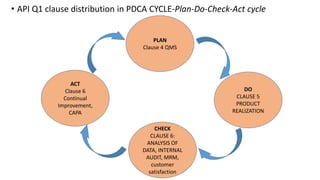
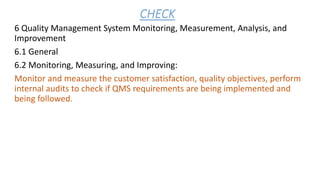
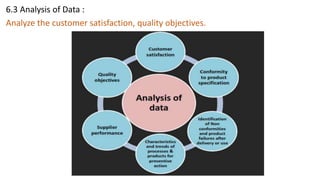
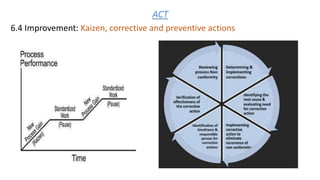
The document provides an overview of API Spec Q1 9th edition, which outlines quality management system requirements for manufacturing organizations in the petroleum and natural gas industry. It discusses key aspects of a quality management system including establishing quality policies and objectives, planning product realization processes, controlling documentation, monitoring and measuring performance, and continually improving the system. The QMS is based on the PDCA cycle and aims to meet customer and applicable requirements through planning, implementing controls, checking conformance, and taking actions for improvement.