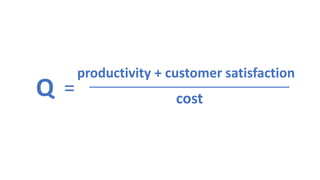
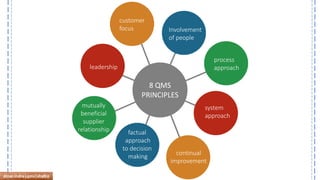
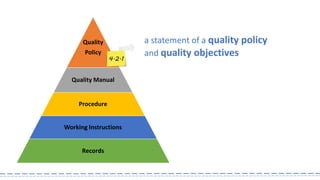
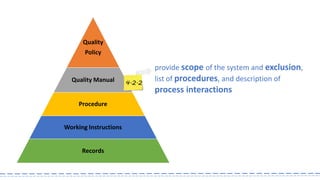
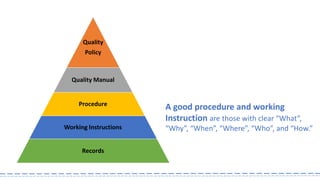
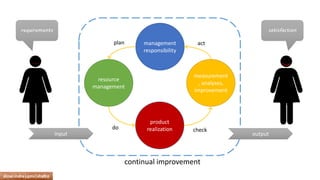
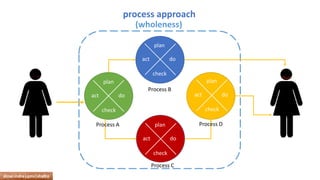
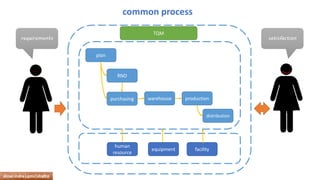
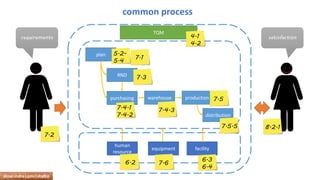
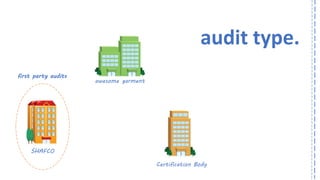
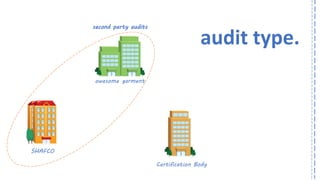
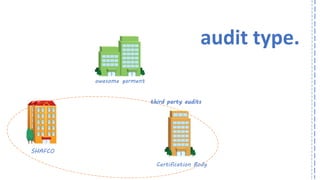
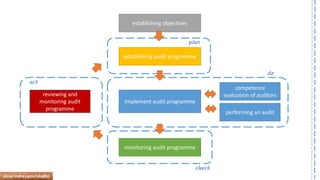
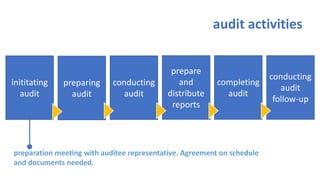
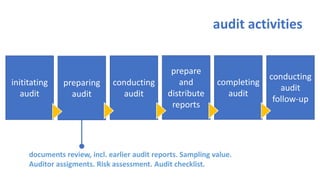
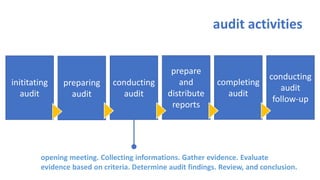
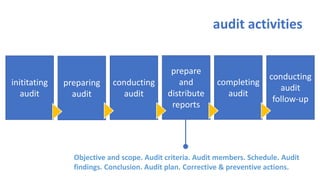
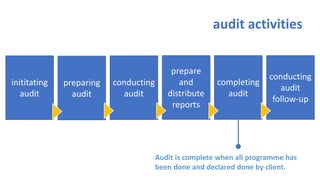
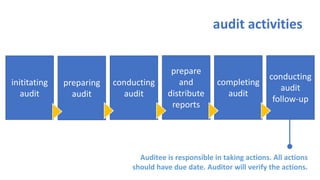
The document provides an overview of ISO 9001:2008 and Quality Management Systems (QMS) for beginner auditors, outlining definitions, principles, and implementation steps. It emphasizes the importance of documentation, continual improvement, and process approach to ensure customer satisfaction and product quality. The content also includes guidance on conducting internal audits, detailing the audit process, objectives, and best practices.