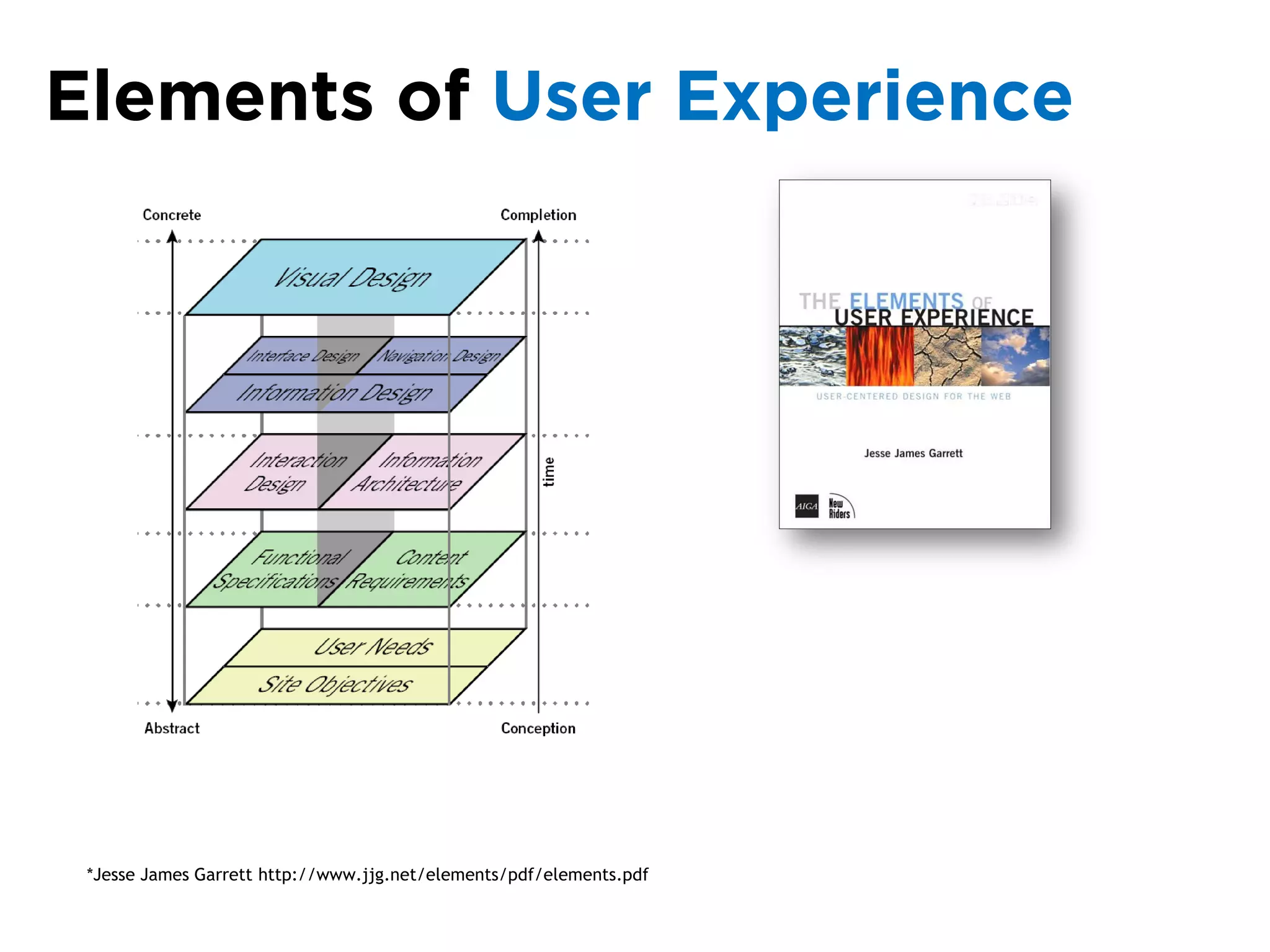
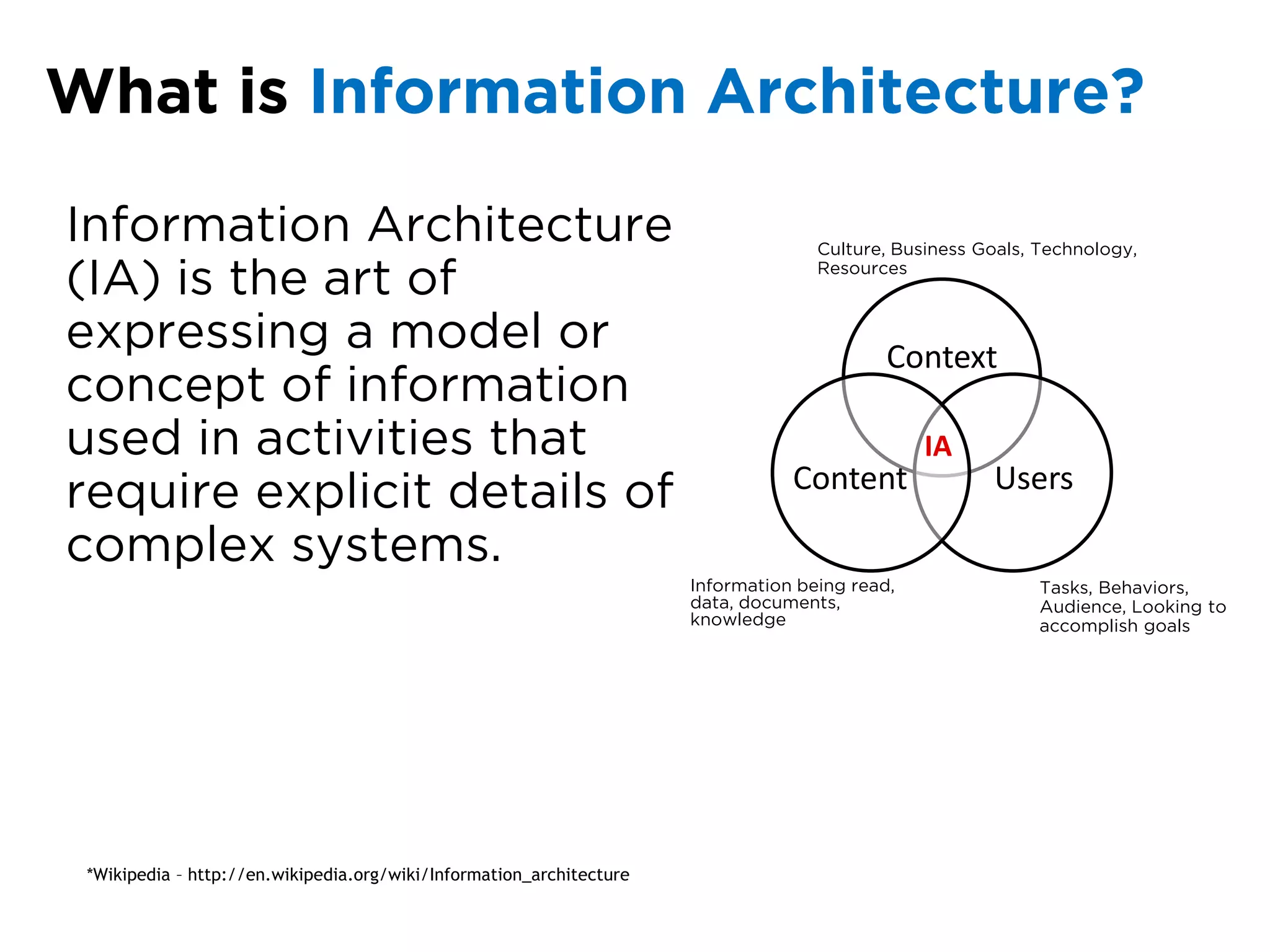
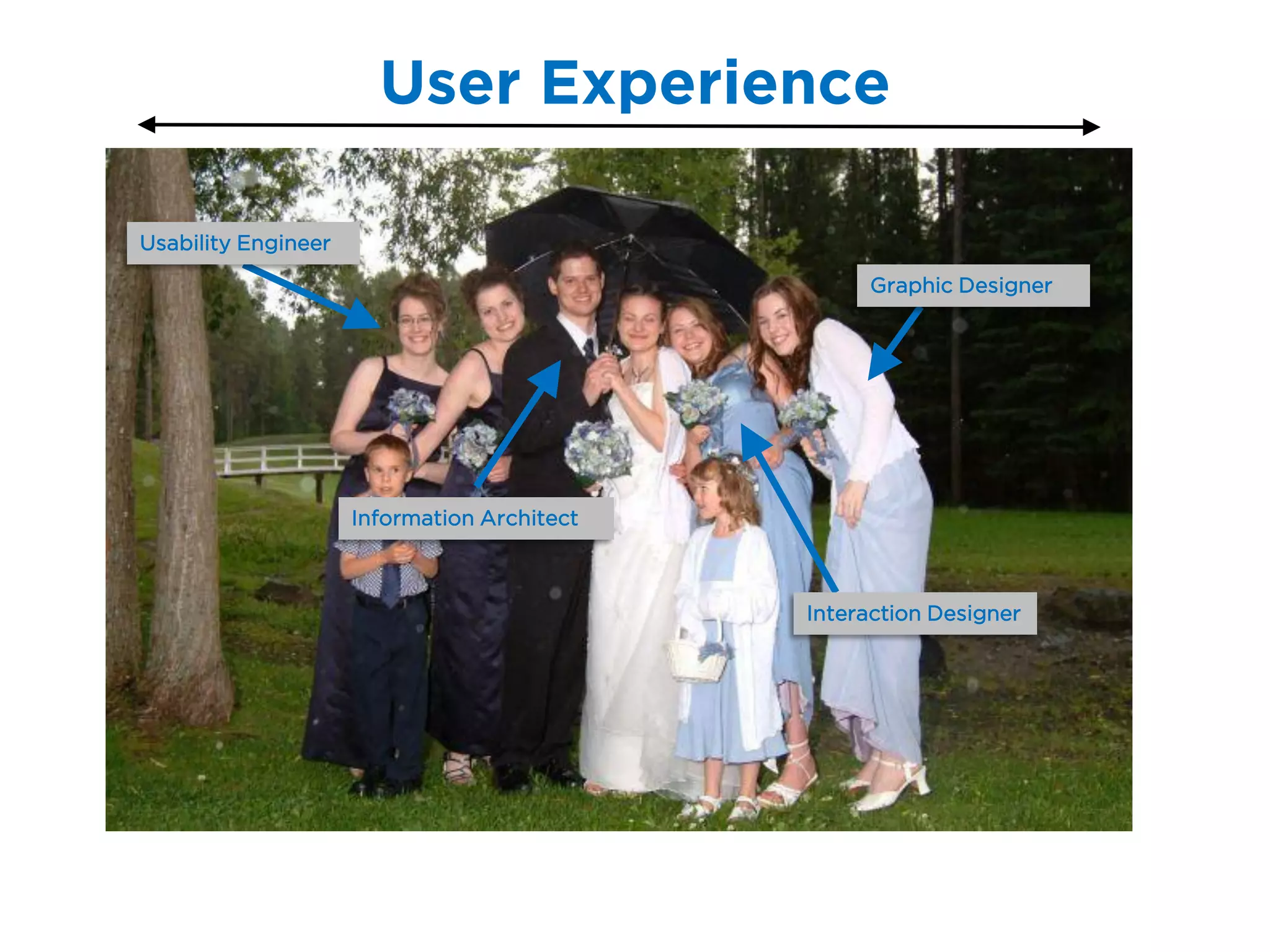
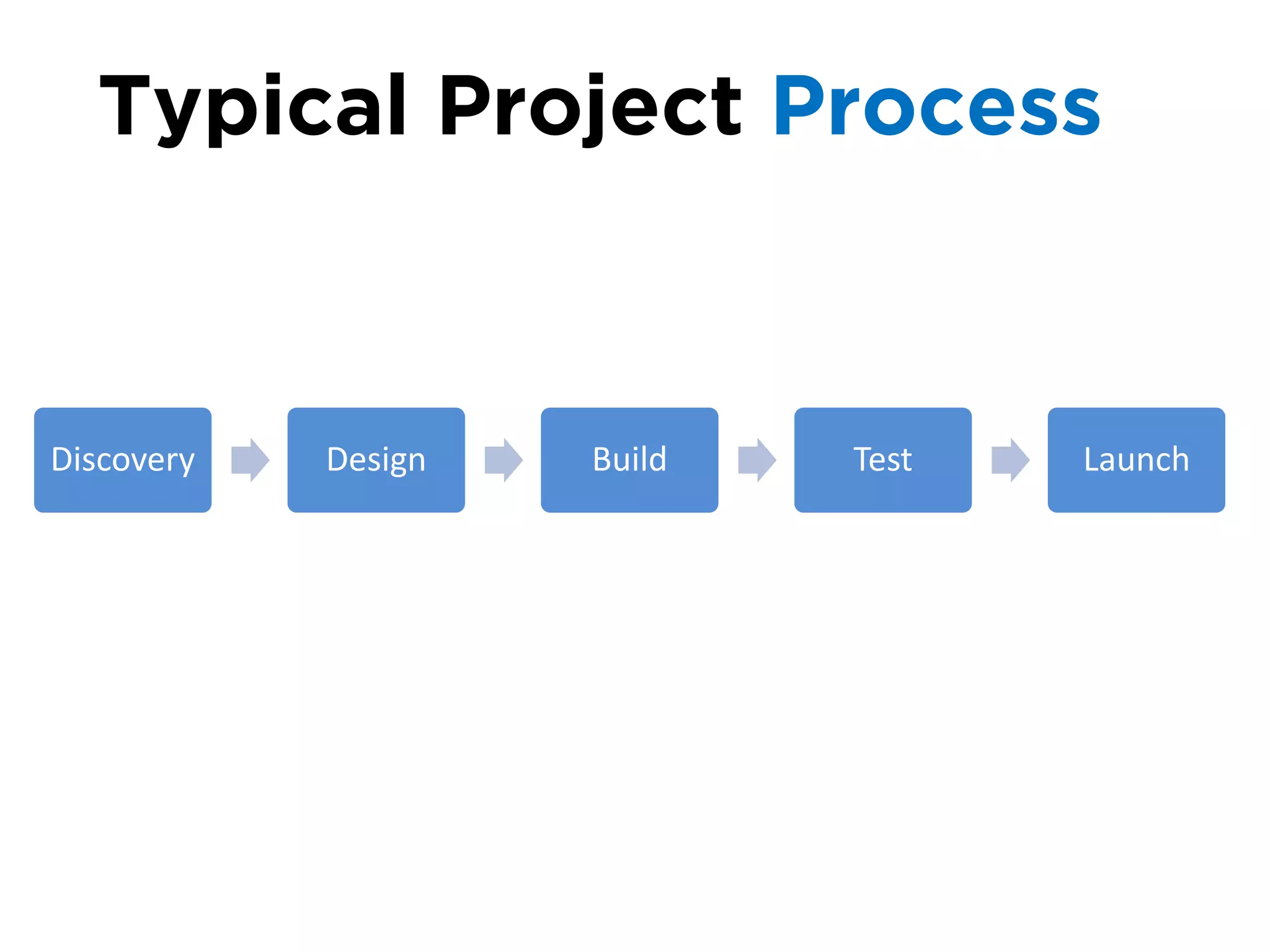
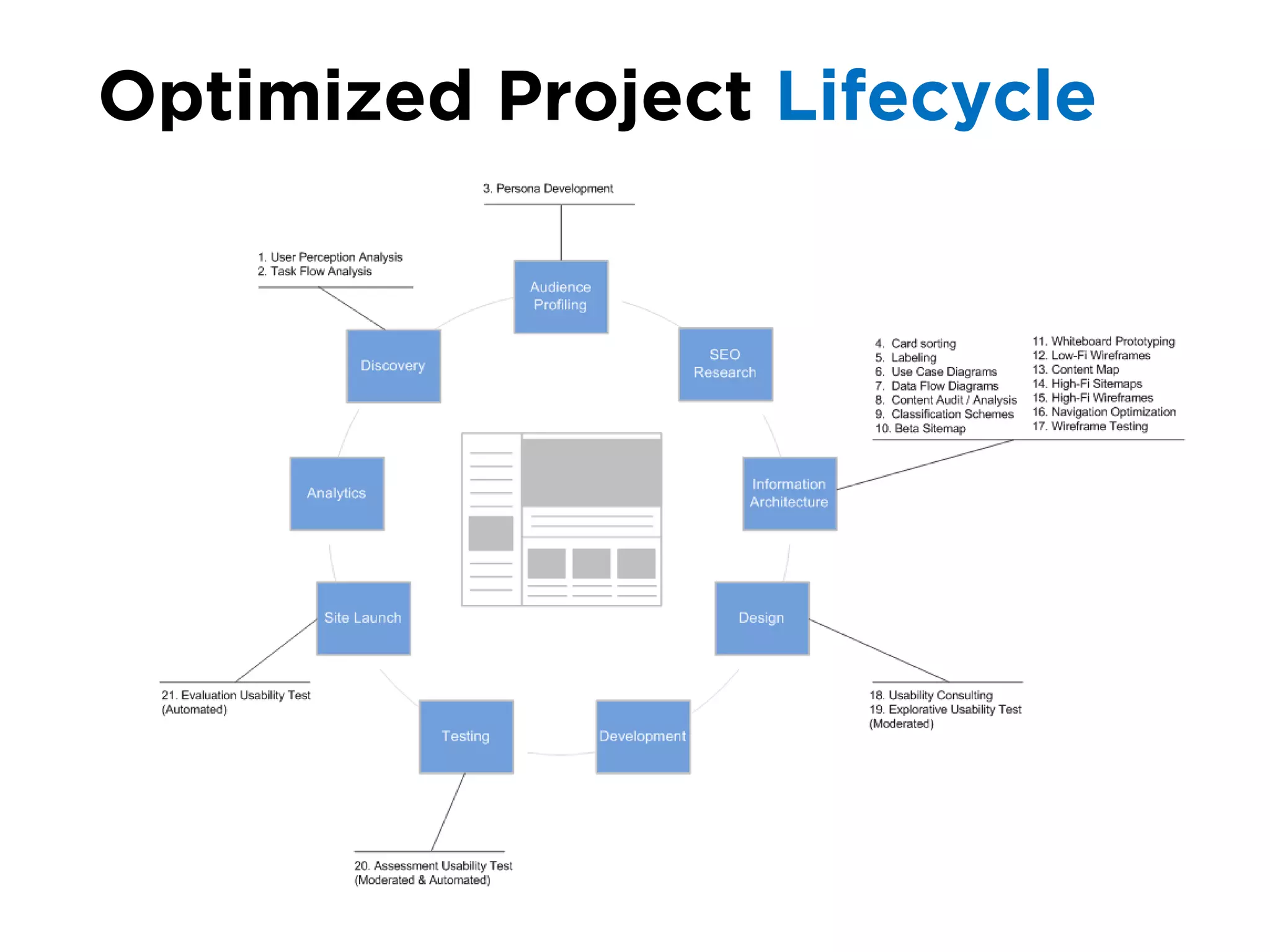
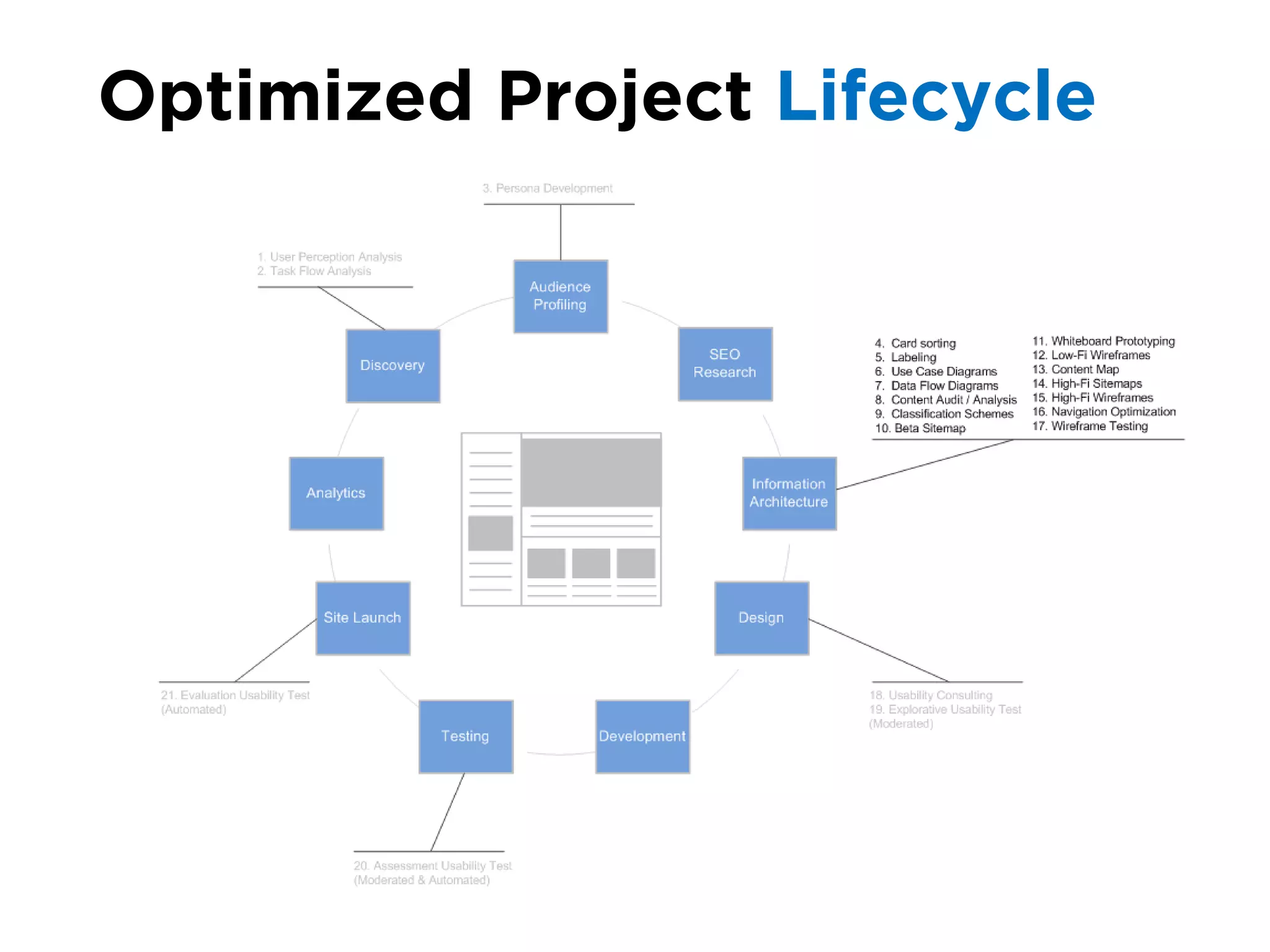
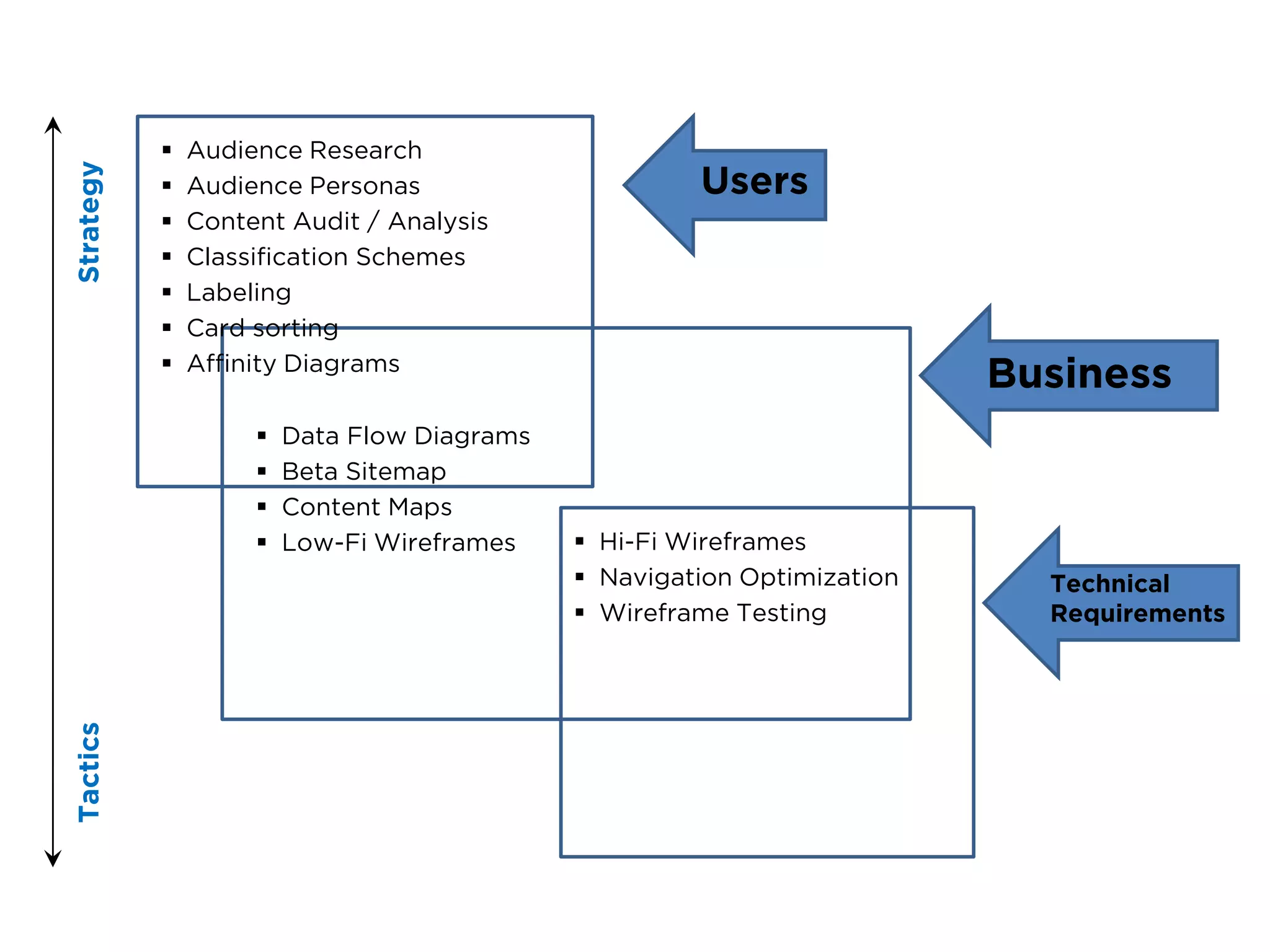
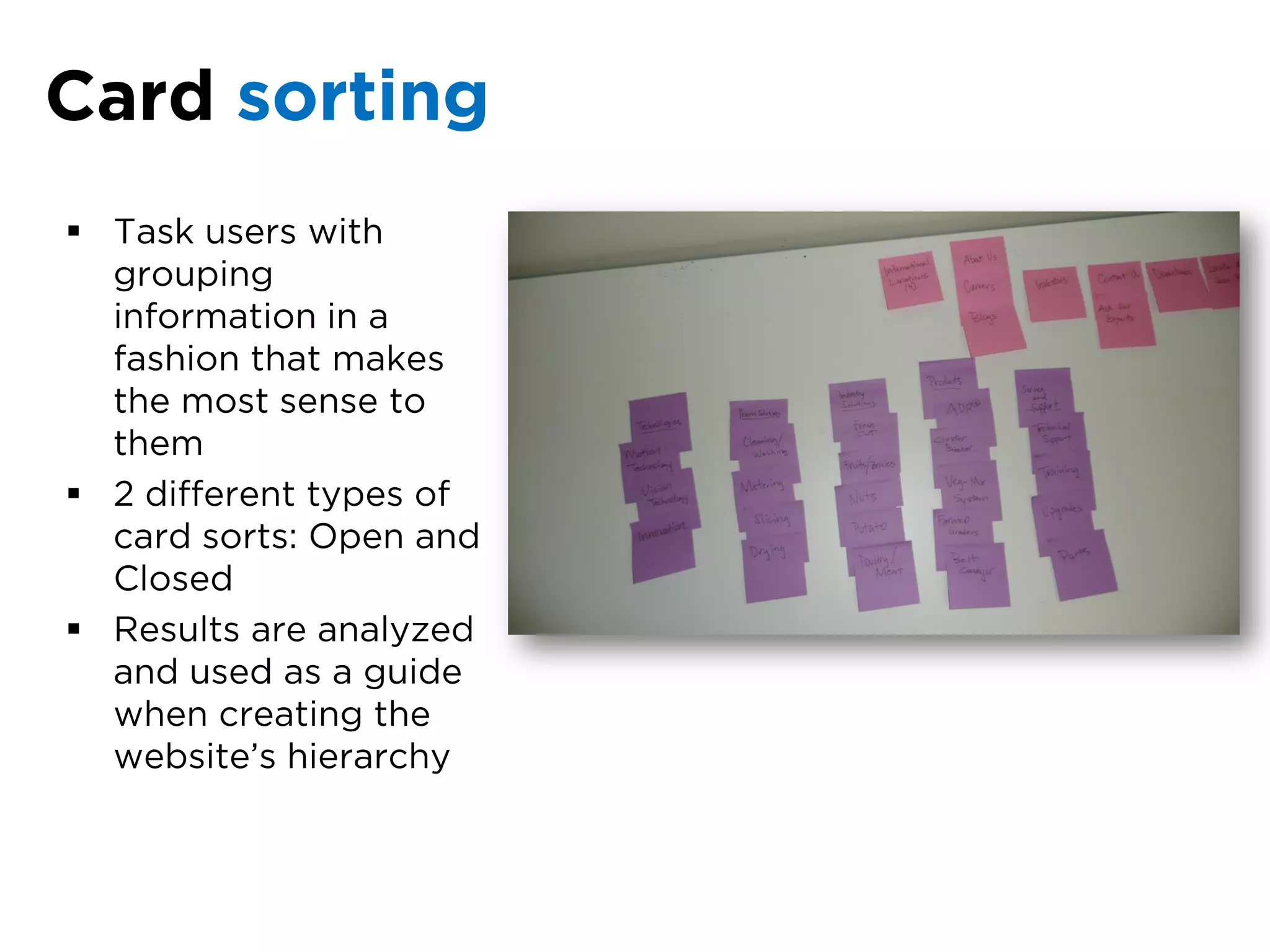
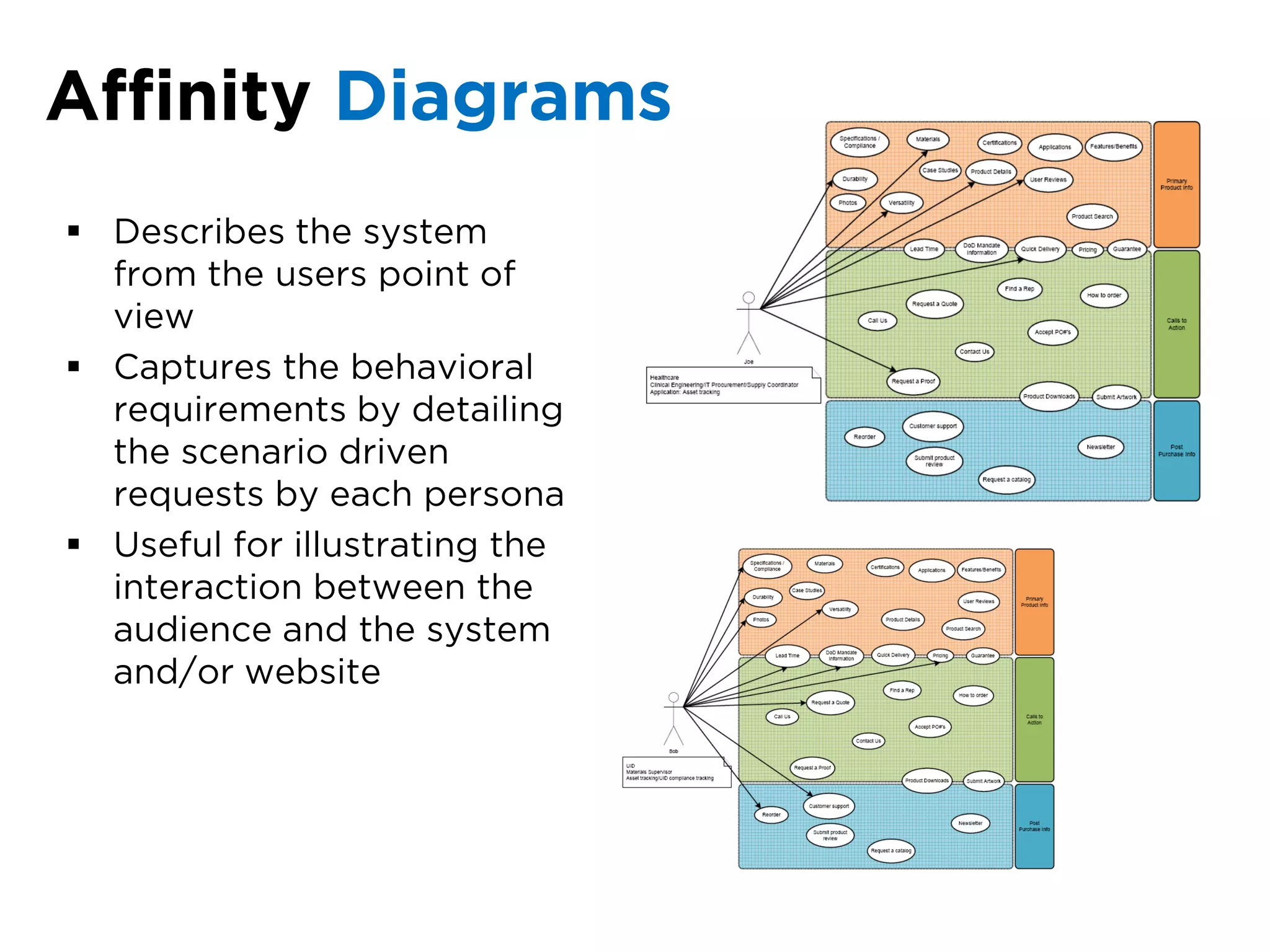
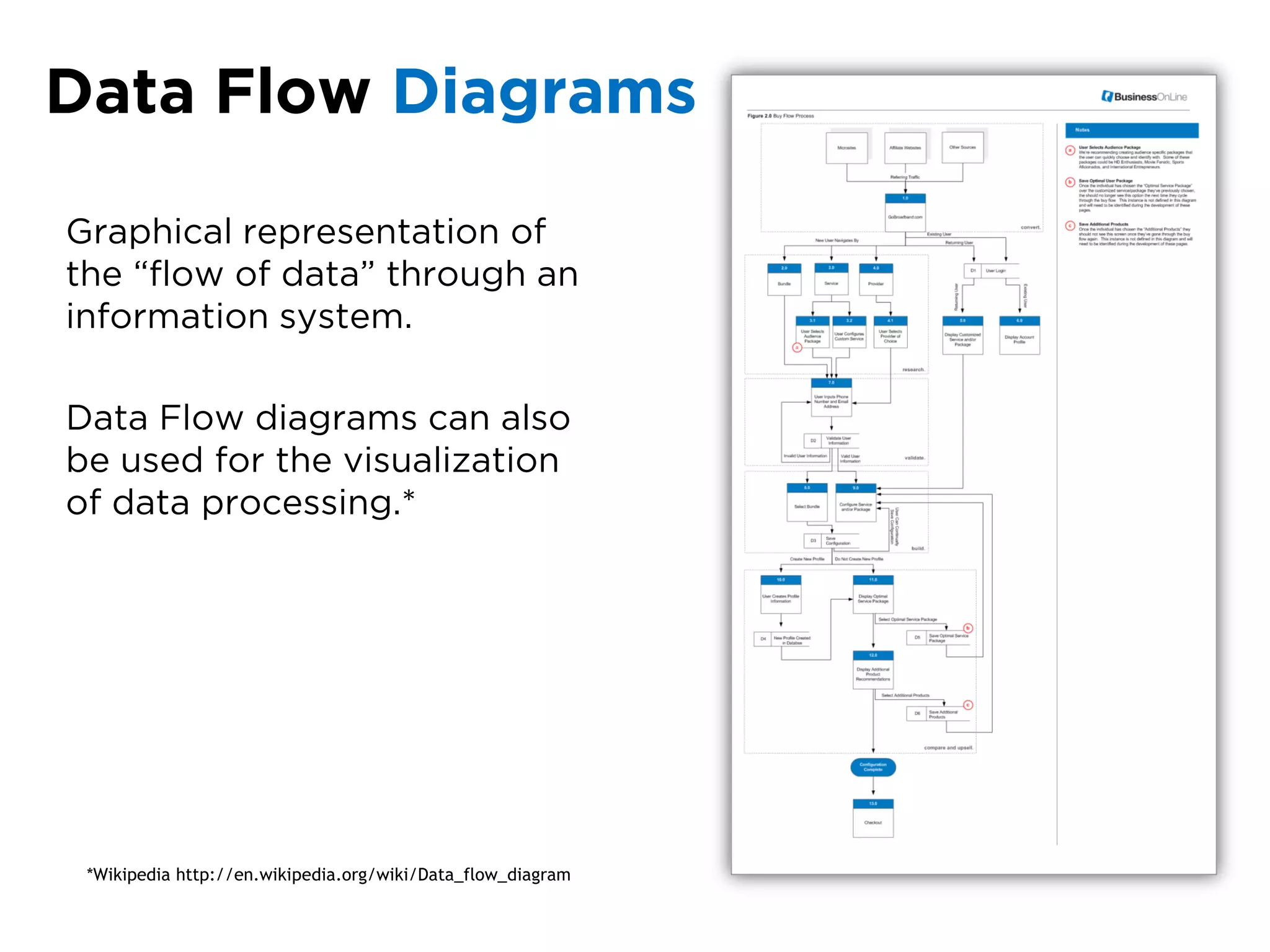
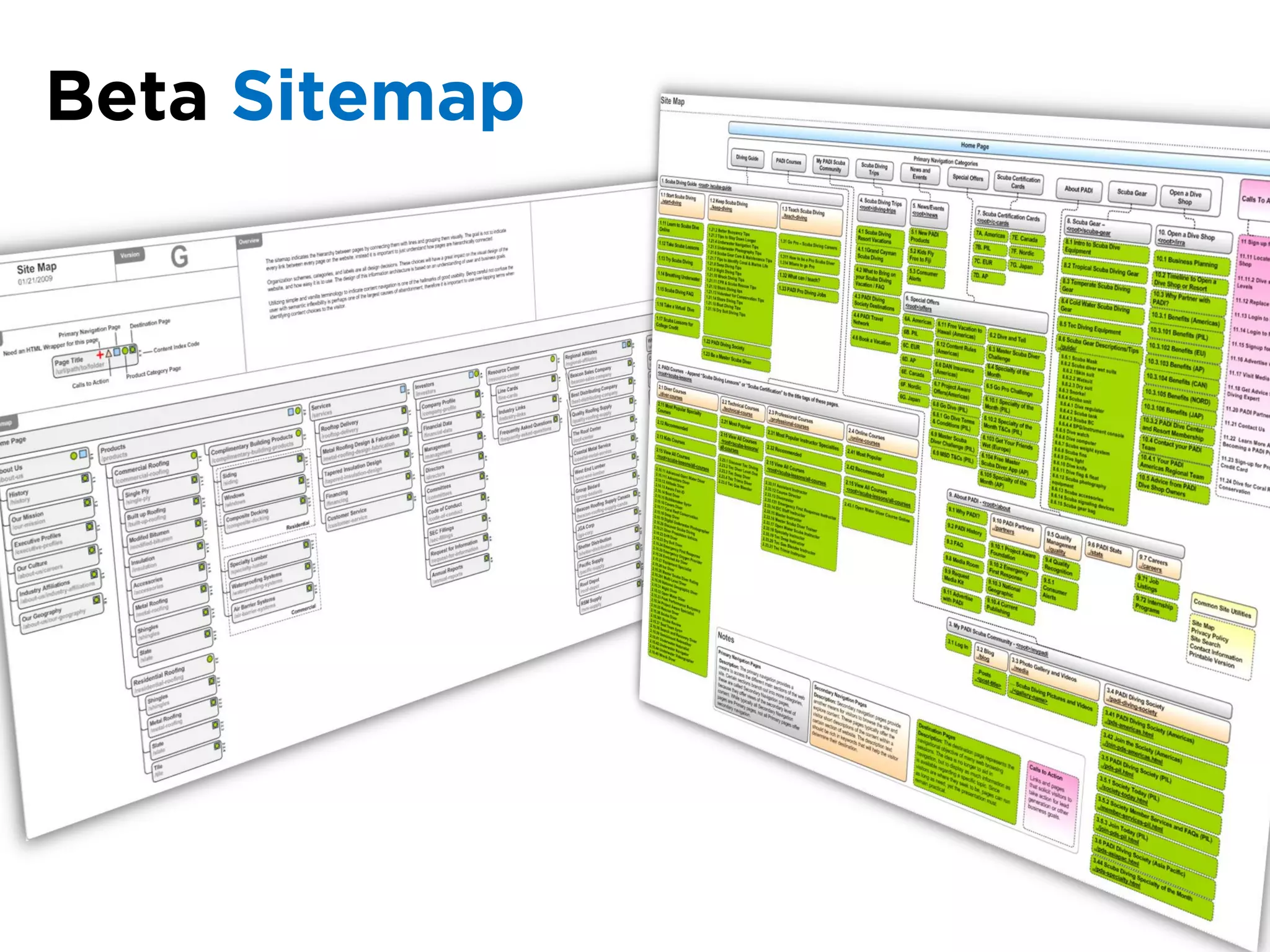
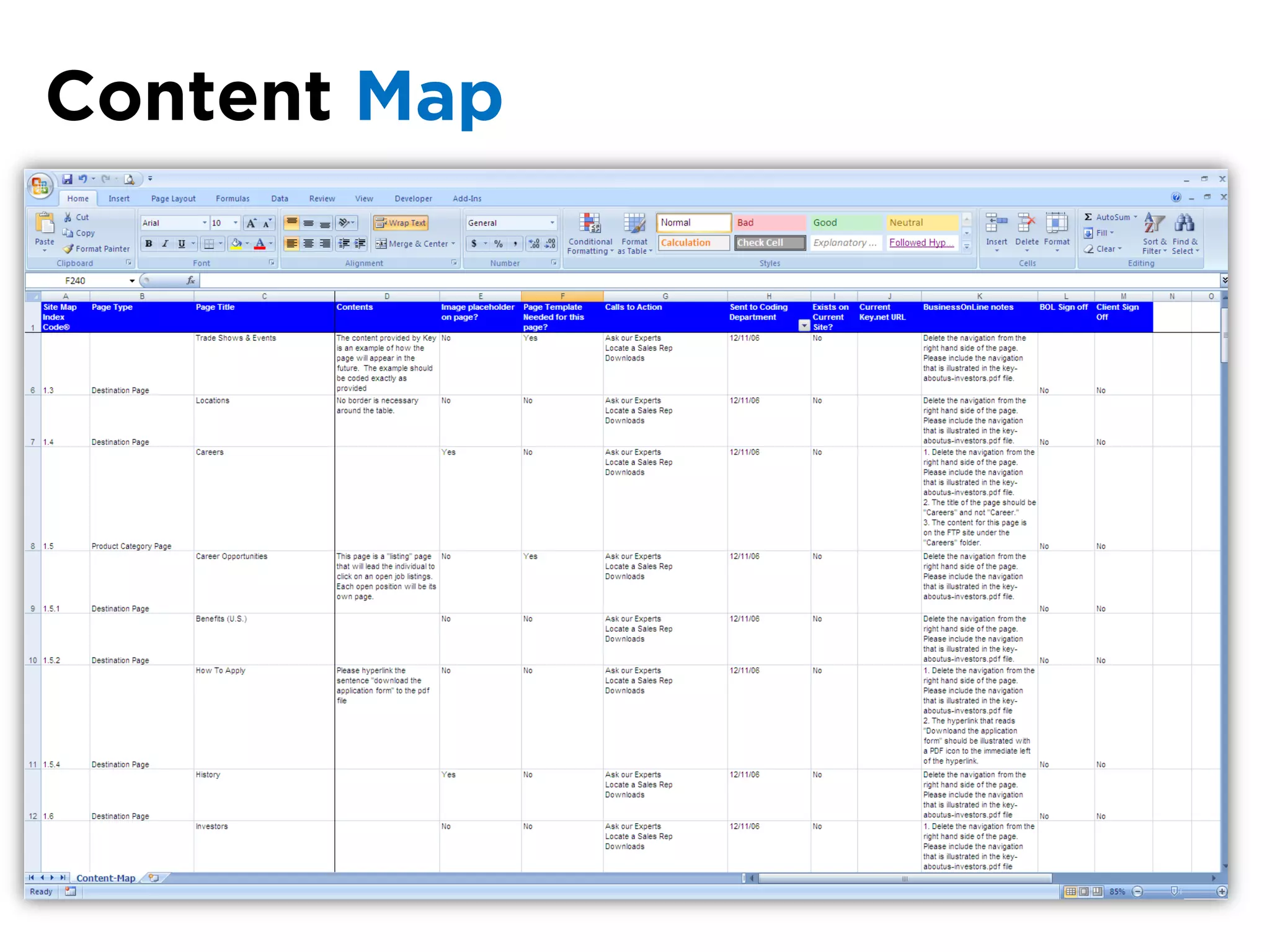
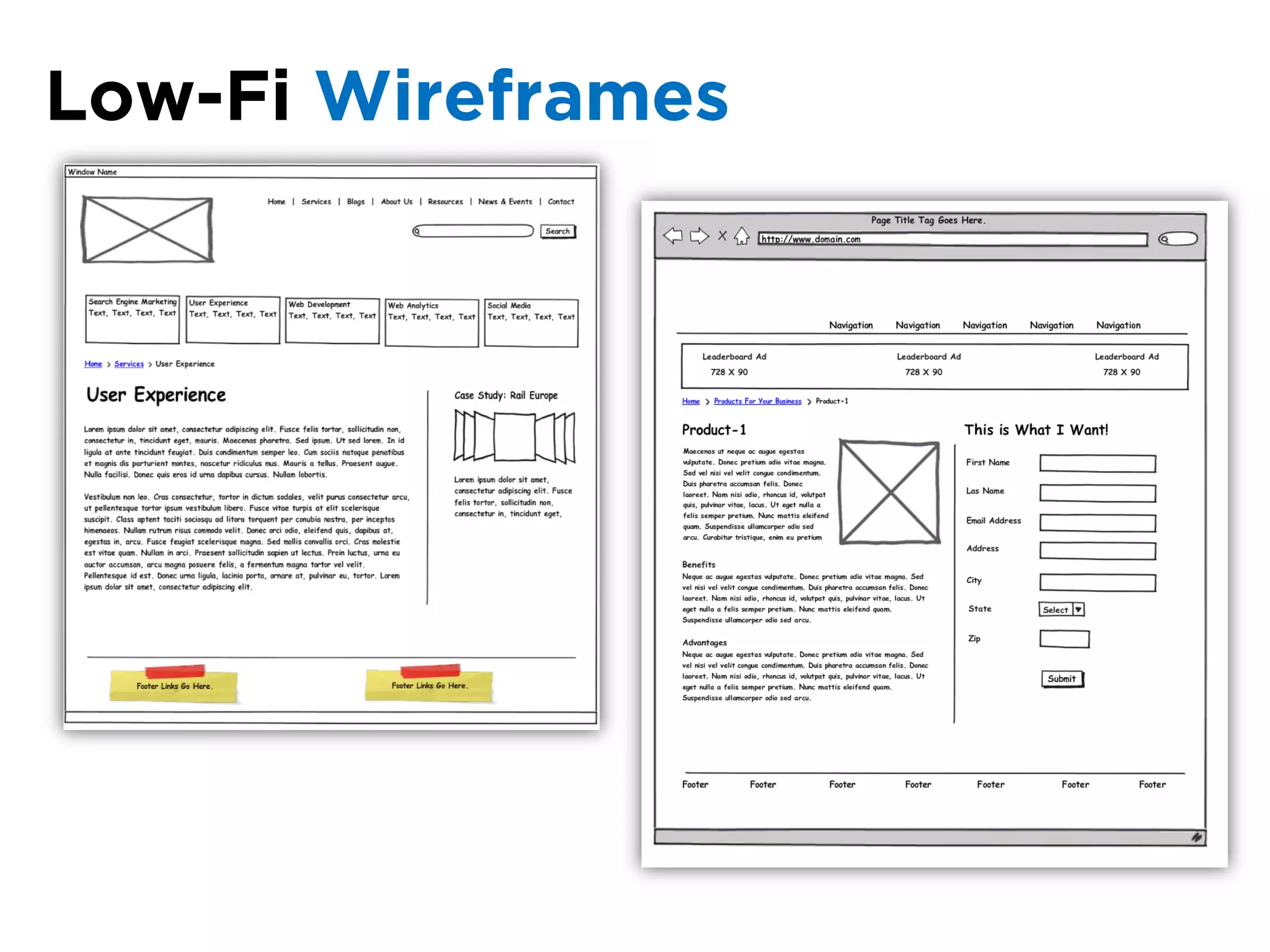
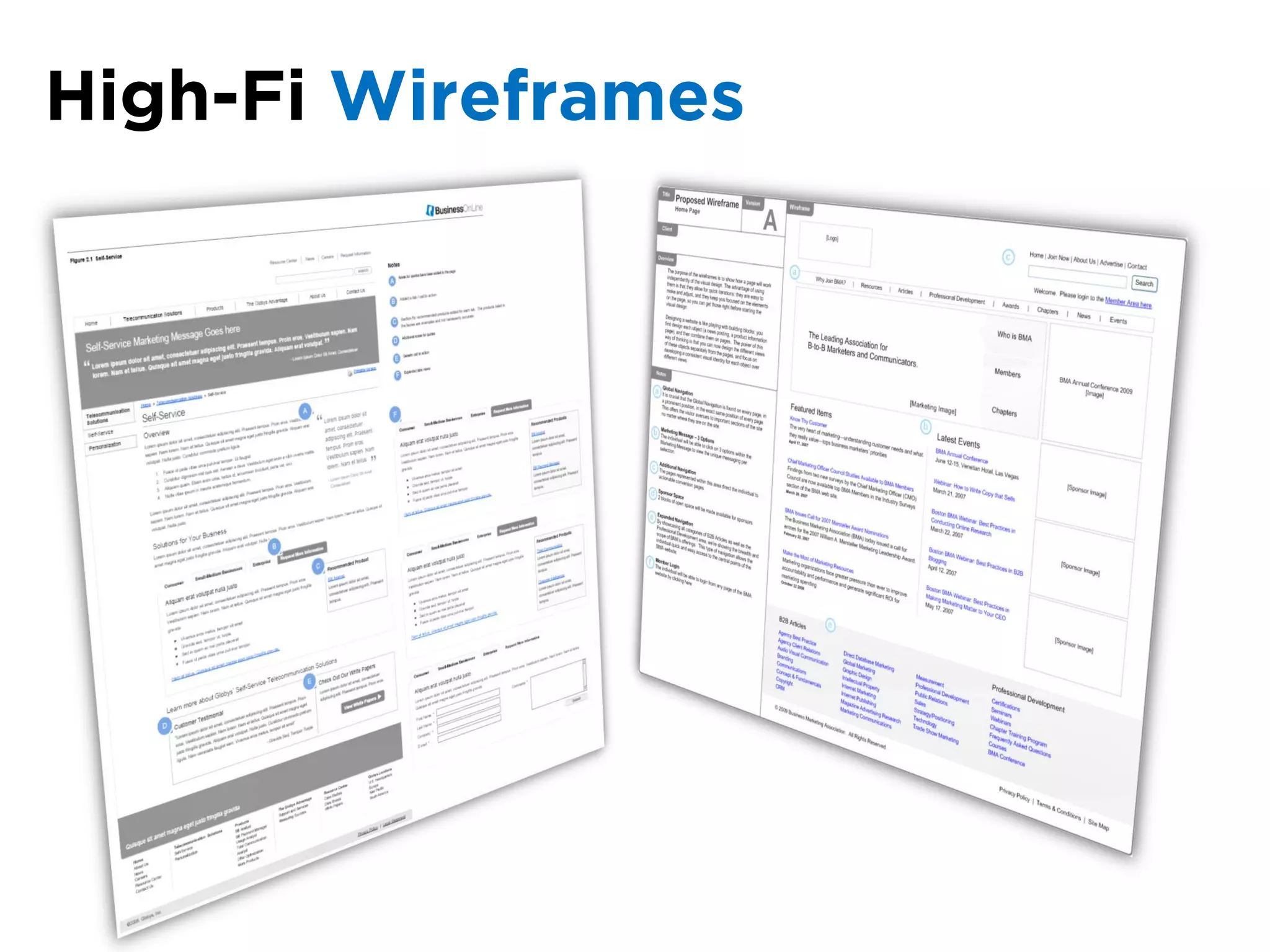
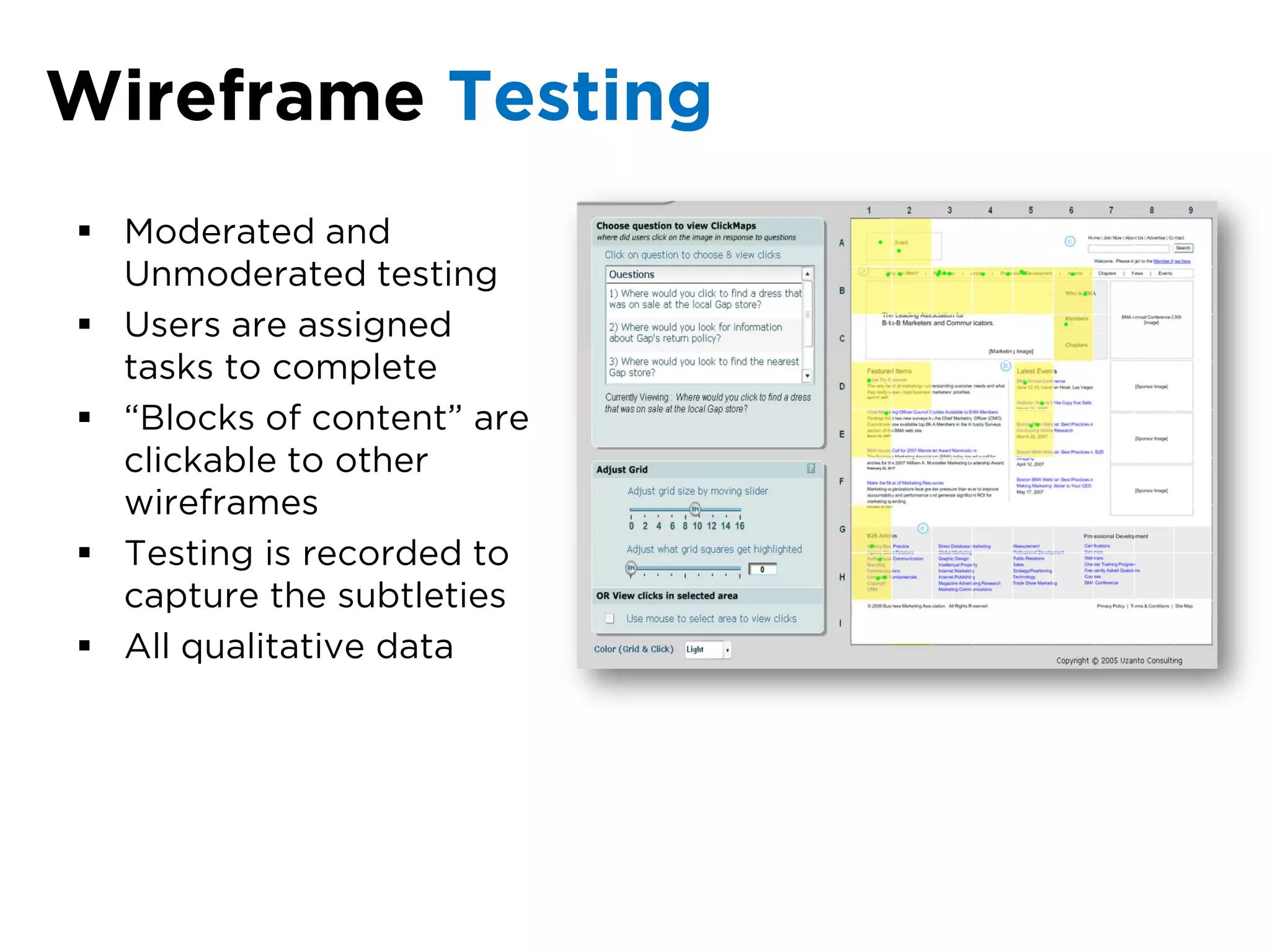
The document discusses the principles of information architecture (IA) and its importance in enhancing user experience (UX) by effectively organizing and labeling content. It outlines the project lifecycle of IA, including strategies, tactics, audience research, and various methods such as wireframing and card sorting. The document emphasizes the impact of poor navigation on business performance and provides resources for continued IA education.