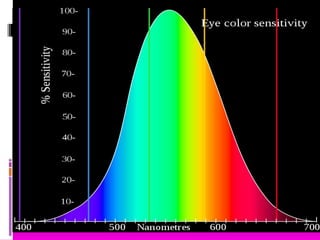
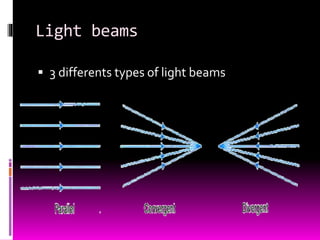
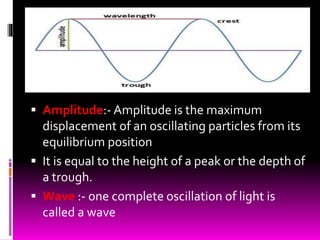
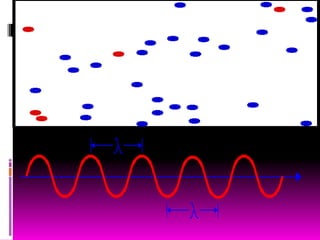
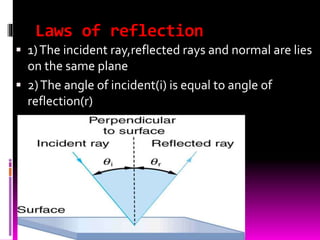
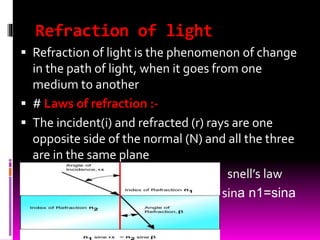
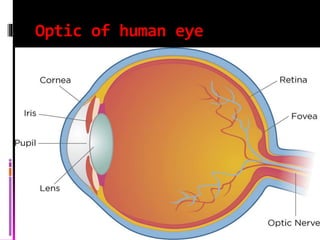
This document discusses optics and the human eye. It begins by explaining the nature of light as electromagnetic waves that can behave as both particles and waves. It then covers properties of light such as its speed and propagation in straight lines. The document discusses how the eye is sensitive to wavelengths between 600-350nm and absorbs shorter wavelengths. It explains light rays and beams and the dual wave-particle nature of light. Key optics concepts like reflection and refraction are summarized according to their laws. The document concludes by mentioning optics of the human eye.