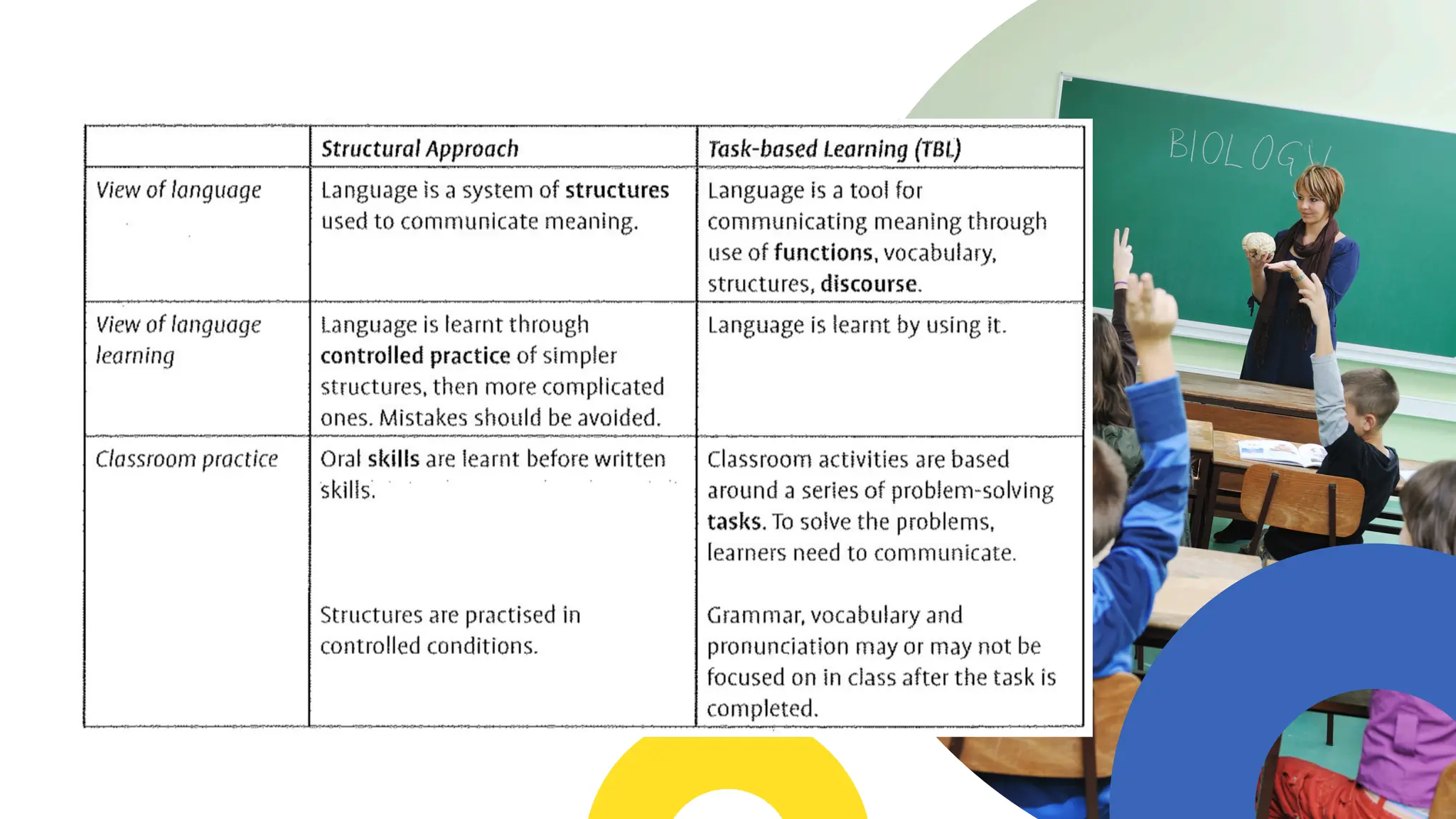
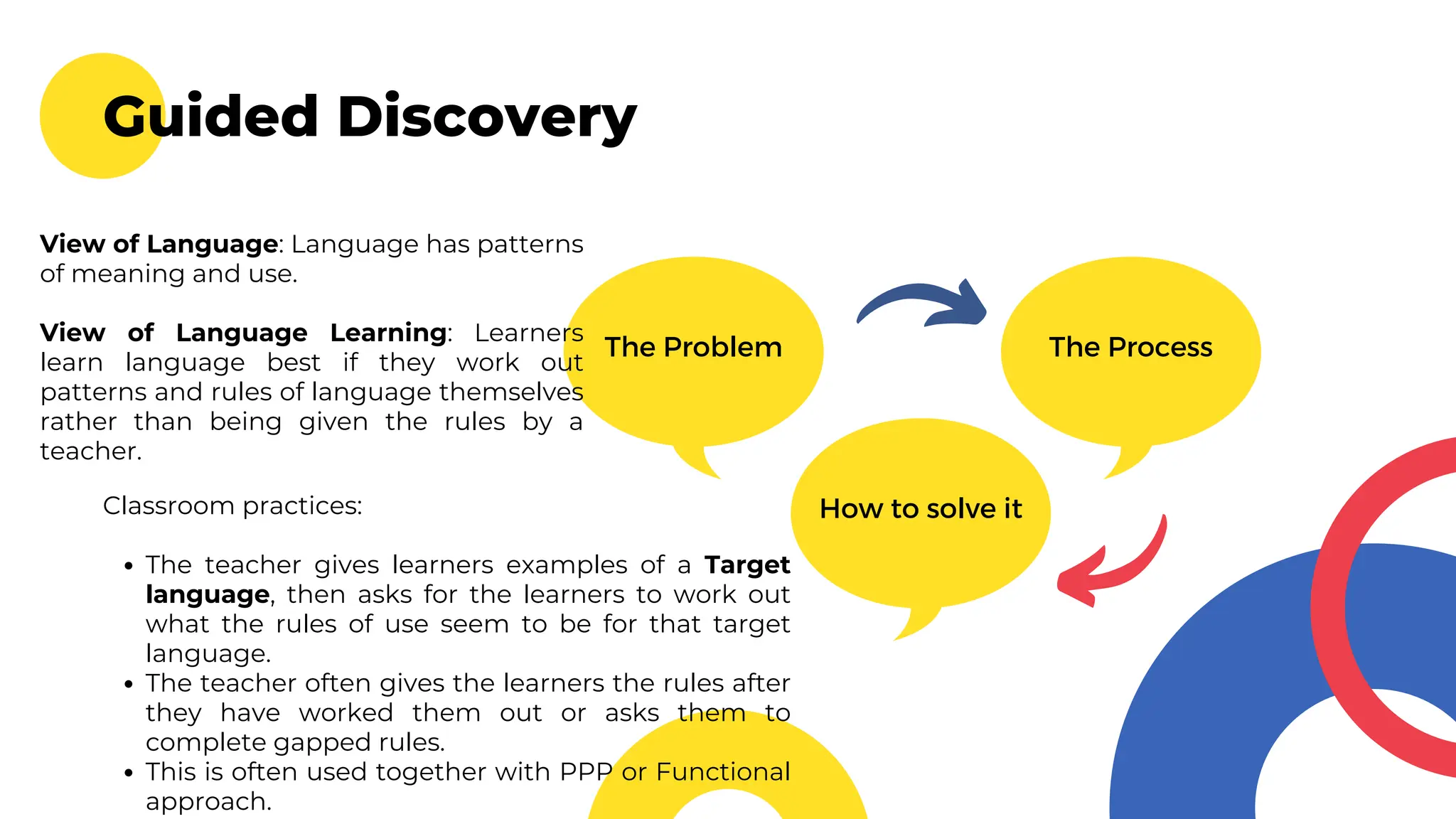
The document outlines various approaches to language teaching, defining 'approaches' and 'methods' interchangeably, while emphasizing the significance of grammar rules, vocabulary, and communicative practices. It describes several specific teaching methods including Presentation, Practice, and Production (PPP), Total Physical Response (TPR), the Lexical Approach, and the Communicative Approach, each with distinct views on language and techniques for classroom practice. The document highlights the importance of adapting teaching strategies to enhance language acquisition through meaningful interactions and contextual learning.