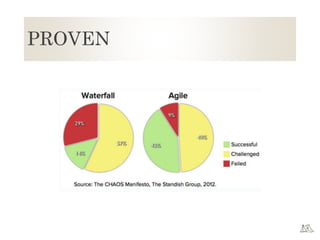
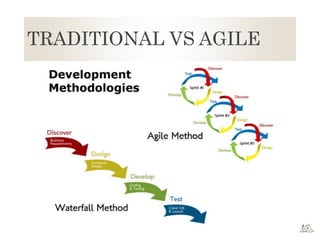
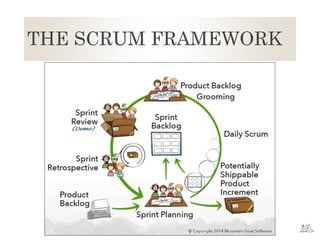
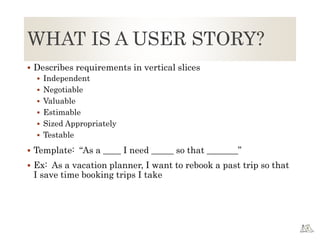
The document provides an overview of Agile principles and the Scrum framework. It describes key Scrum roles like the Product Owner and Scrum Master. It also summarizes Scrum ceremonies such as Sprint Planning, Daily Standup, Sprint Review, and Retrospective. User stories and tracking work using a Kanban or Scrum board in TFS are also covered at a high level.