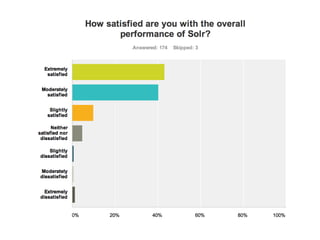
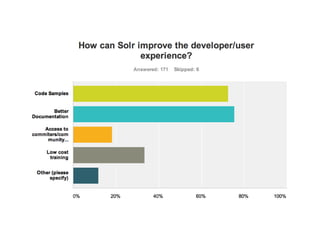
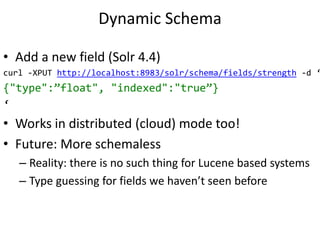
This document provides a roadmap and history of the Lucene and Solr projects:
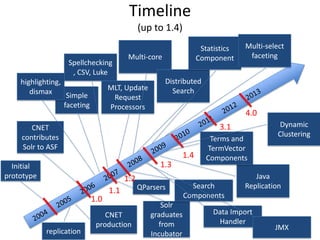
- It outlines key dates and developments from 1997 to the present for Lucene and from 2004 to the present for Solr, including major releases and new features.
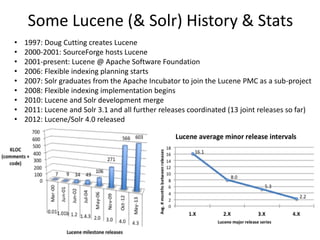
- Lucene 4.0 introduced flexible indexing, faster multithreaded indexing, and other performance improvements. Lucene 4.1-4.3 added additional features like compressed stored fields and term vectors.
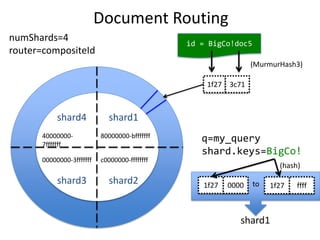
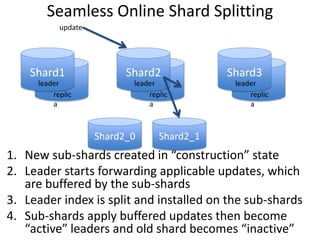
- The document discusses recent enhancements to Solr like document routing, seamless online shard splitting, and cloud enhancements; and previews future directions like greater scalability, more "NoSQL" capabilities, and improved analytics.



![Lucene 4.3 Highlights
• minShouldMatch BooleanQuery major performance
improvement
• SortingAtomicReader and SortingMergePolicy
• DocIdSetIterator and Scorer now has a cost API
• Analyzing/FuzzySuggester now enable recording an
arbitrary byte[] as a payload
• Spatial module: support for query relations Within,
Contains, and Disjoint
• Facet module: new method computes facet counts
using SortedSetDocValuesField, without a separate
taxonomy index.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/keynote-seeleyrowelucenesolrroadmap-130529114821-phpapp01/85/KEYNOTE-Lucene-Solr-road-map-5-320.jpg)