Embed presentation
Downloaded 26 times















![The sum of the first n terms of an AP
is given by S = 2/n[2n + (n – 1) d]
We can also write this as S = 2/n[a
+ a + (n-1)d] i.e., S = n/2 (a + an)
Now , if there are only n terms in an
AP, then an = 1, the last term. From
(3), we see that S = n/ (a + 1)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arithmeticprogressions-141117041518-conversion-gate02/75/Arithmetic-progressions-19-2048.jpg)

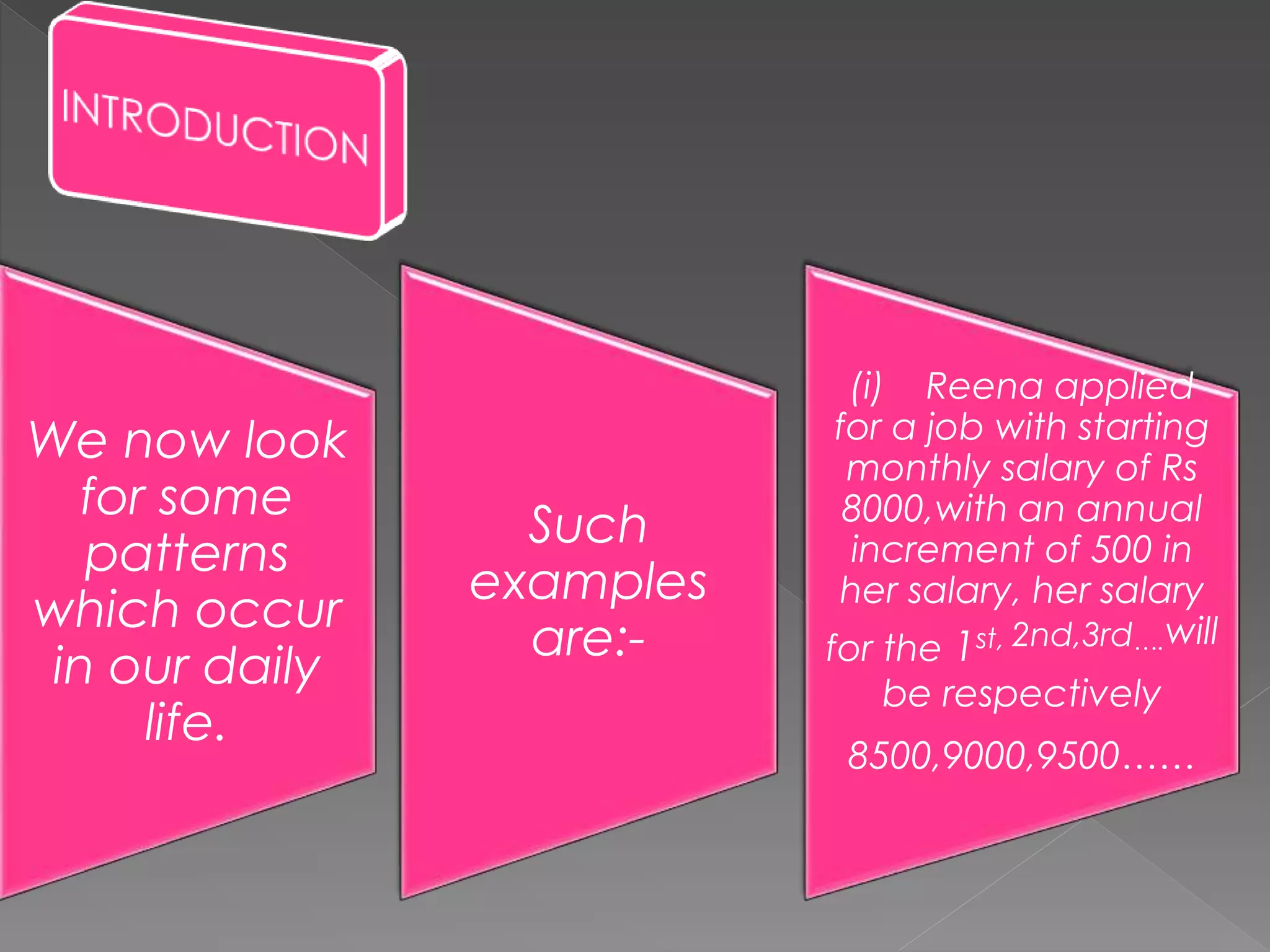
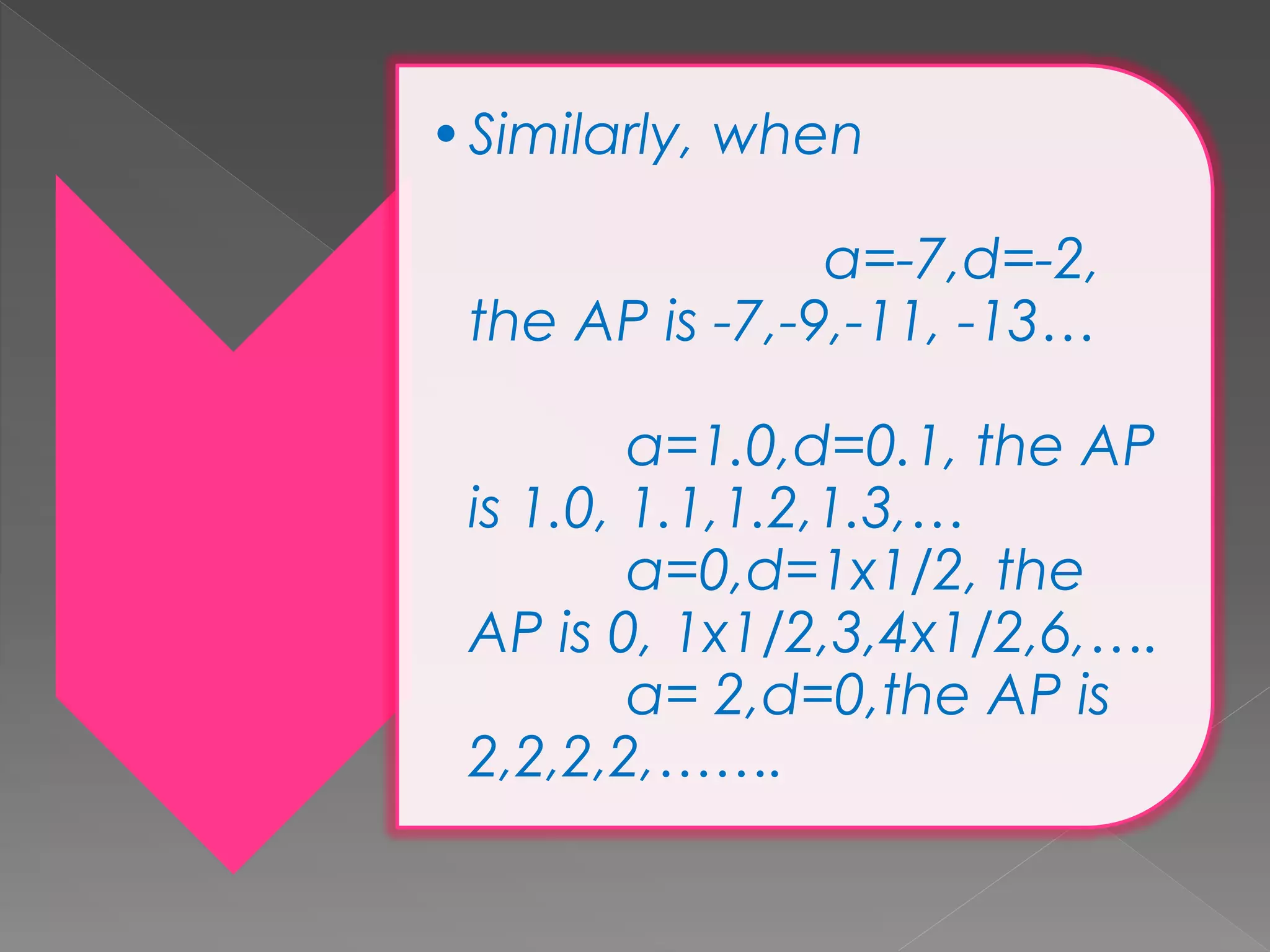
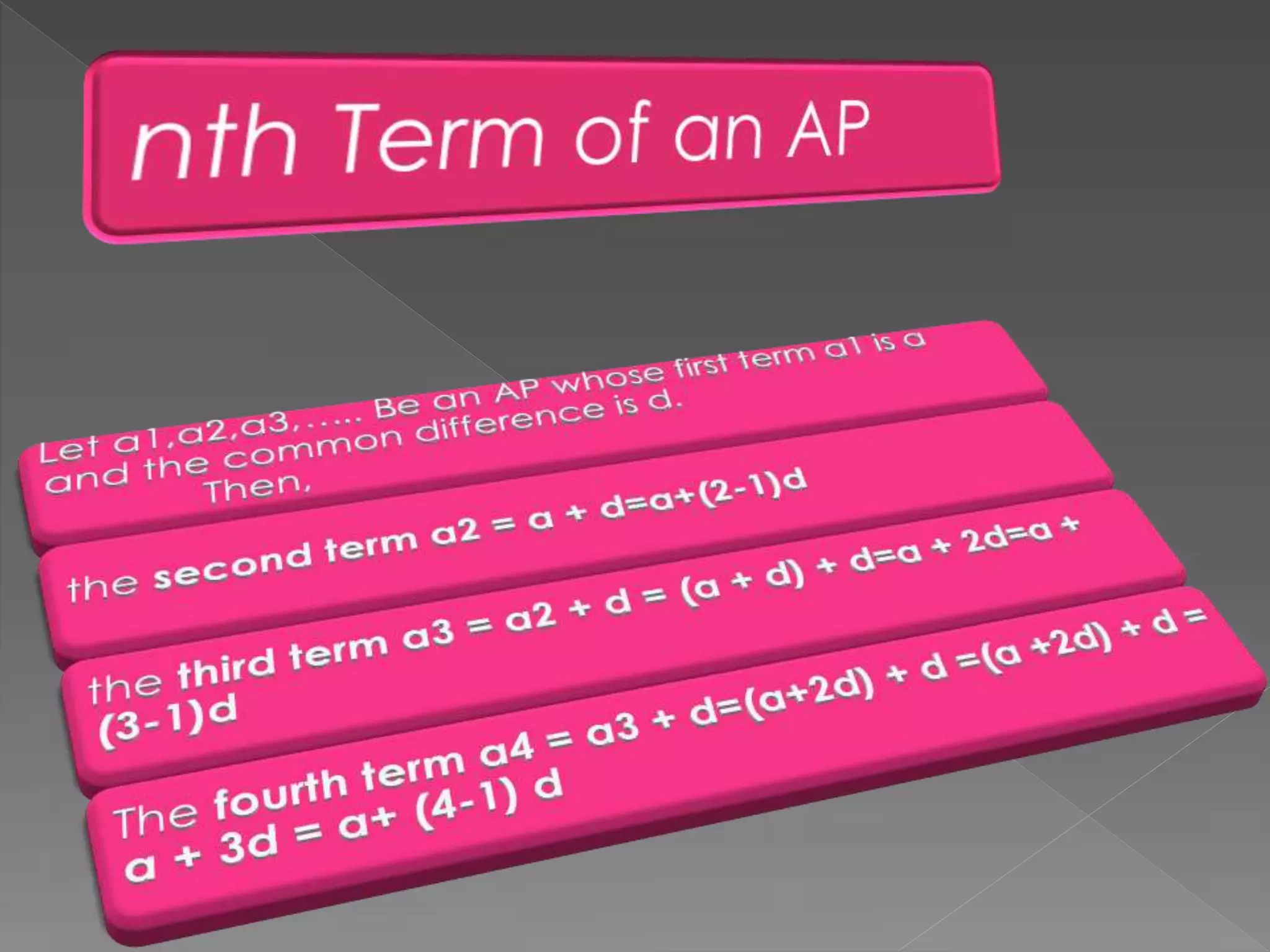
The document provides examples of arithmetic progressions and their patterns. It defines an arithmetic progression as a series of terms where the difference between consecutive terms is constant. It gives examples of arithmetic progressions with varying first terms and common differences. It also provides formulas for calculating the sum of the first n terms of an arithmetic progression based on the first term, last term, and common difference.


















![The sum of the first n terms of an AP
is given by S = 2/n[2n + (n – 1) d]
We can also write this as S = 2/n[a
+ a + (n-1)d] i.e., S = n/2 (a + an)
Now , if there are only n terms in an
AP, then an = 1, the last term. From
(3), we see that S = n/ (a + 1)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arithmeticprogressions-141117041518-conversion-gate02/75/Arithmetic-progressions-19-2048.jpg)
