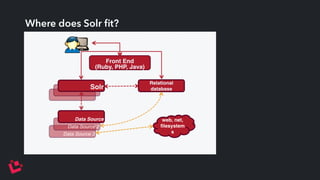
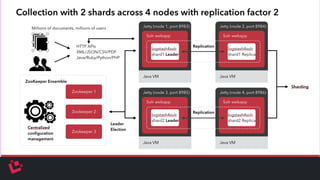
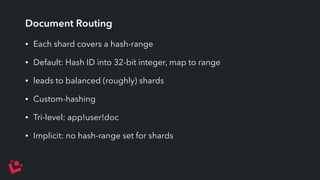
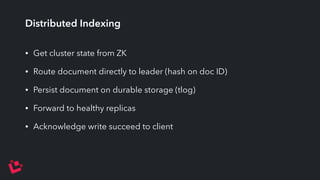
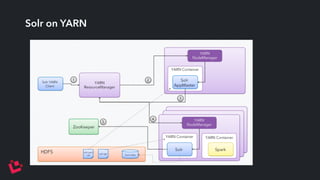
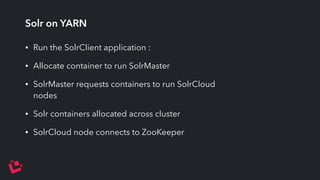
Apache Solr is a highly scalable search platform with over 250,000 installations and remarkable features including support for large index sizes, distributed indexing, and replicas for high availability. SolrCloud enhances scalability and performance by enabling horizontal scaling through sharding and replication, while utilizing Zookeeper for centralized management and coordination. Key functionalities of Solr include near-real-time search, partial document updates, and transaction logs for improved recoverability.