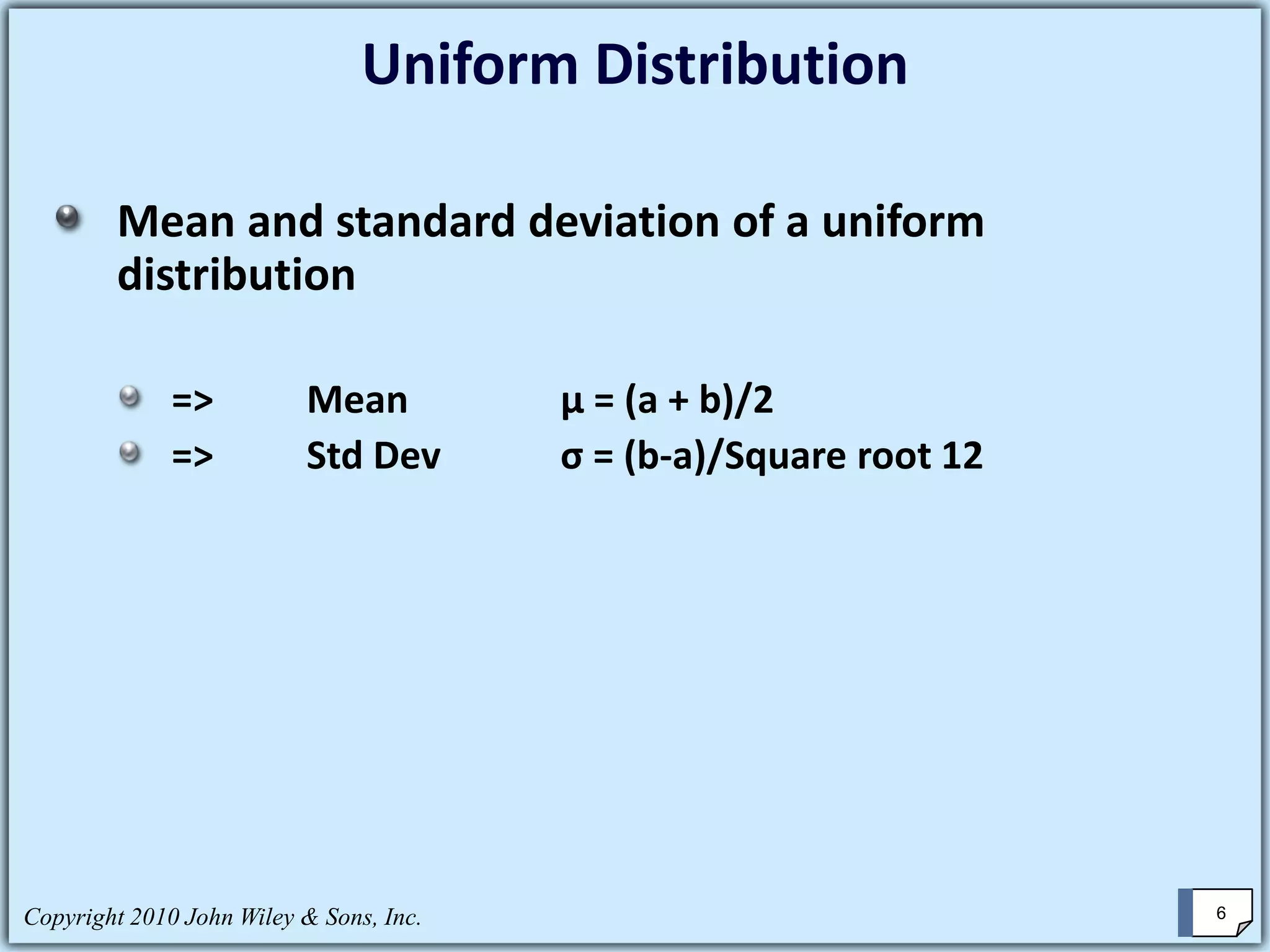
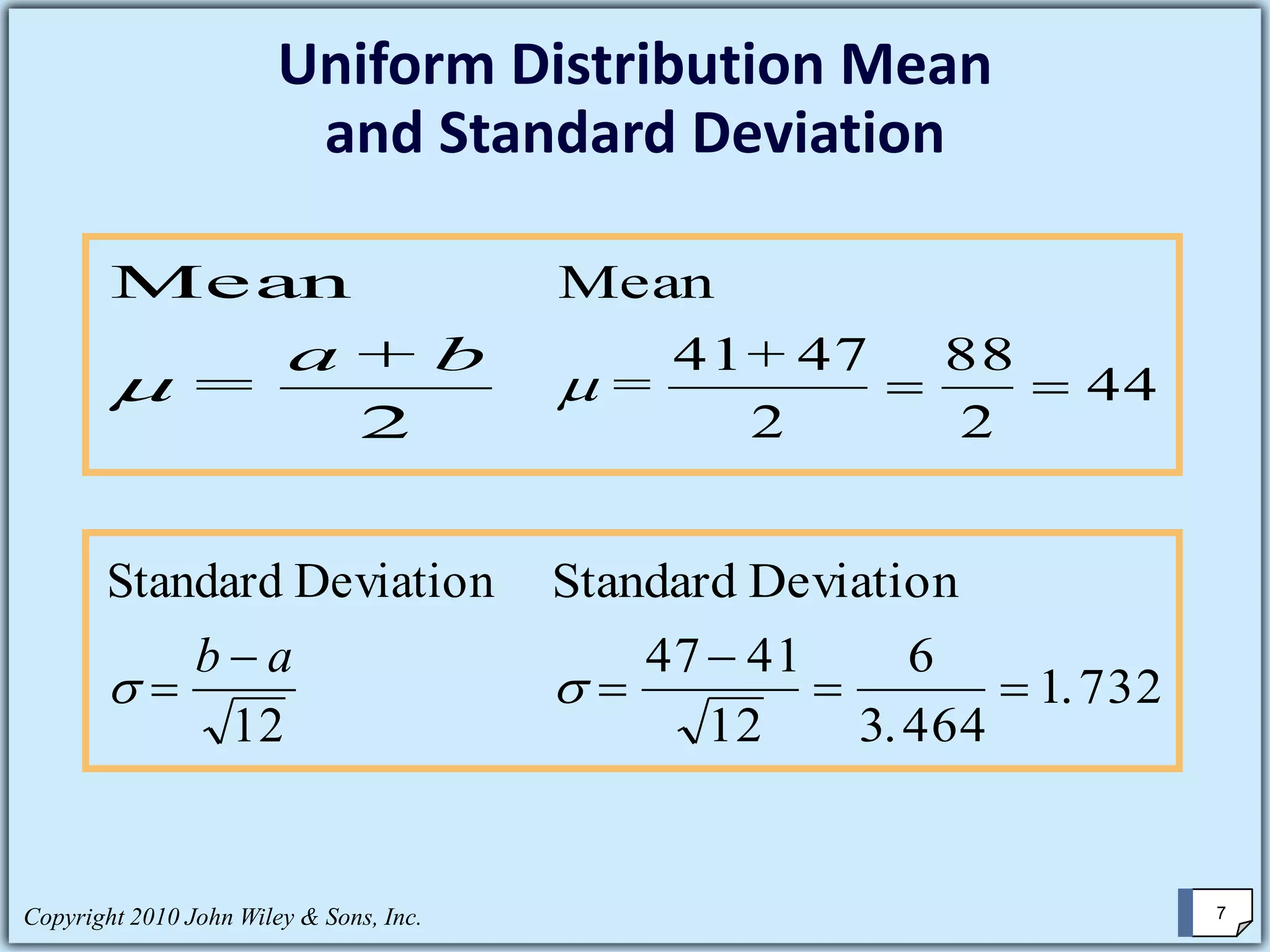
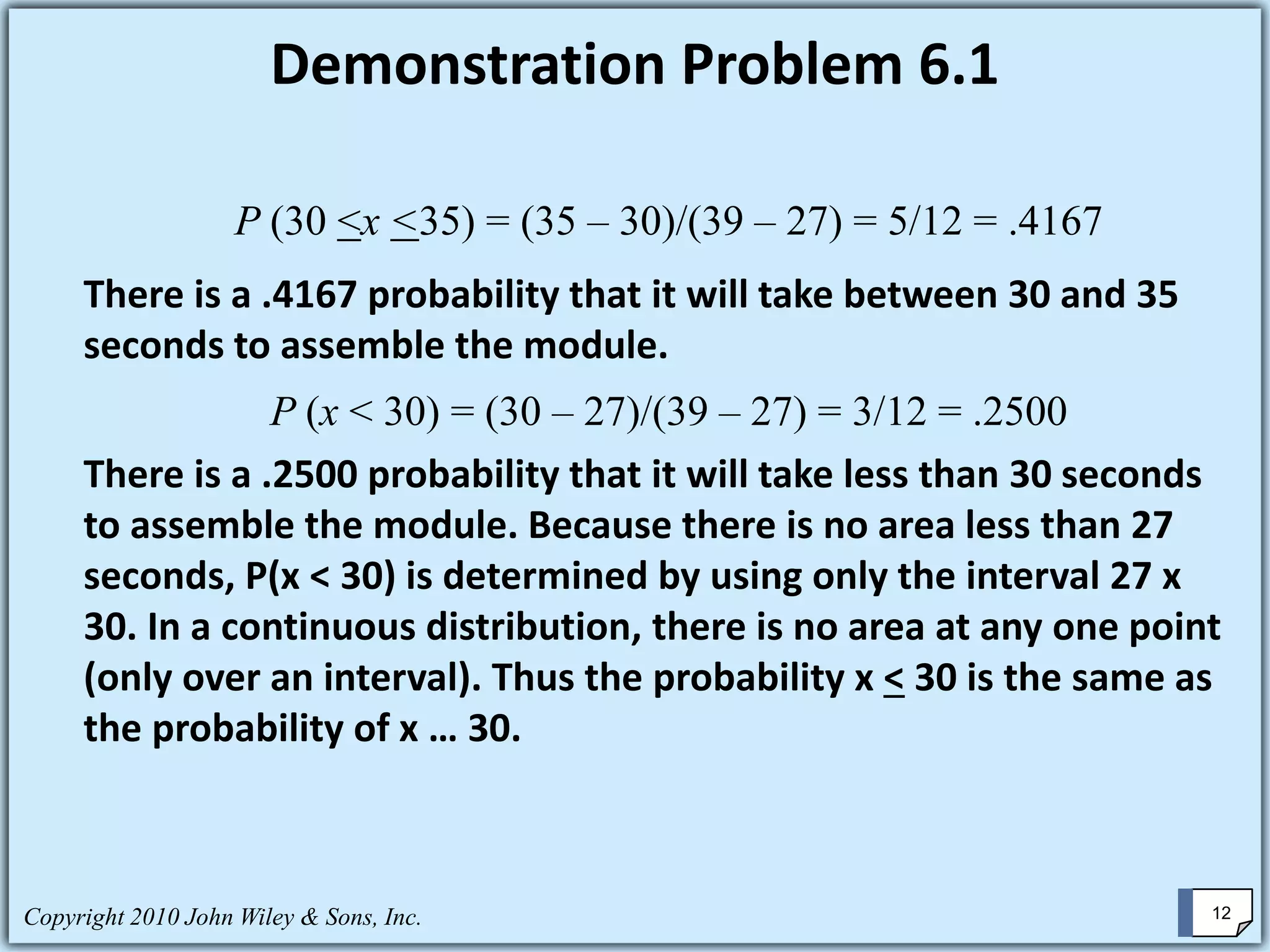
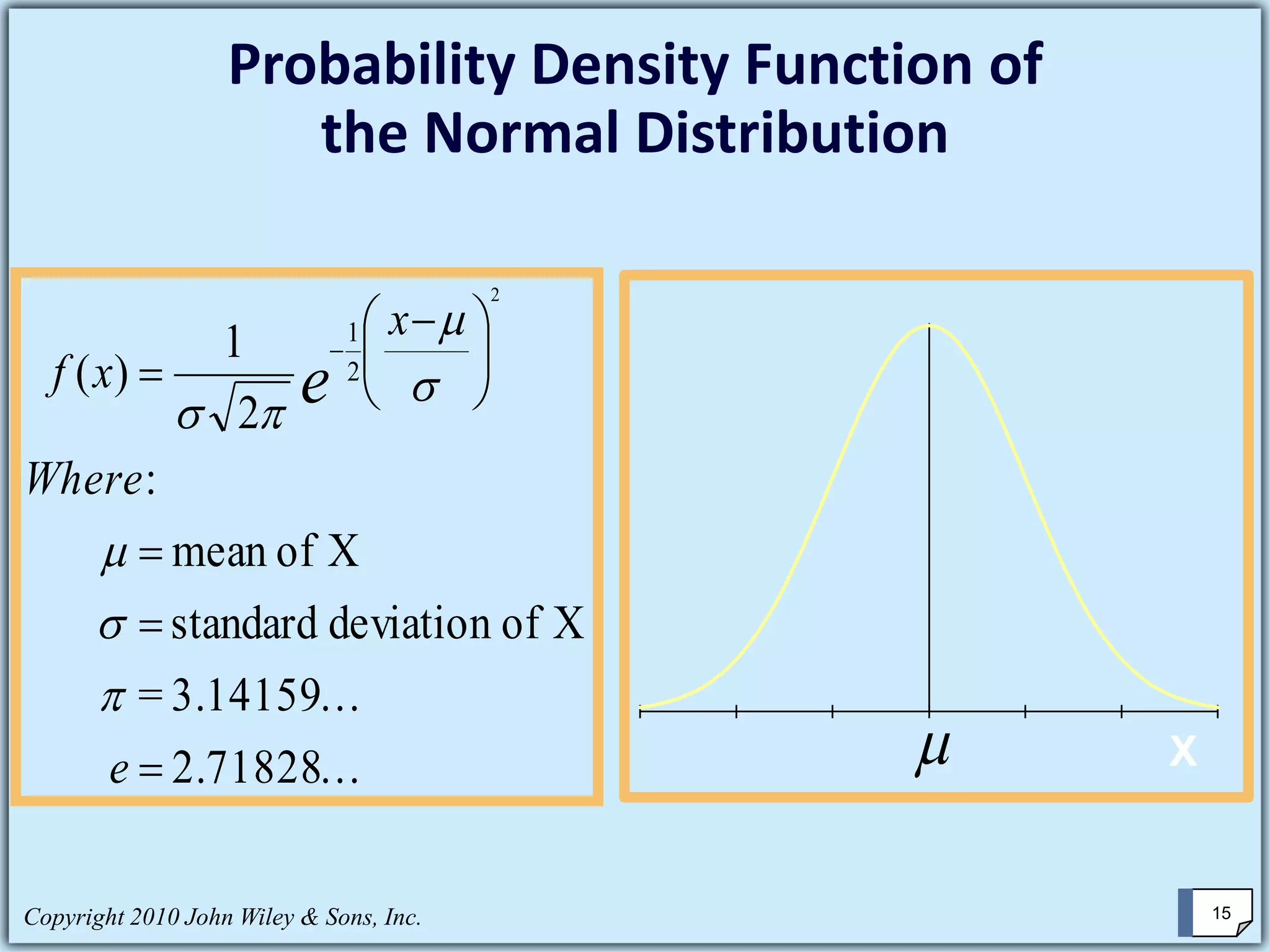
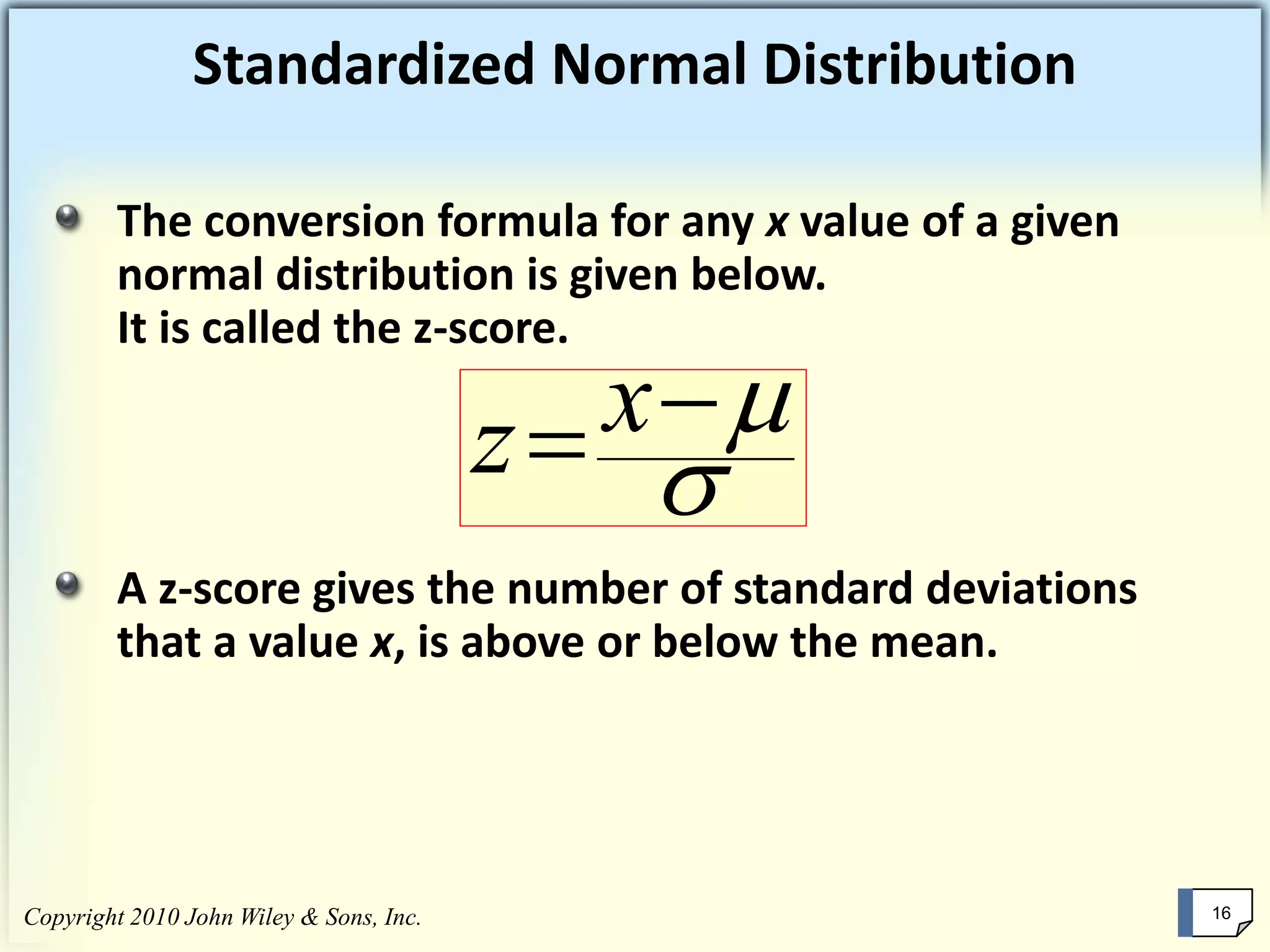
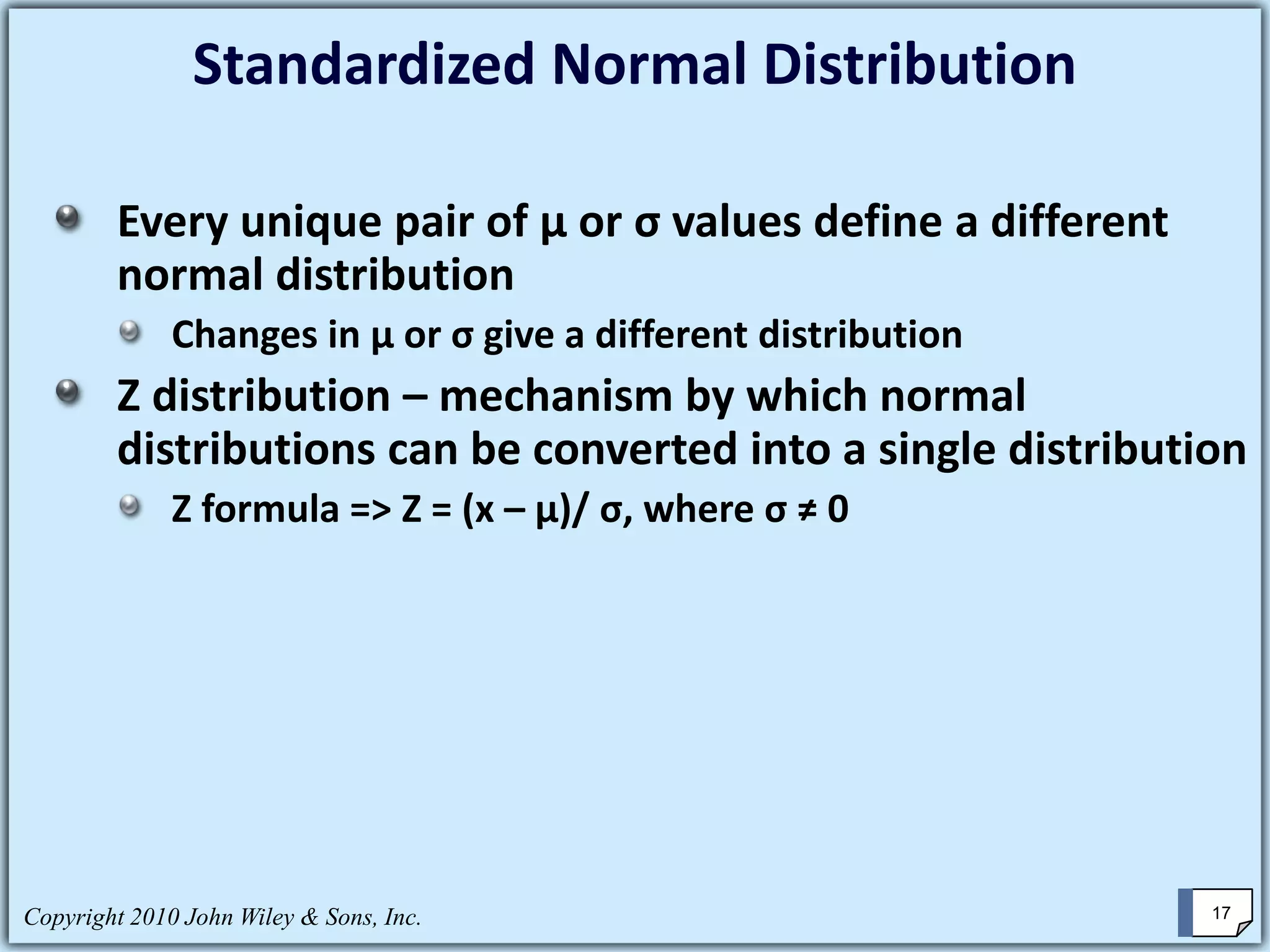
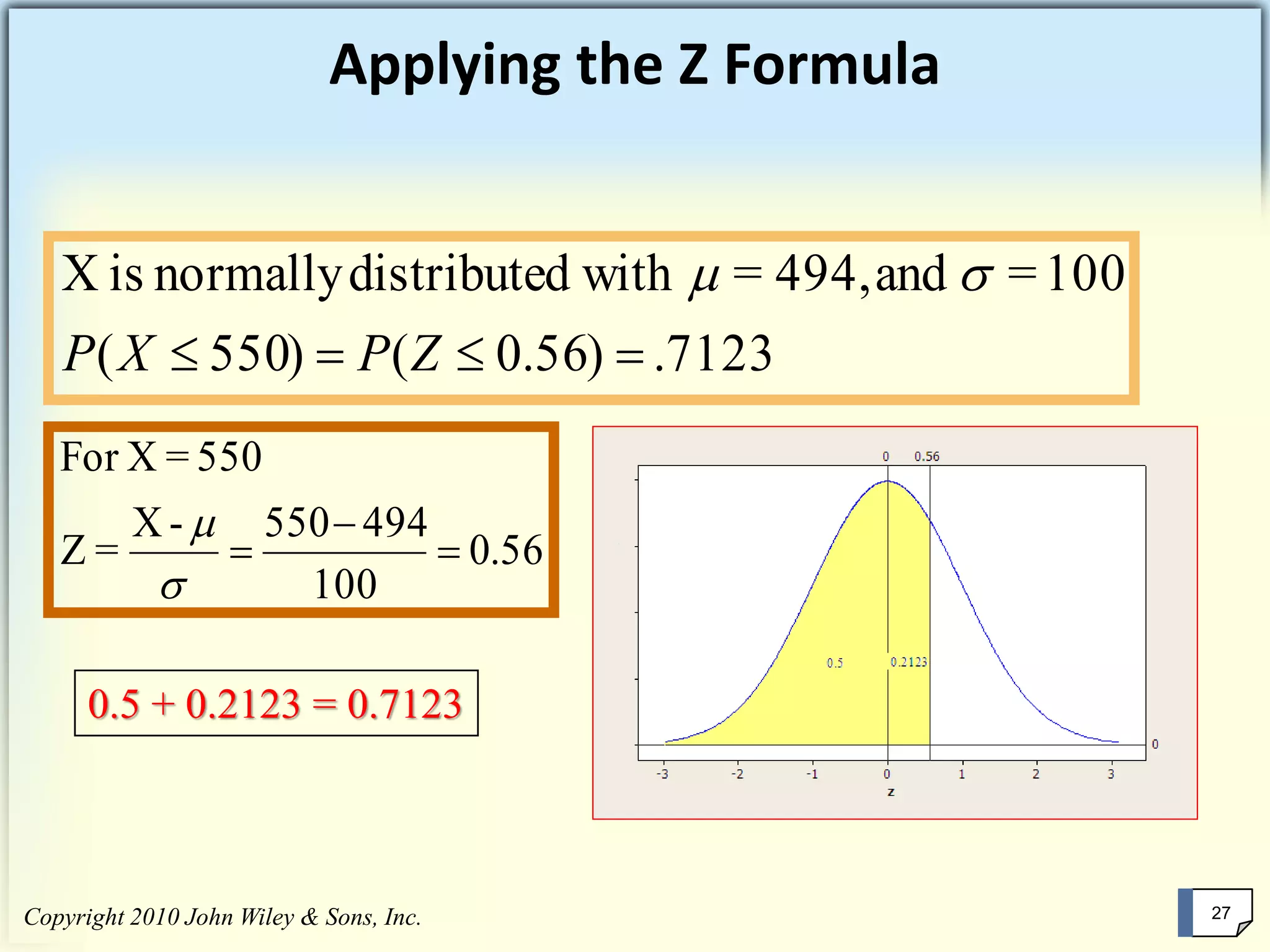
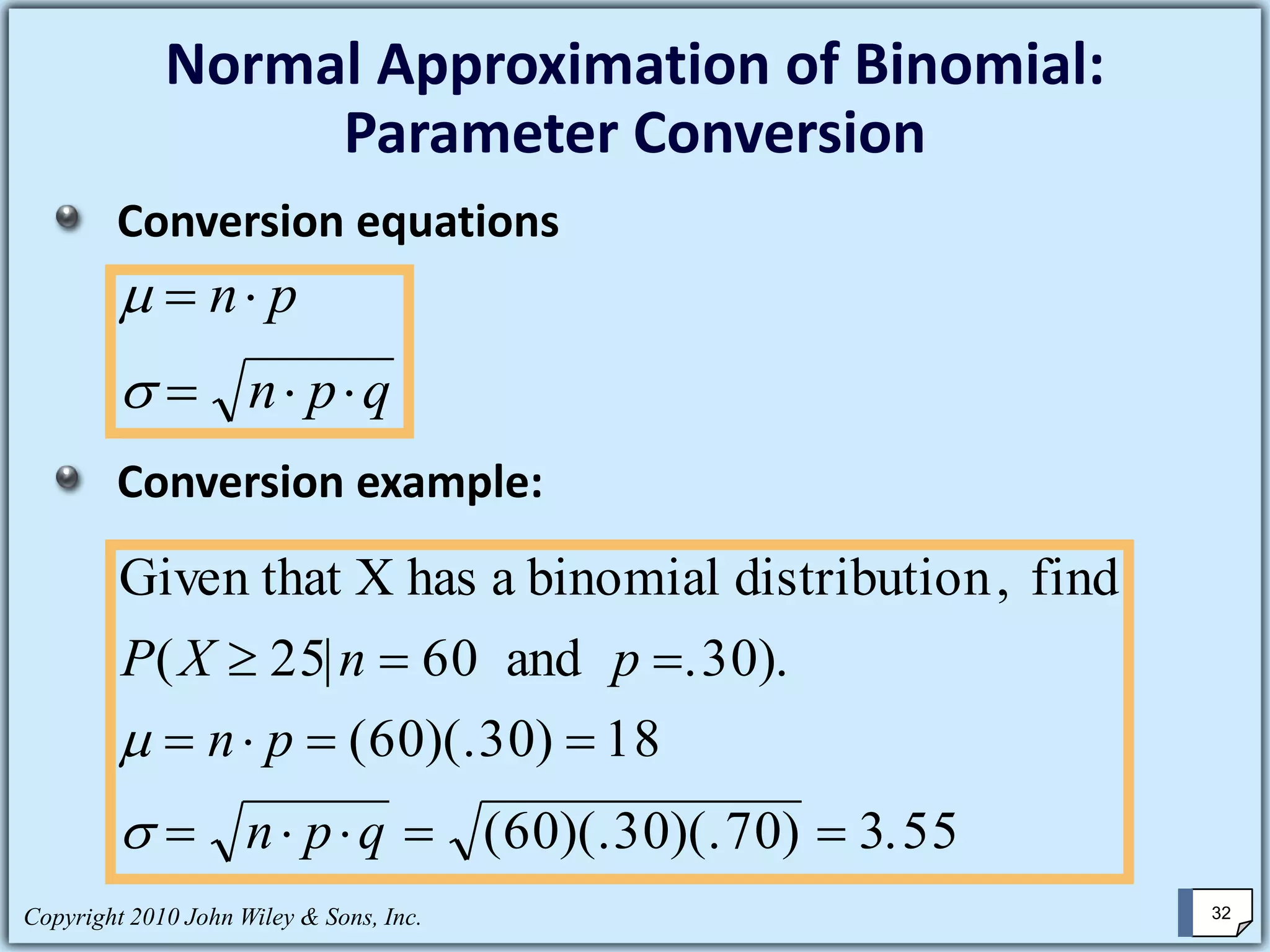
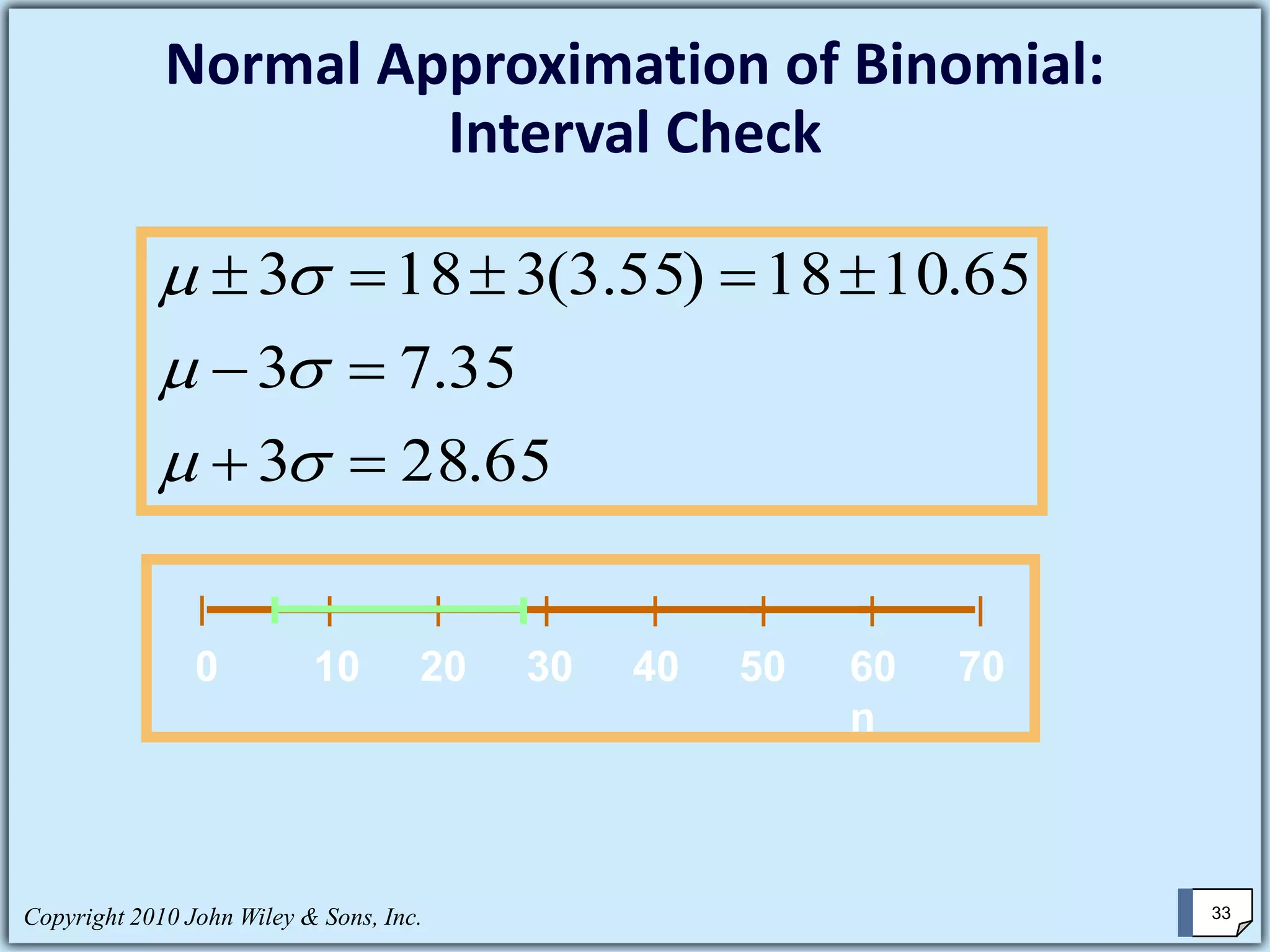
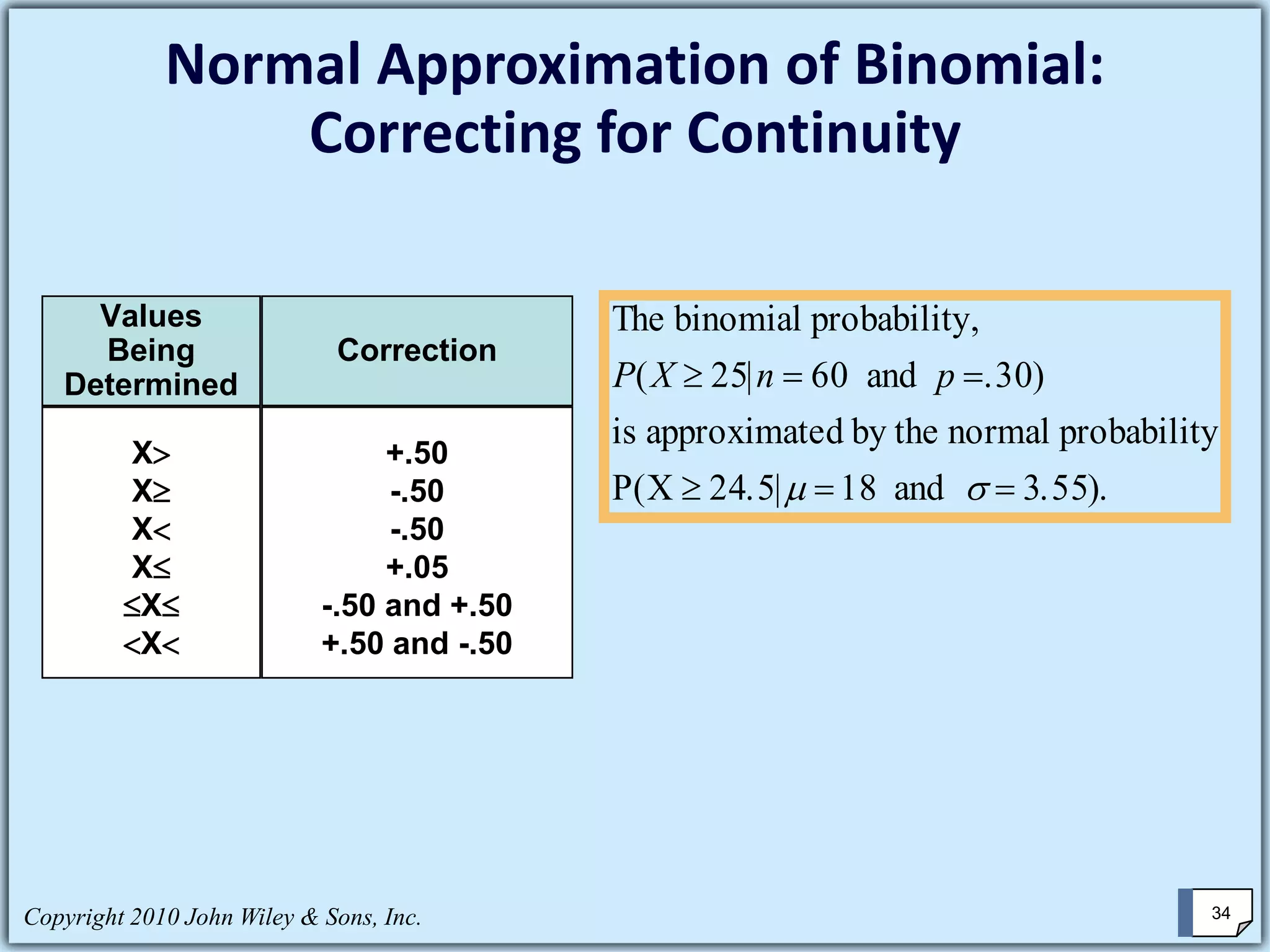
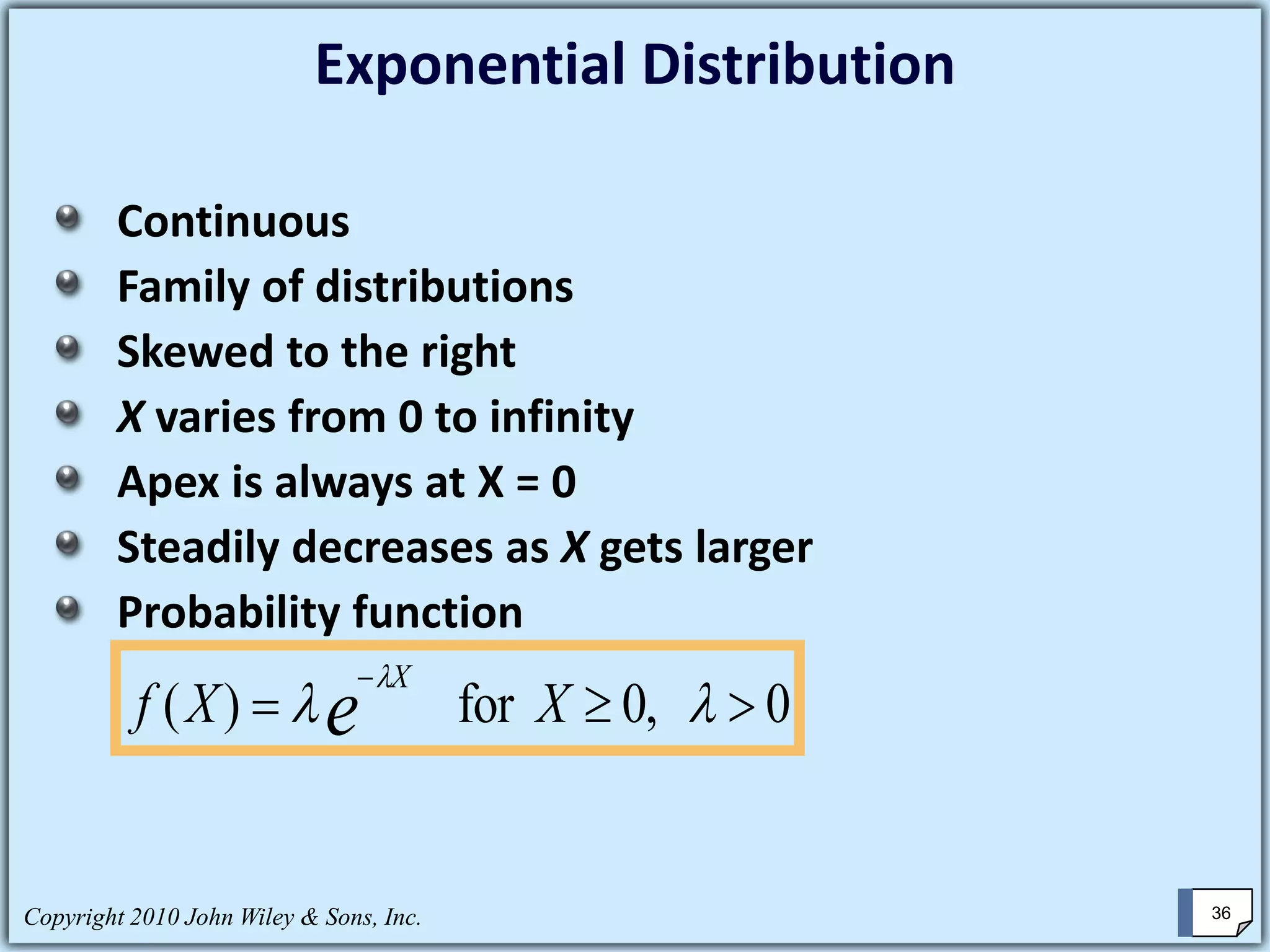
This chapter summary covers key concepts about continuous probability distributions discussed in Chapter 6 of the textbook "Business Statistics, 6th ed." by Ken Black. The chapter objectives are to understand the uniform distribution, appreciate the importance of the normal distribution, and know how to solve normal distribution problems. It discusses the uniform, normal, and exponential distributions. It explains how to calculate probabilities using the normal distribution and z-scores. It also discusses when the normal distribution can be used to approximate the binomial distribution.