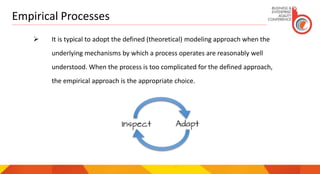
The document discusses the concept of an agile mindset, emphasizing that agile is a philosophy, not just a process or framework. It highlights the importance of embracing change, fostering teamwork, collective ownership, and sustainable work practices, while promoting transparency and collaboration within teams. The author also touches upon the role of leadership in transitioning to a more servant-oriented approach.