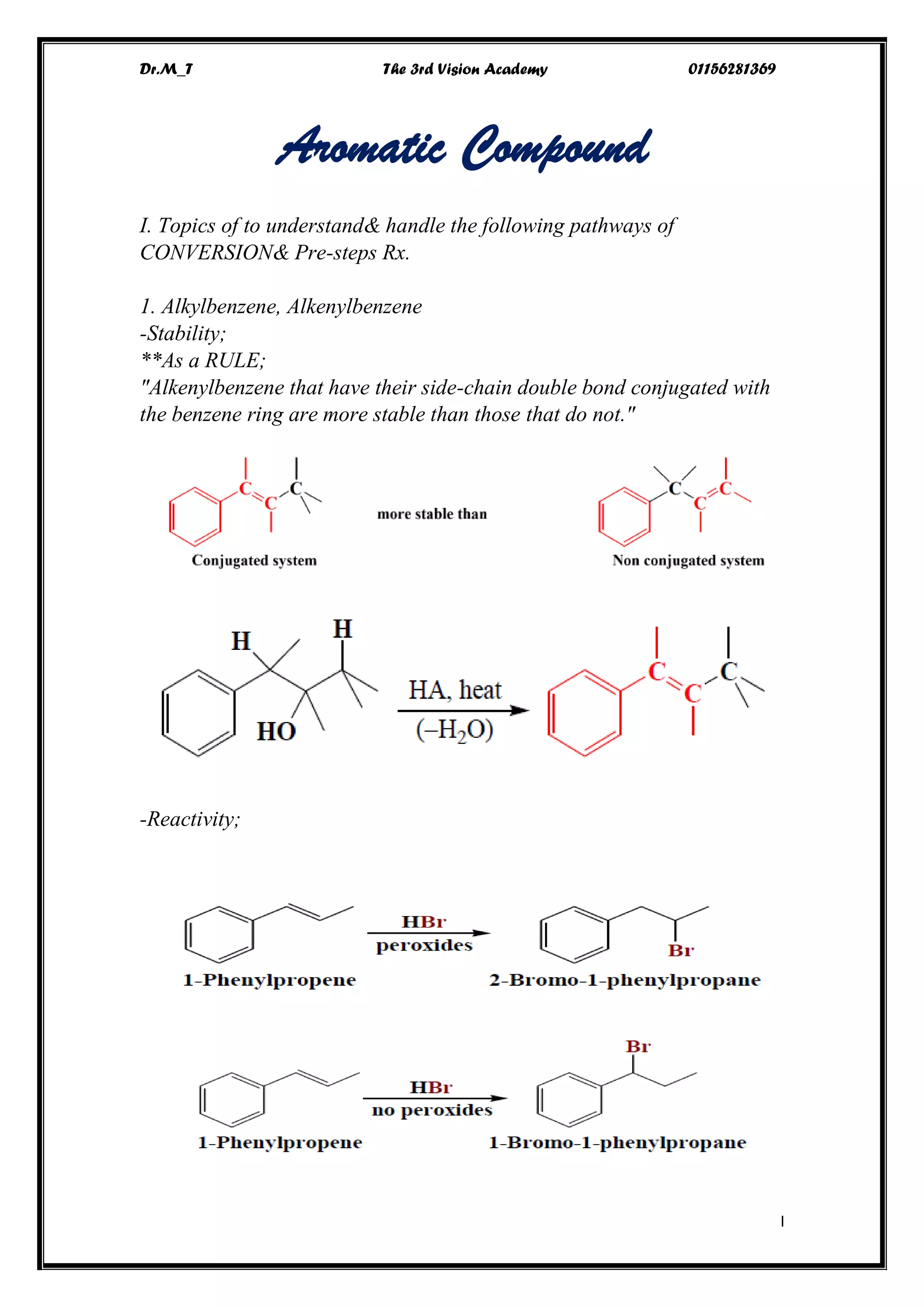
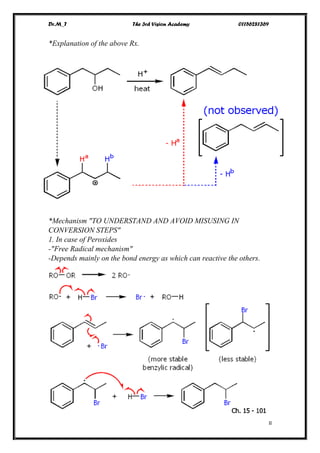
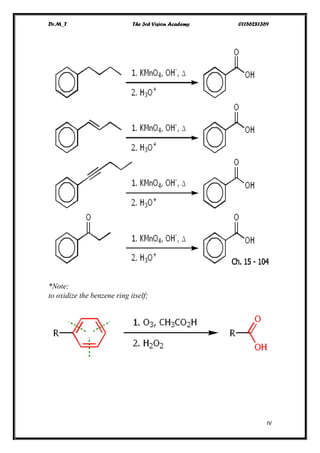
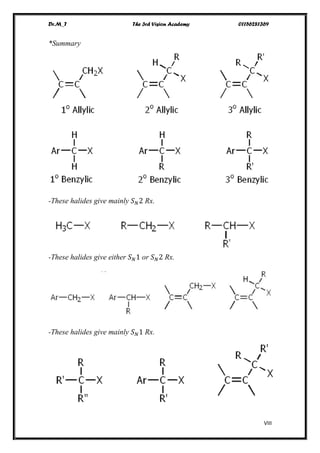
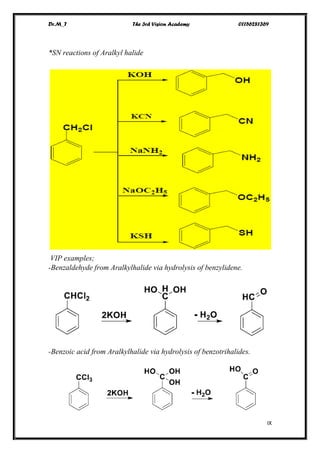
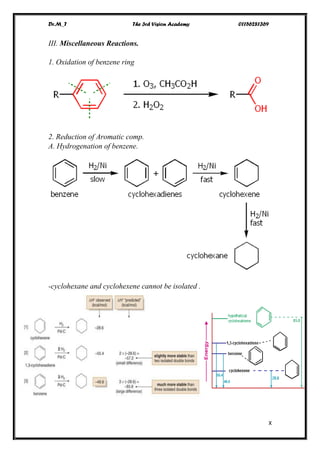
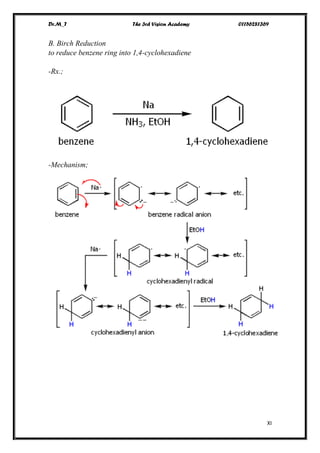
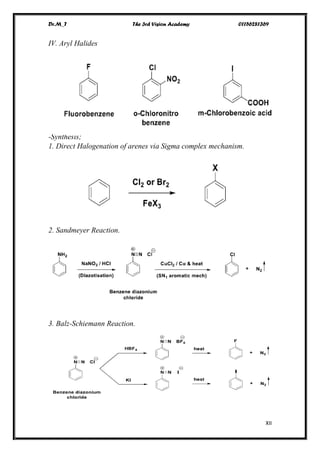
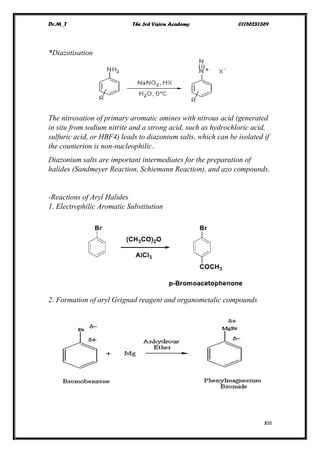
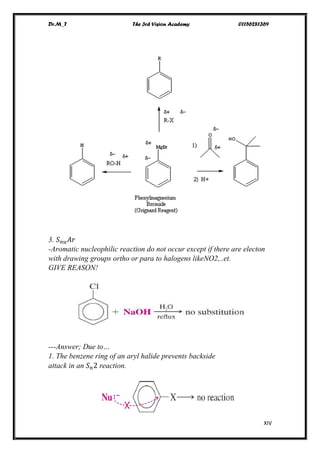
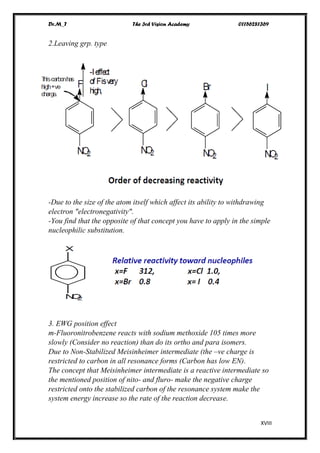
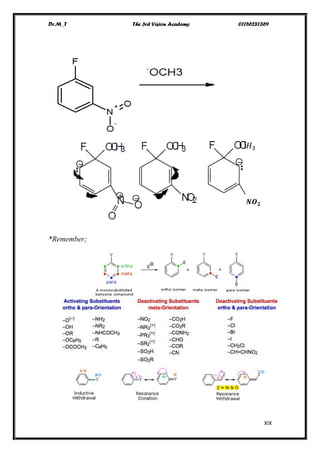
The document discusses various pathways of conversion and mechanisms in organic chemistry, focusing on alkyl and alkenyl benzenes, oxidation, and nucleophilic substitutions. It highlights the stability and reactivity differences between different types of benzylic and aryl halides, explaining the conditions under which certain reactions occur, such as SN1 and SN2 mechanisms. Additionally, it covers the synthesis of important compounds like styrene and various reaction methods including diazotization and Birch reduction.