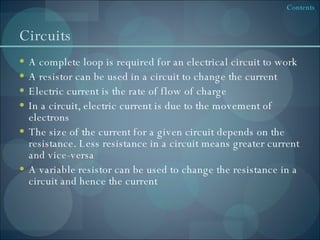
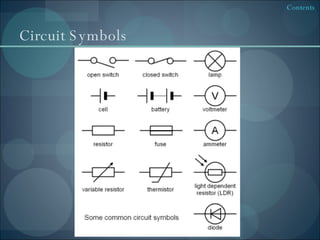
This document provides an overview of physics concepts related to electricity and nuclear physics. It discusses electrostatics, including charging insulators and generating electric sparks. It also covers uses of electrostatics like in photocopiers and defibrillators. The document discusses nuclear fission in power plants and the challenges of nuclear waste disposal. Safety topics like circuit components and radiation treatment are also summarized.







![Dangers of Static Charge Electrostatic charge is dangerous when it causes lightning and sparks that can ignite fuel When an aircraft is being refuelled with kerosene (paraffin) and when a car is being refuelled with petrol friction forces cause charge separation Charge separation result in the metal frame of an aircraft gaining an opposite charge to the fuel This could result in a build-up of static charge on the metal frame of the aircraft or metal sleeve of the car refuelling pipe]if the voltage became high enough to cause a spark to earth, it could ignite the fuel To prevent this, the framework of an aircraft is connected to earth before refuelling and the pipe leading to the petrol tank in a car is connected to the body of the car so that the charge can spread out, preventing the build-up of charge in a small area](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physics-090415023543-phpapp01/85/GCSE-Physics-Revision-8-320.jpg)