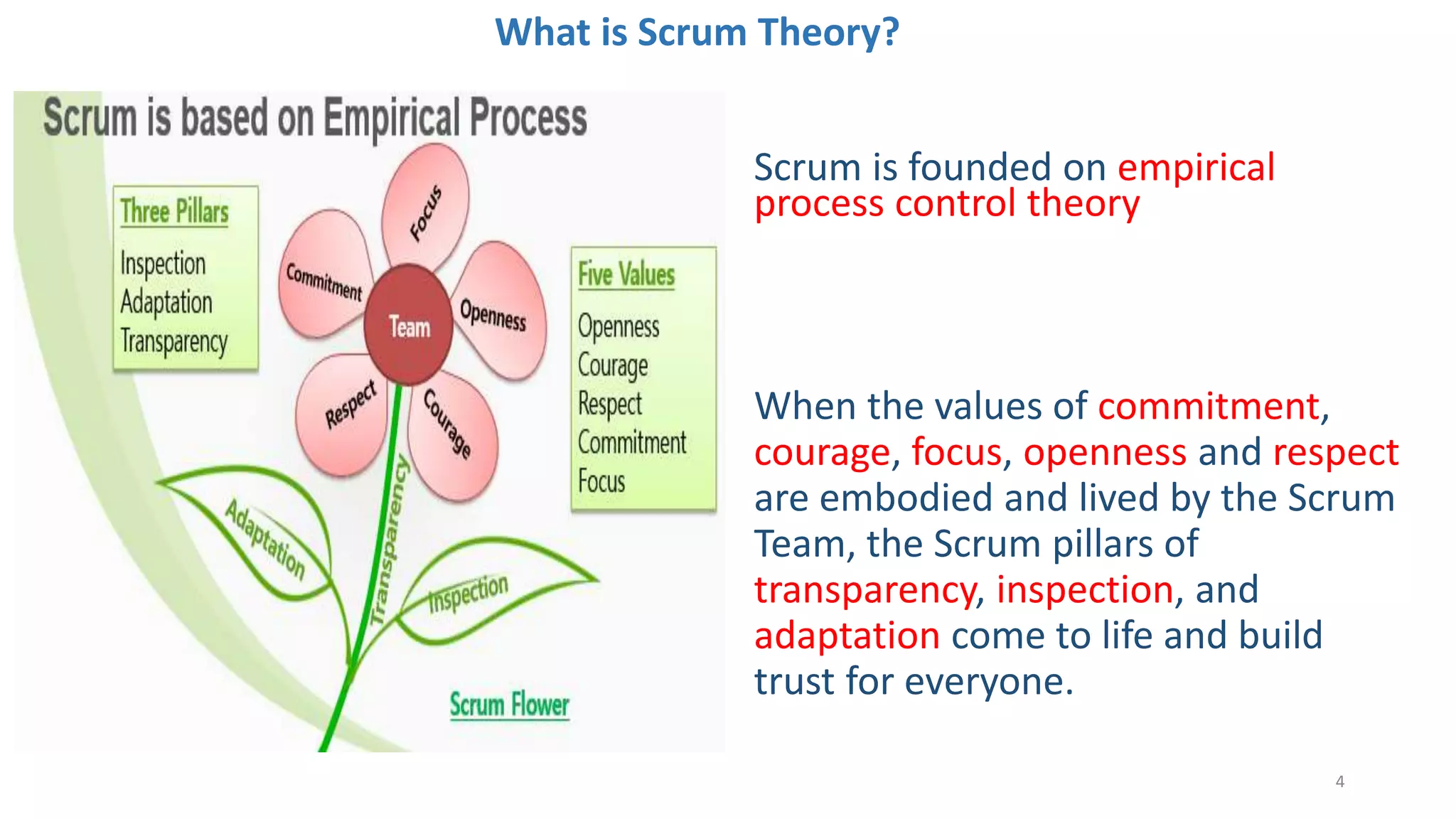
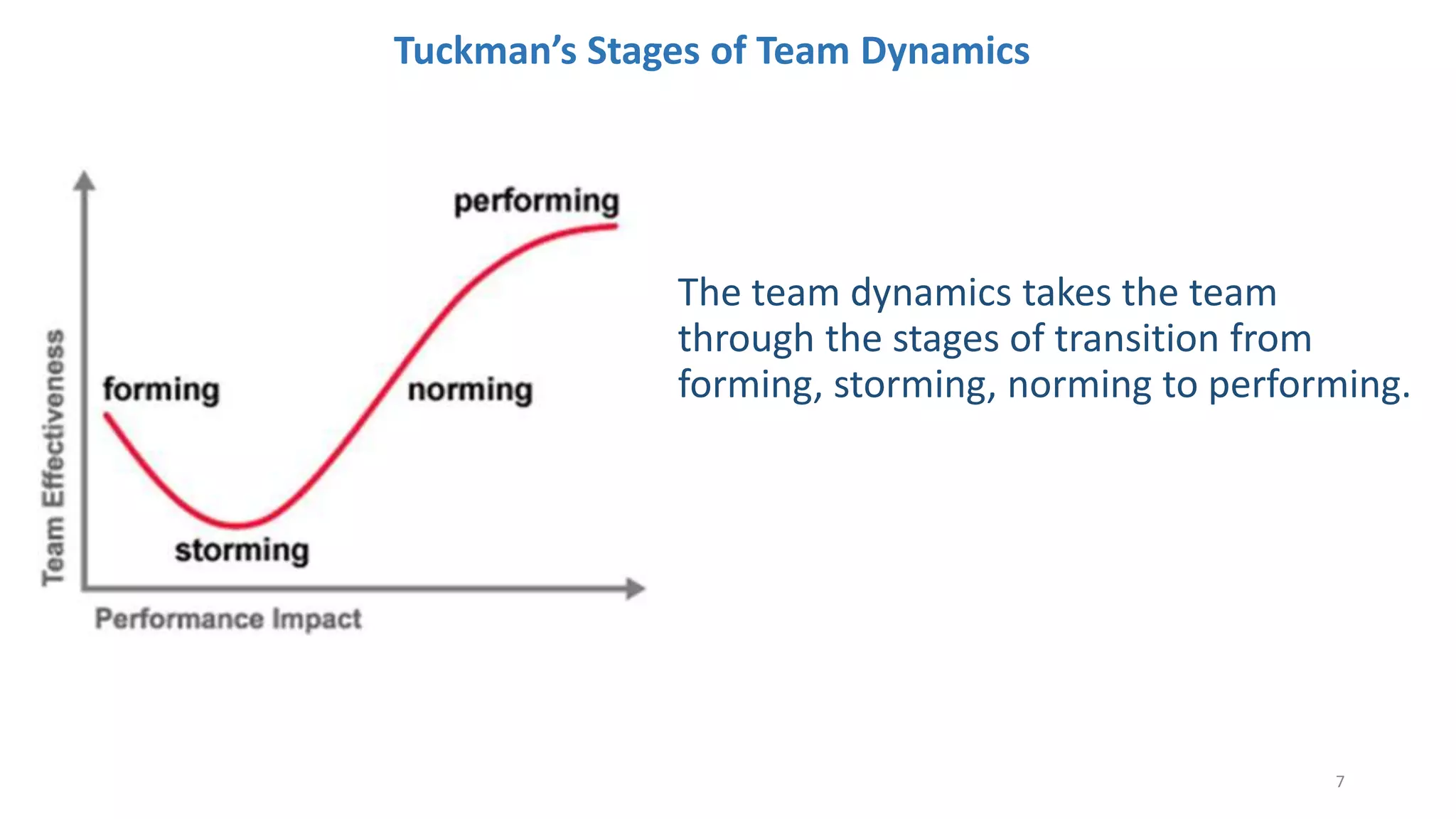
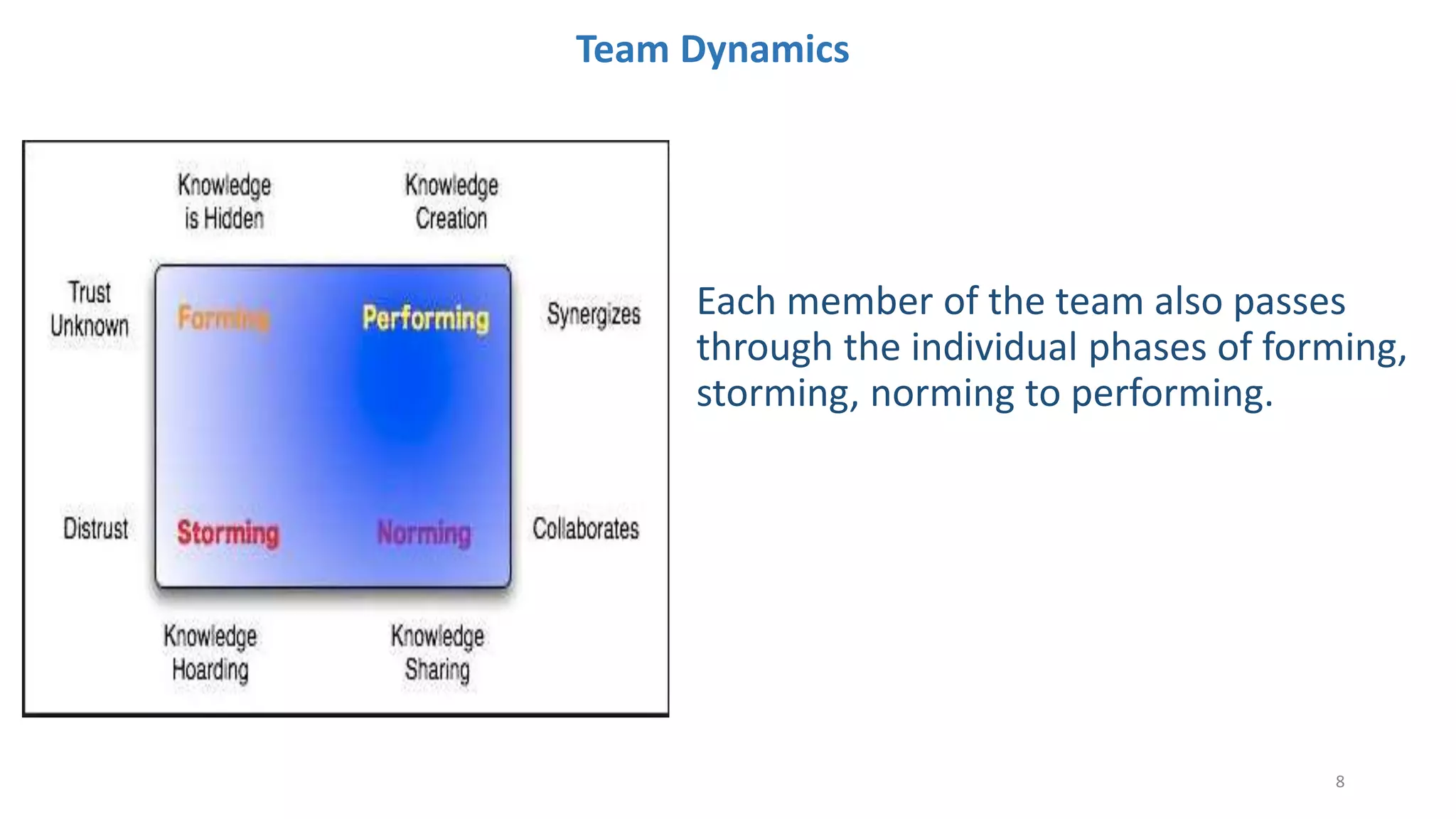
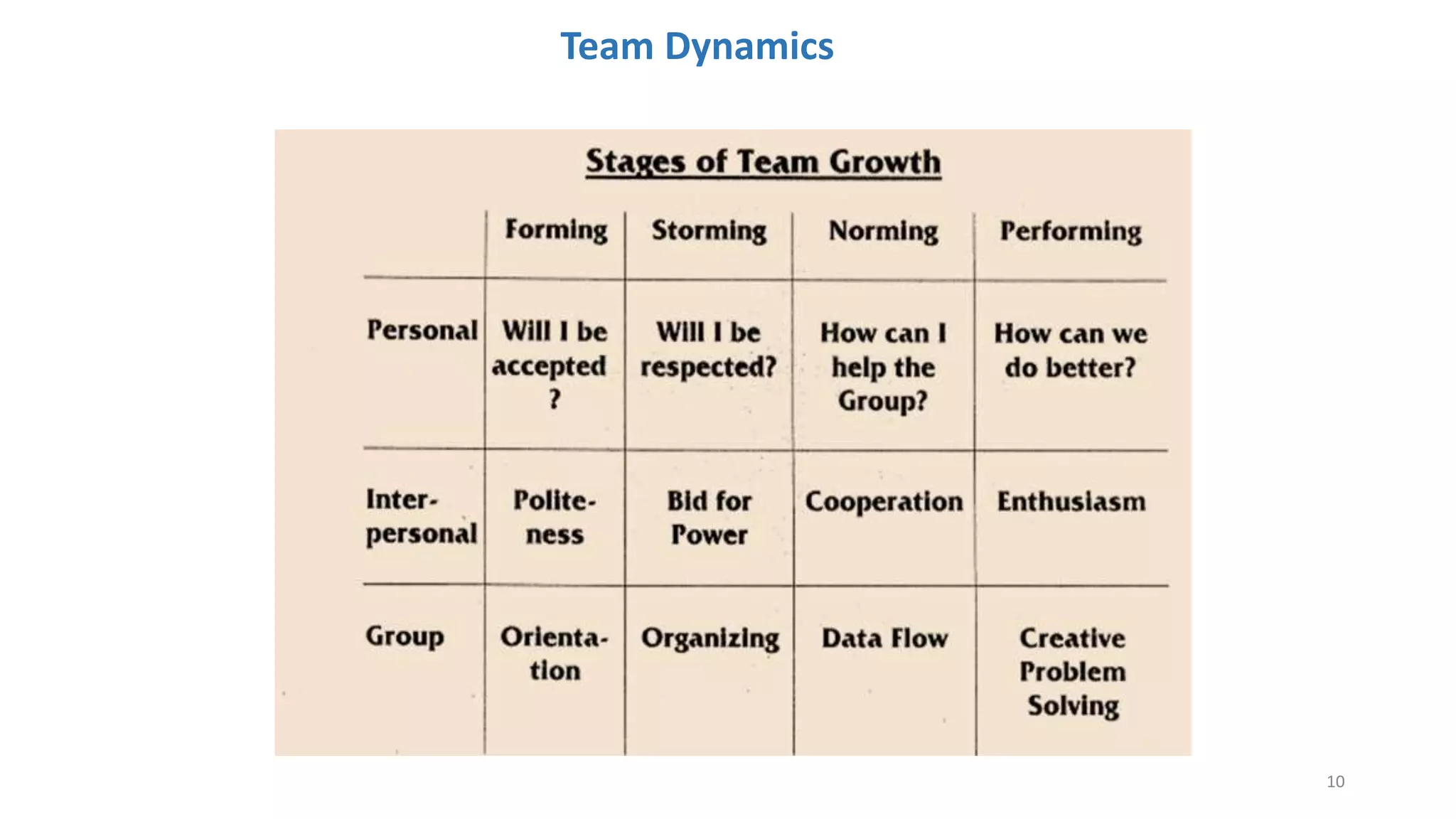
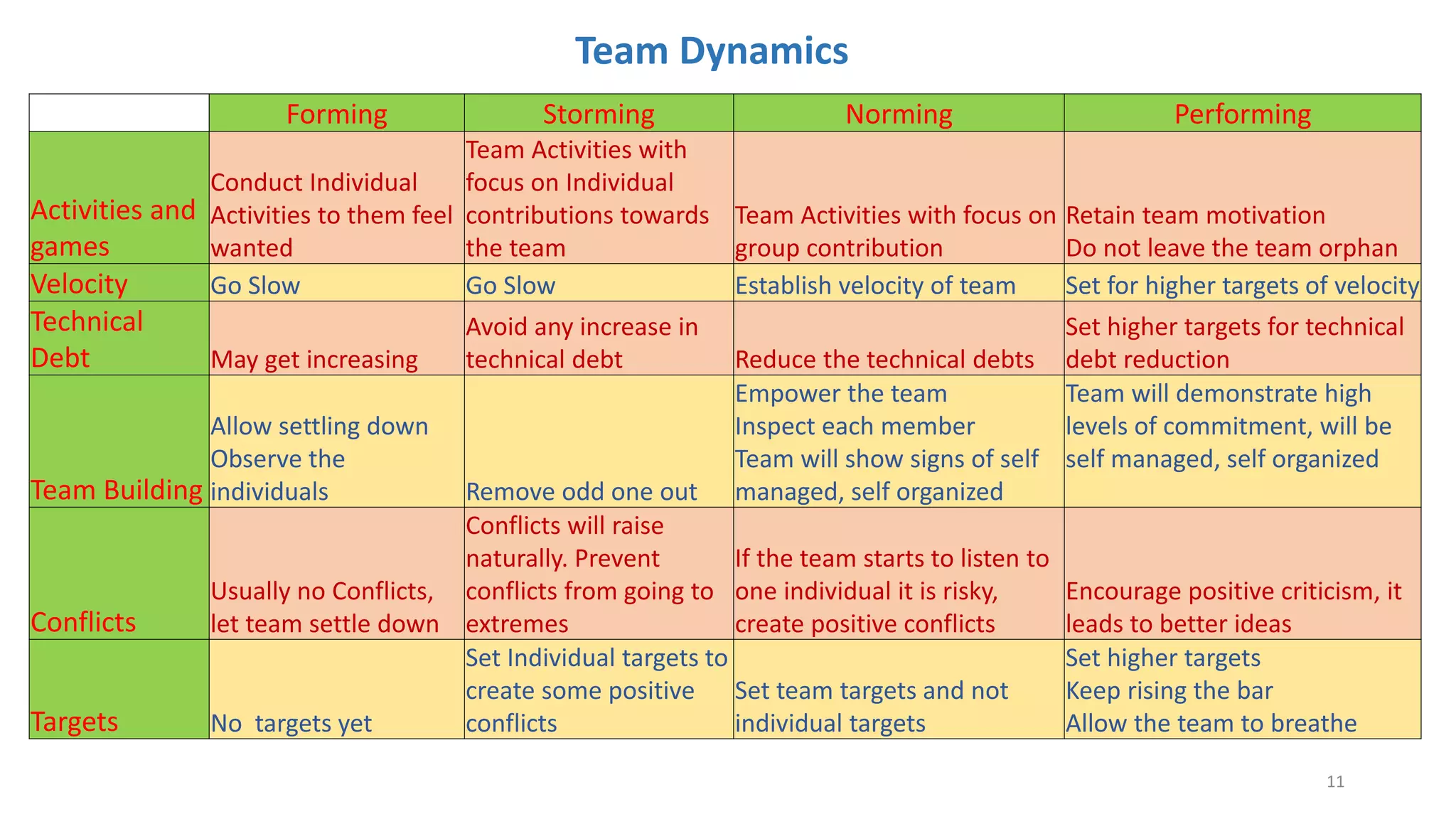
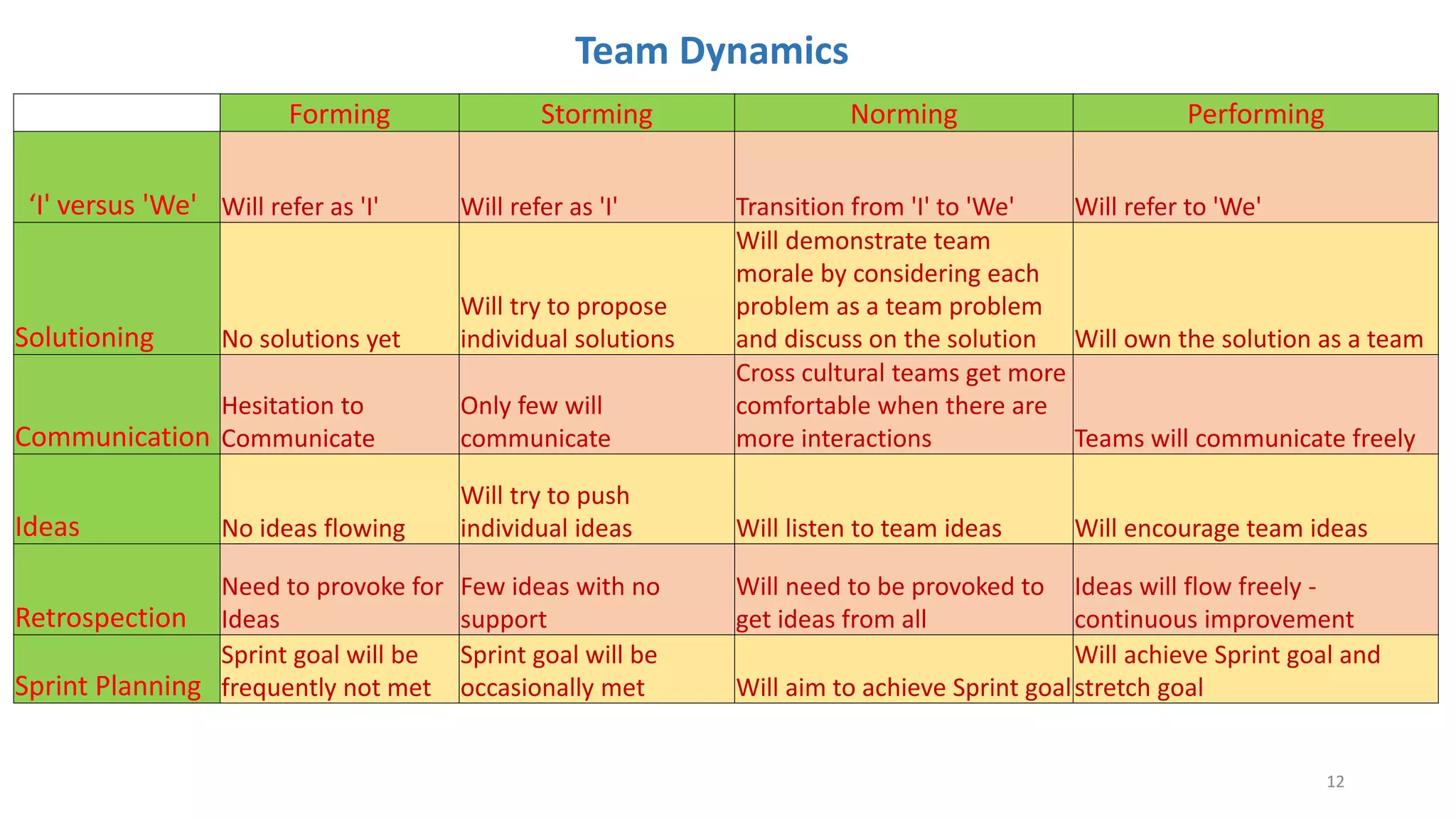
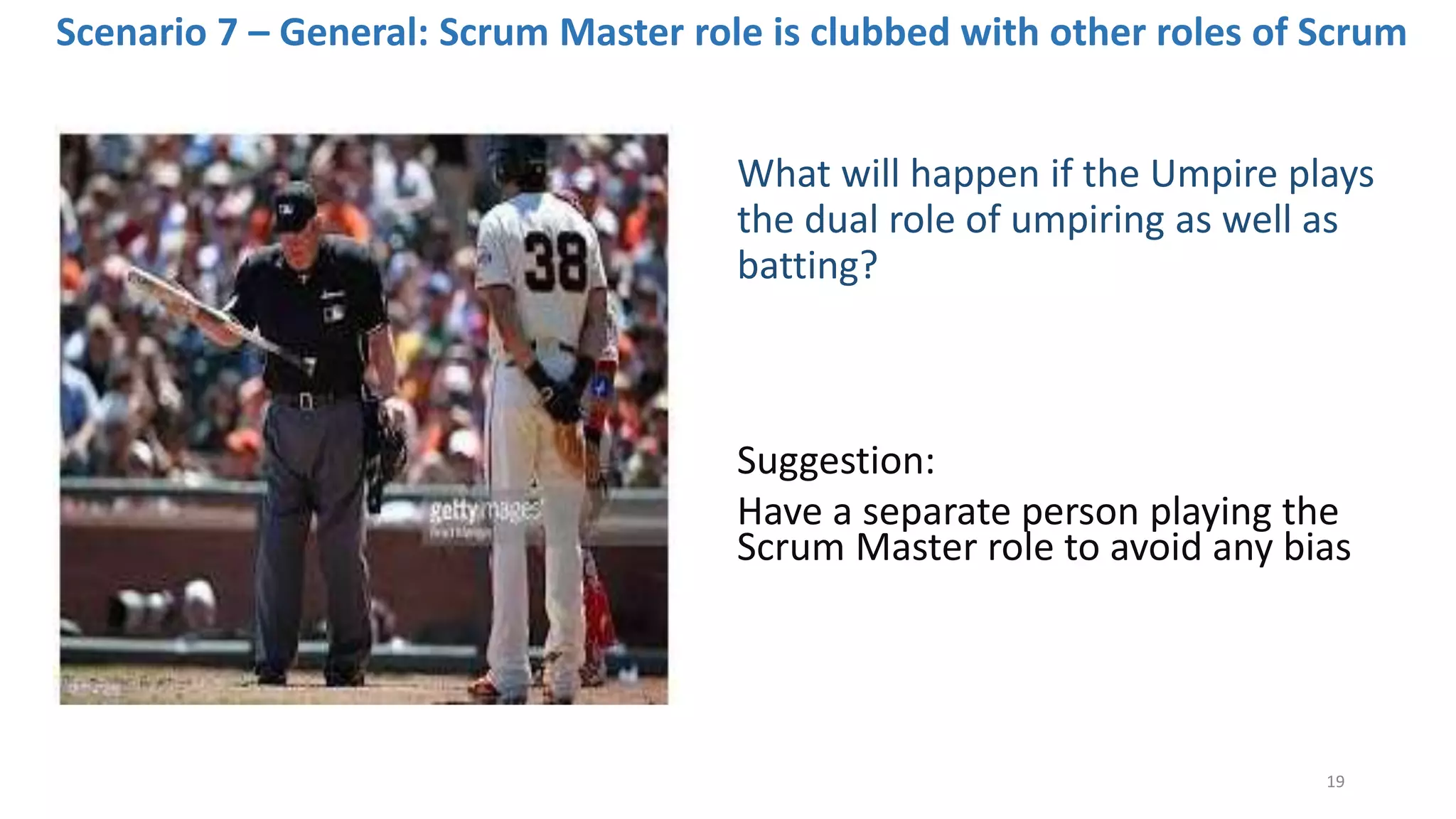
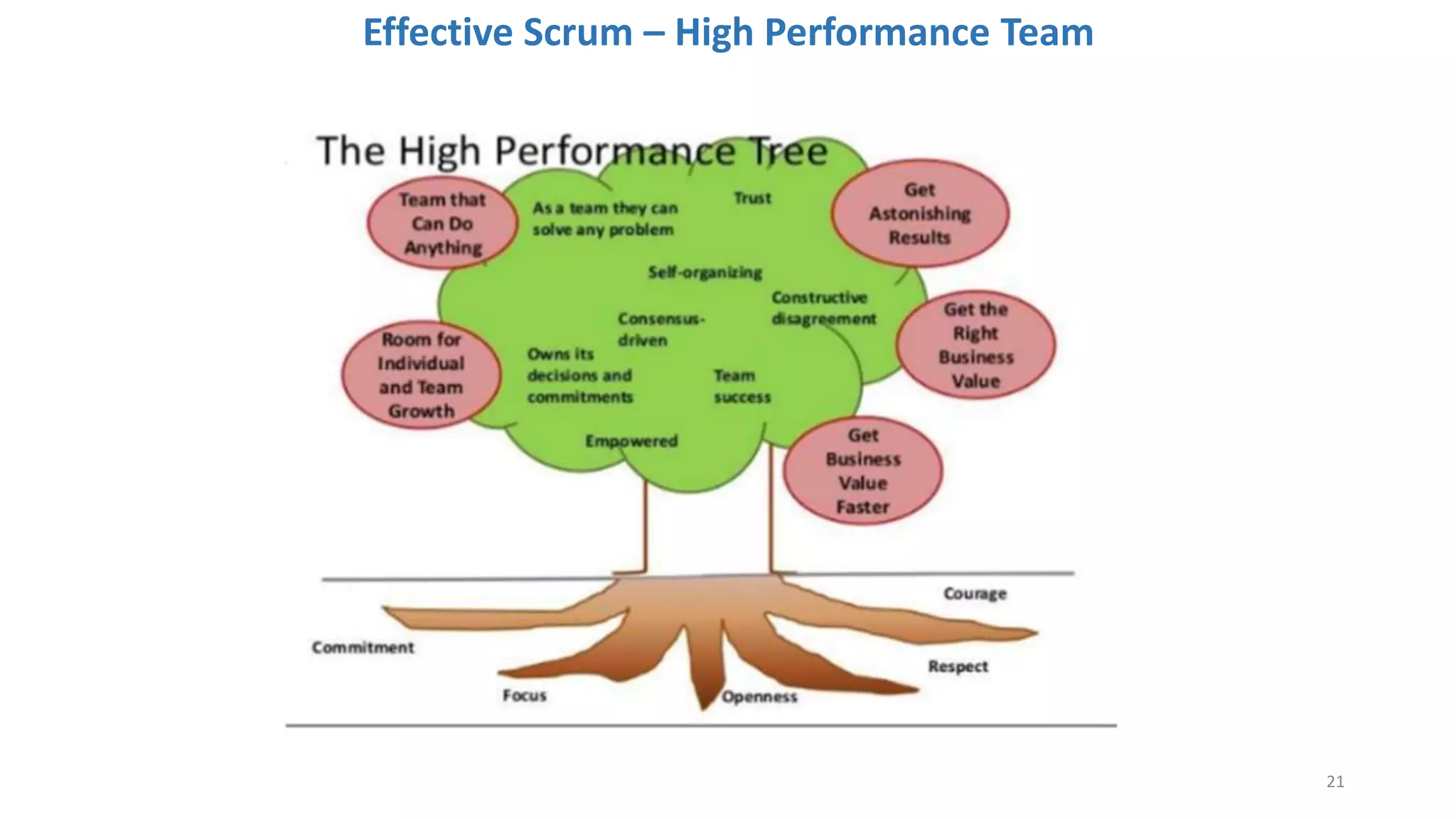
The document discusses the Scrum framework as a method for developing complex products, emphasizing its iterative, flexible nature and the importance of team dynamics. It outlines key principles of Scrum theory, including the values and roles within the framework, and provides practical scenarios and suggestions for improving team performance and addressing common challenges. The focus is on mastering the framework's processes before innovating and ensuring effective communication, commitment, and continuous improvement within Scrum teams.