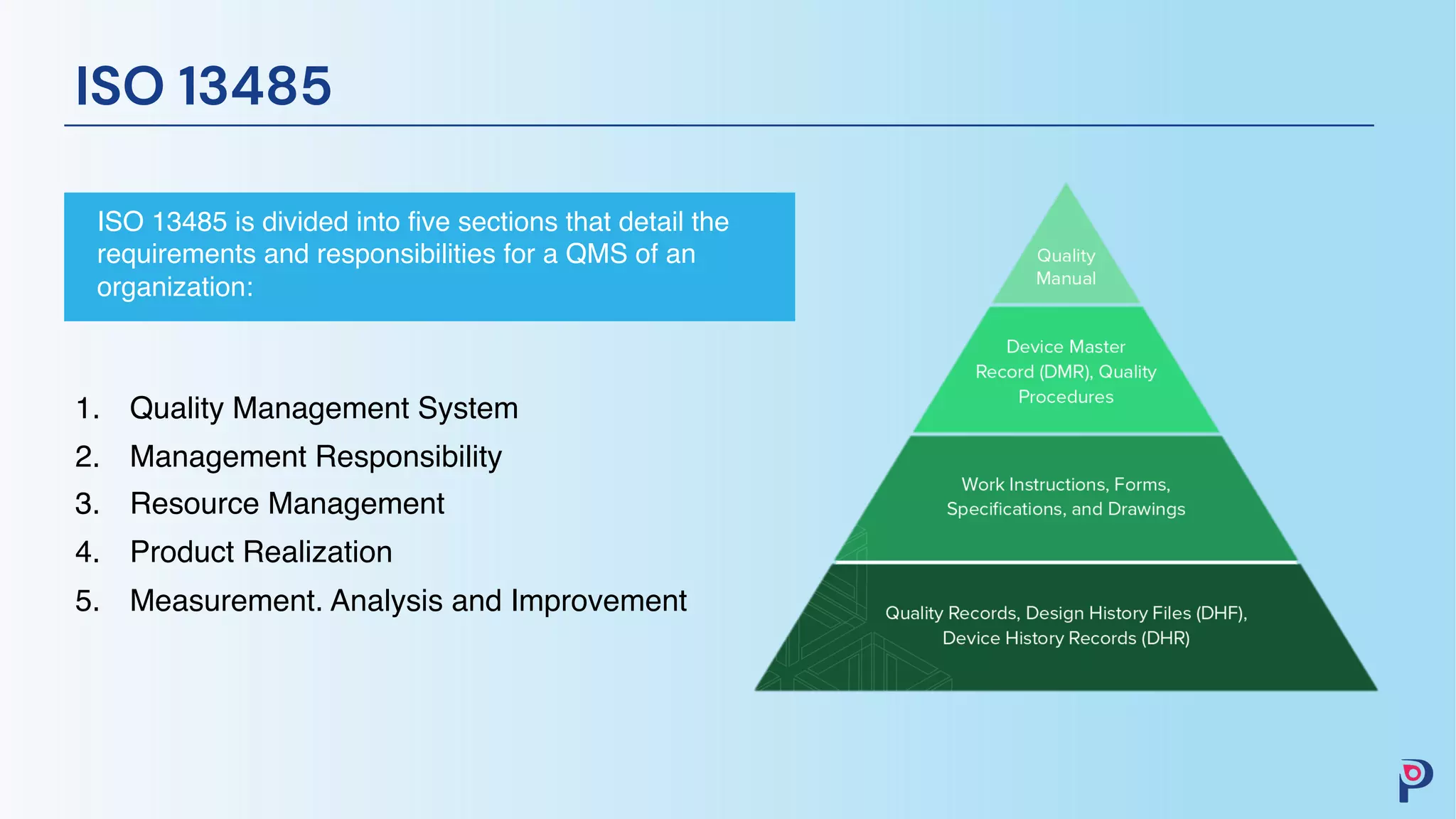
The document provides an overview of ISO 13485, detailing the structure and requirements for a quality management system (QMS) necessary for compliance in the medical device industry. Key sections include quality management, management responsibility, resource management, product realization, and measurement for improvement. It emphasizes the integration of regulatory strategies into quality goals to ensure effectiveness and compliance with evolving regulations.