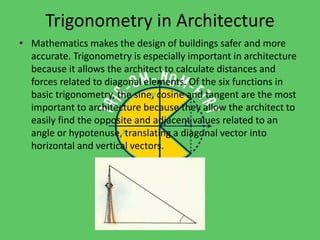
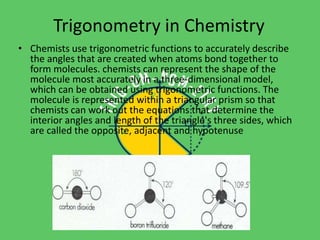
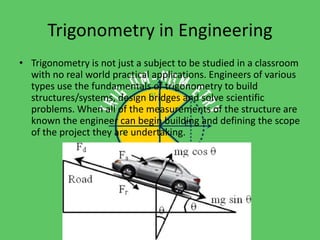
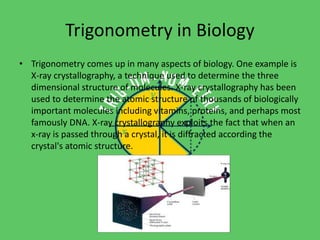
Trigonometry is used in many fields including astronomy, architecture, navigation, chemistry, meteorology, engineering, carpentry, biology, and forensics. It allows measurement of distances to stars, calculation of angles and forces in building design, navigation on land and sea, modeling molecular structures, tracking weather balloons, structural design, angled cuts in carpentry, determining molecular structures through x-ray crystallography, and analyzing crime scenes. Trigonometric functions like sine, cosine, and tangent are essential mathematical tools across diverse applications in science and technology.