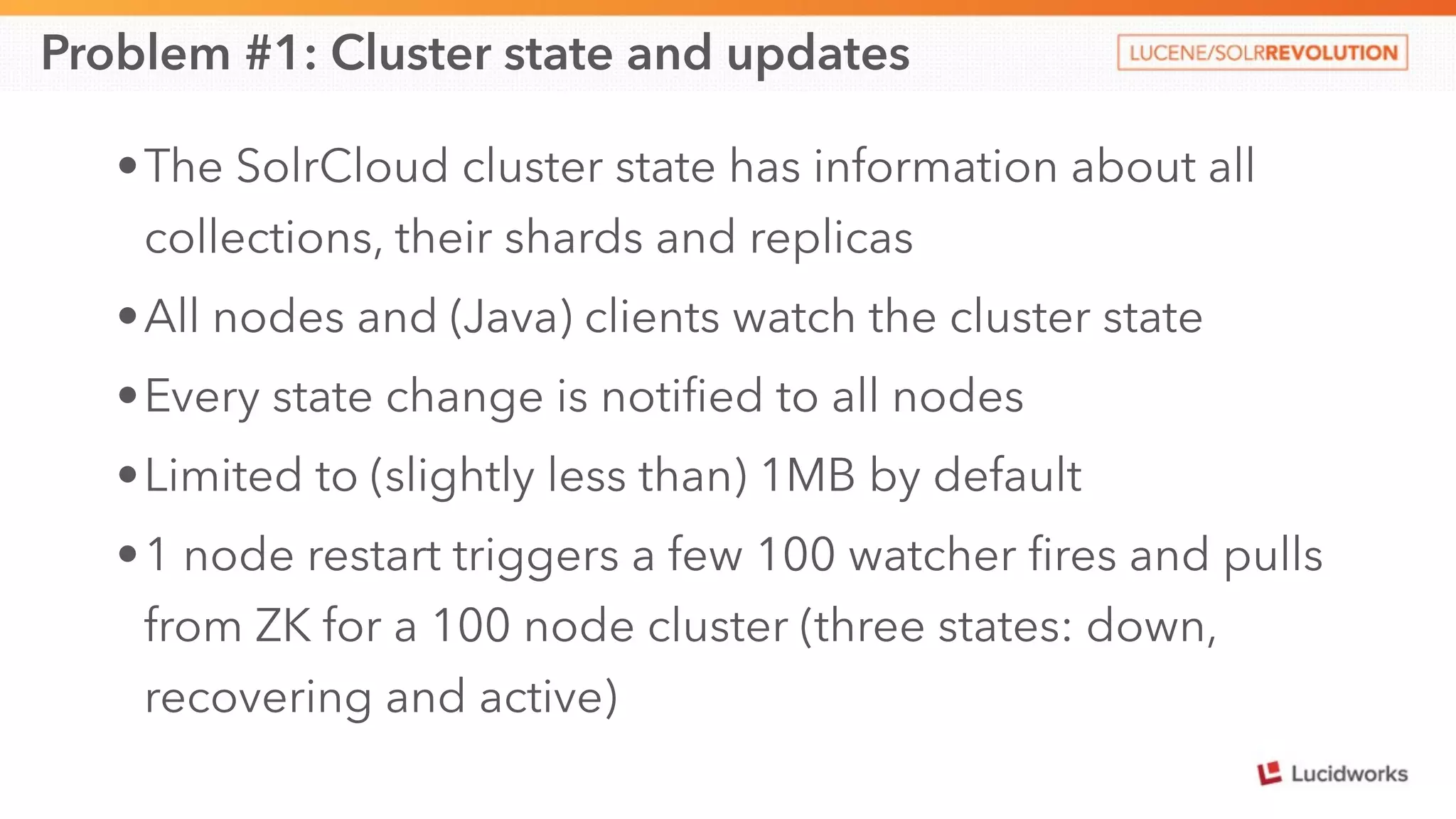
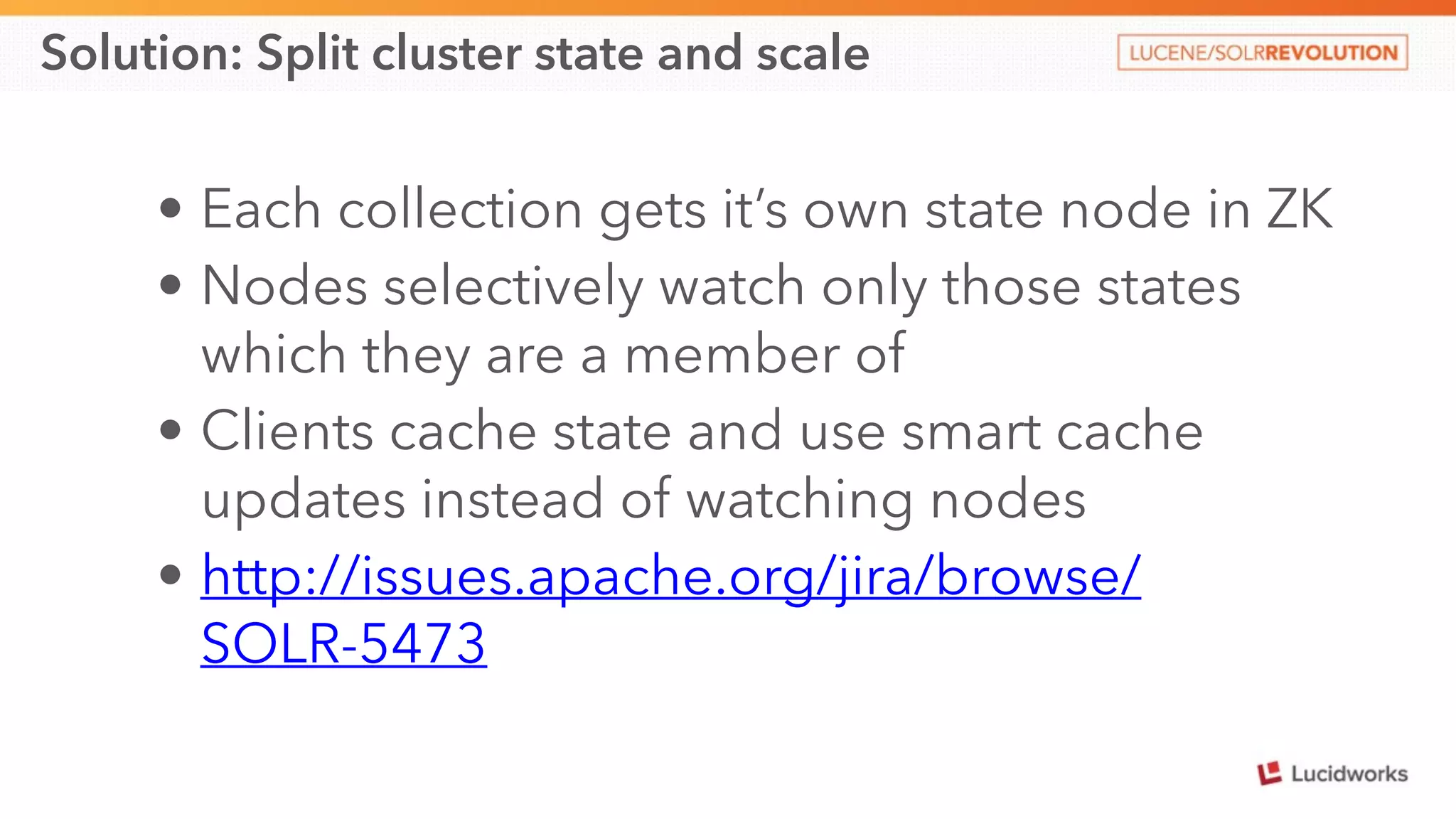
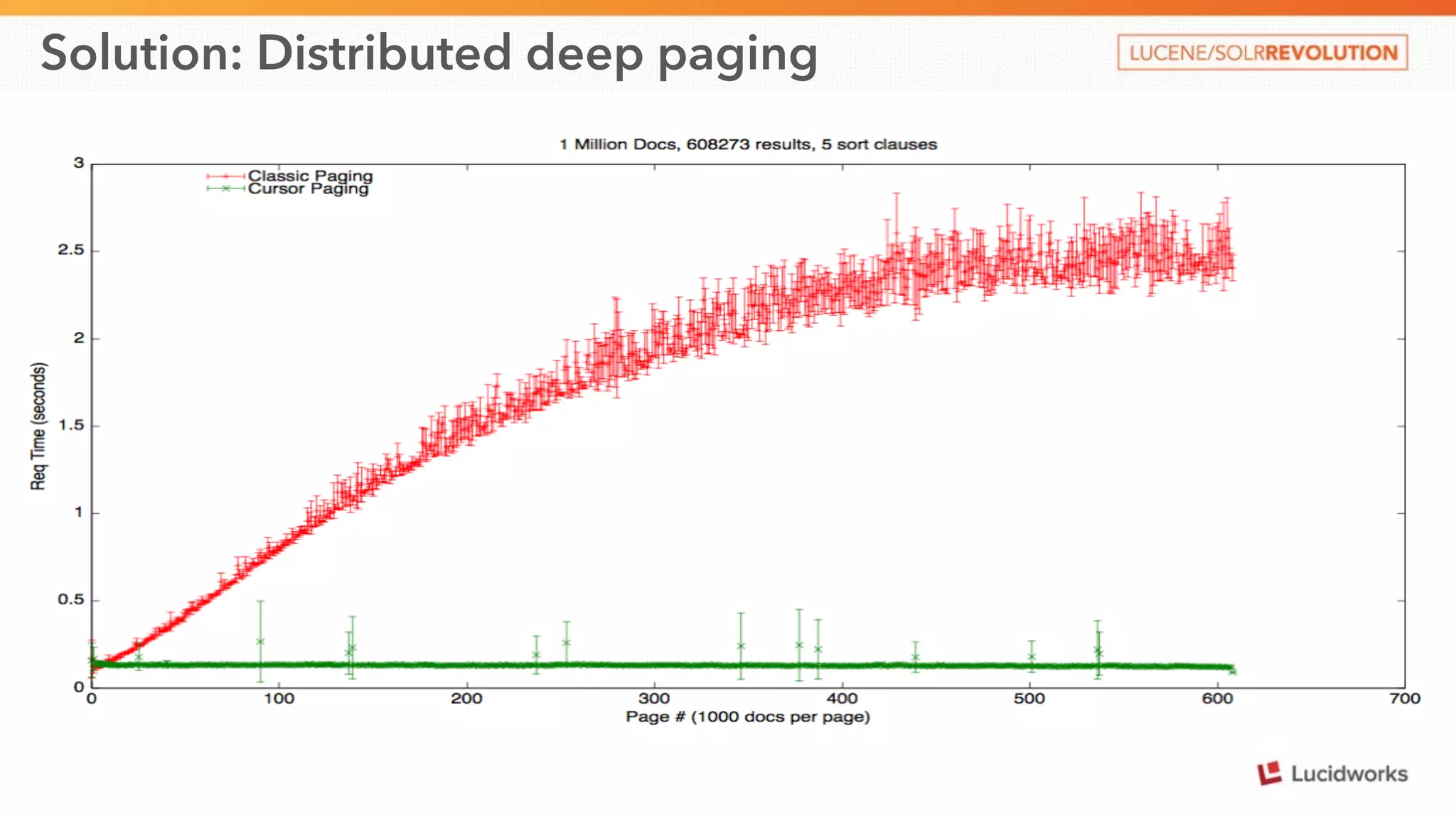
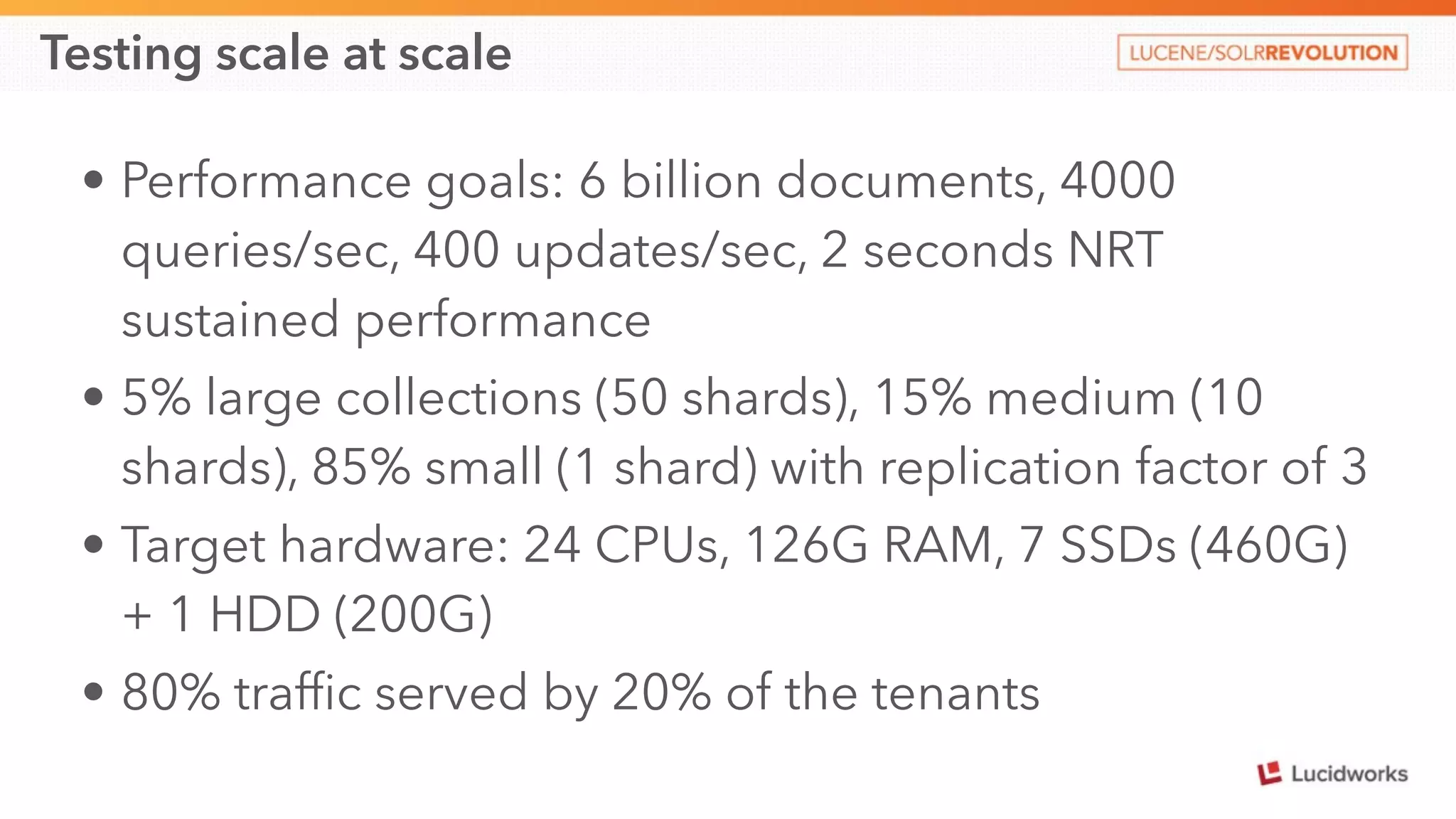
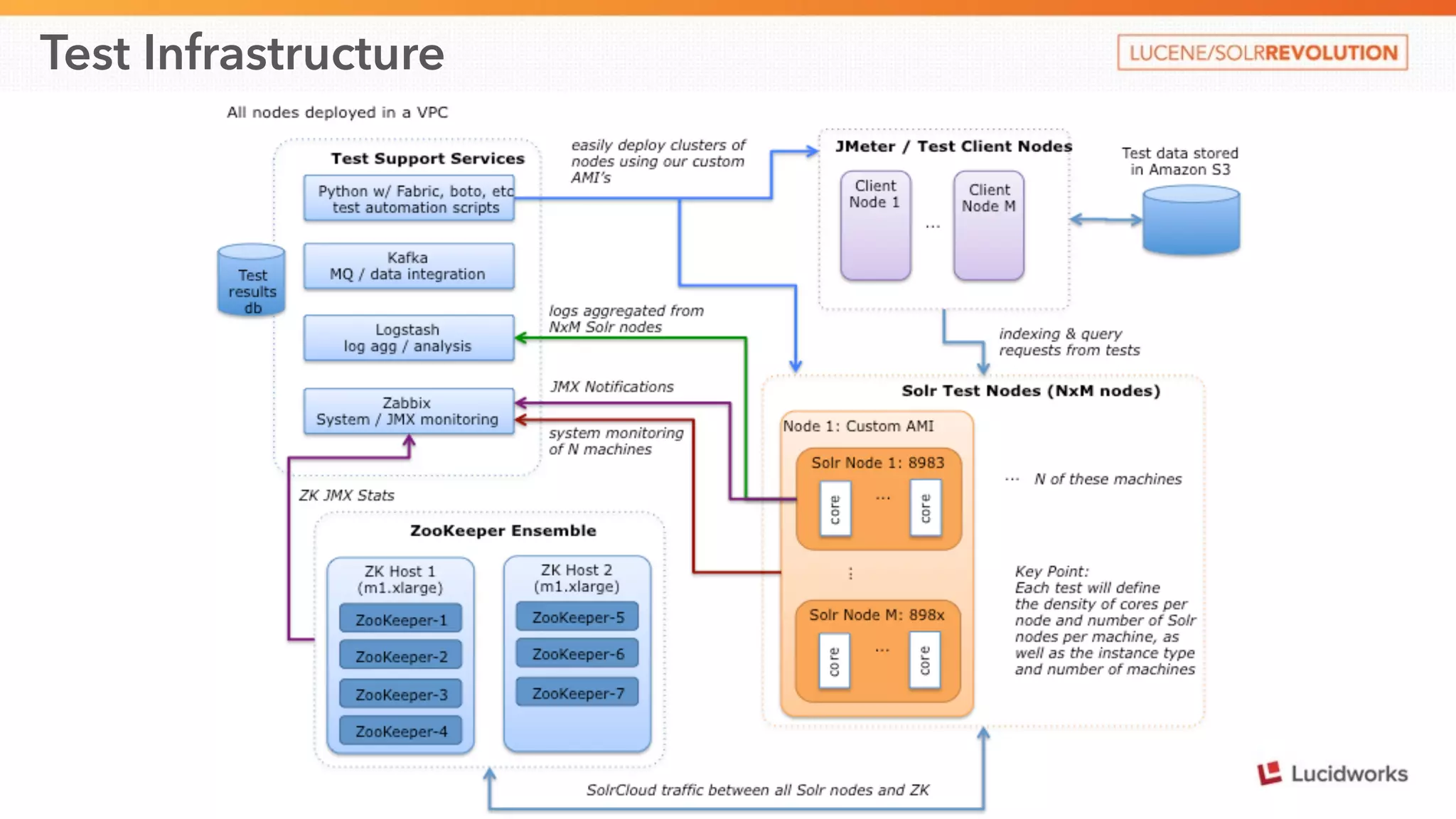
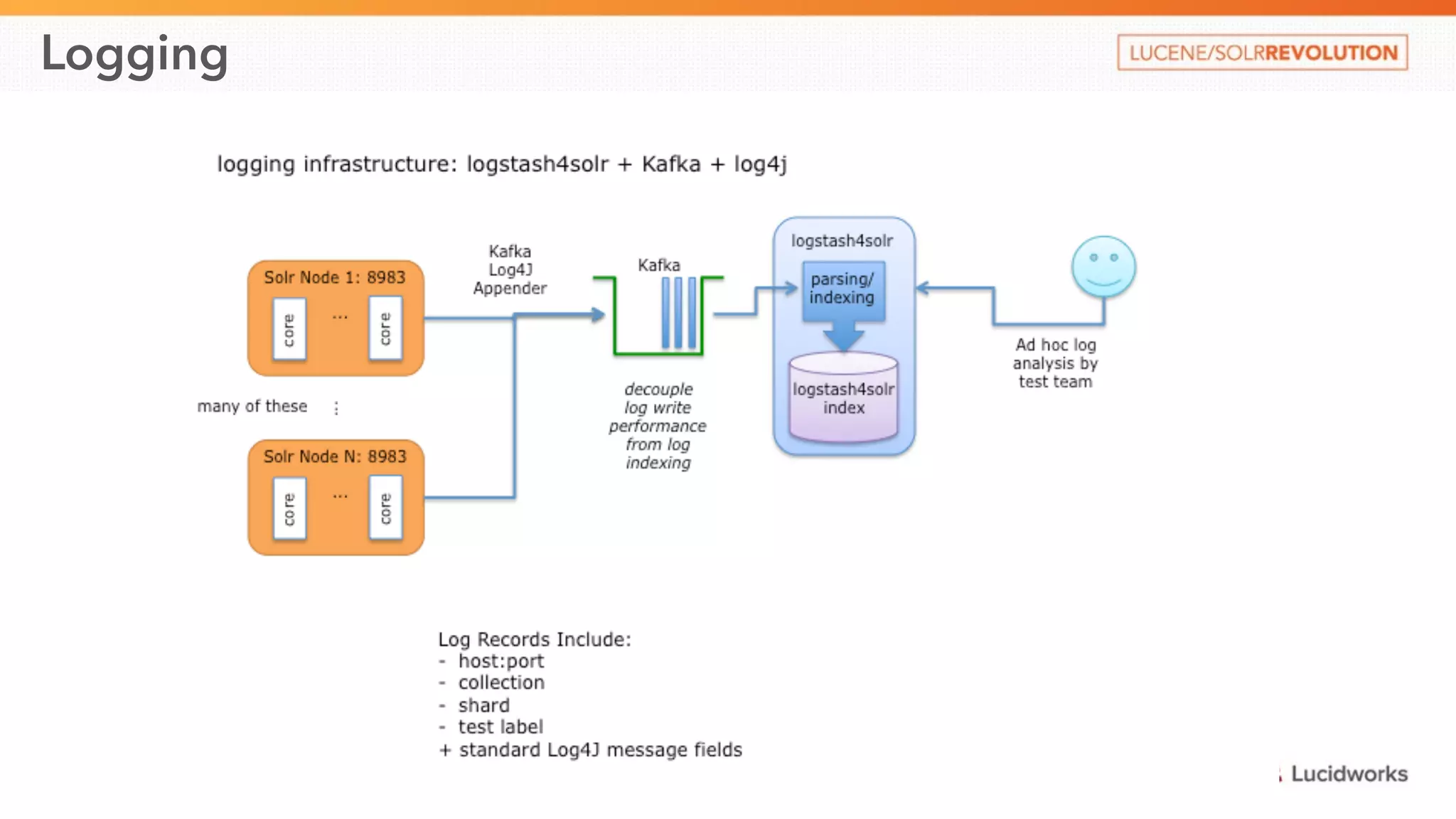
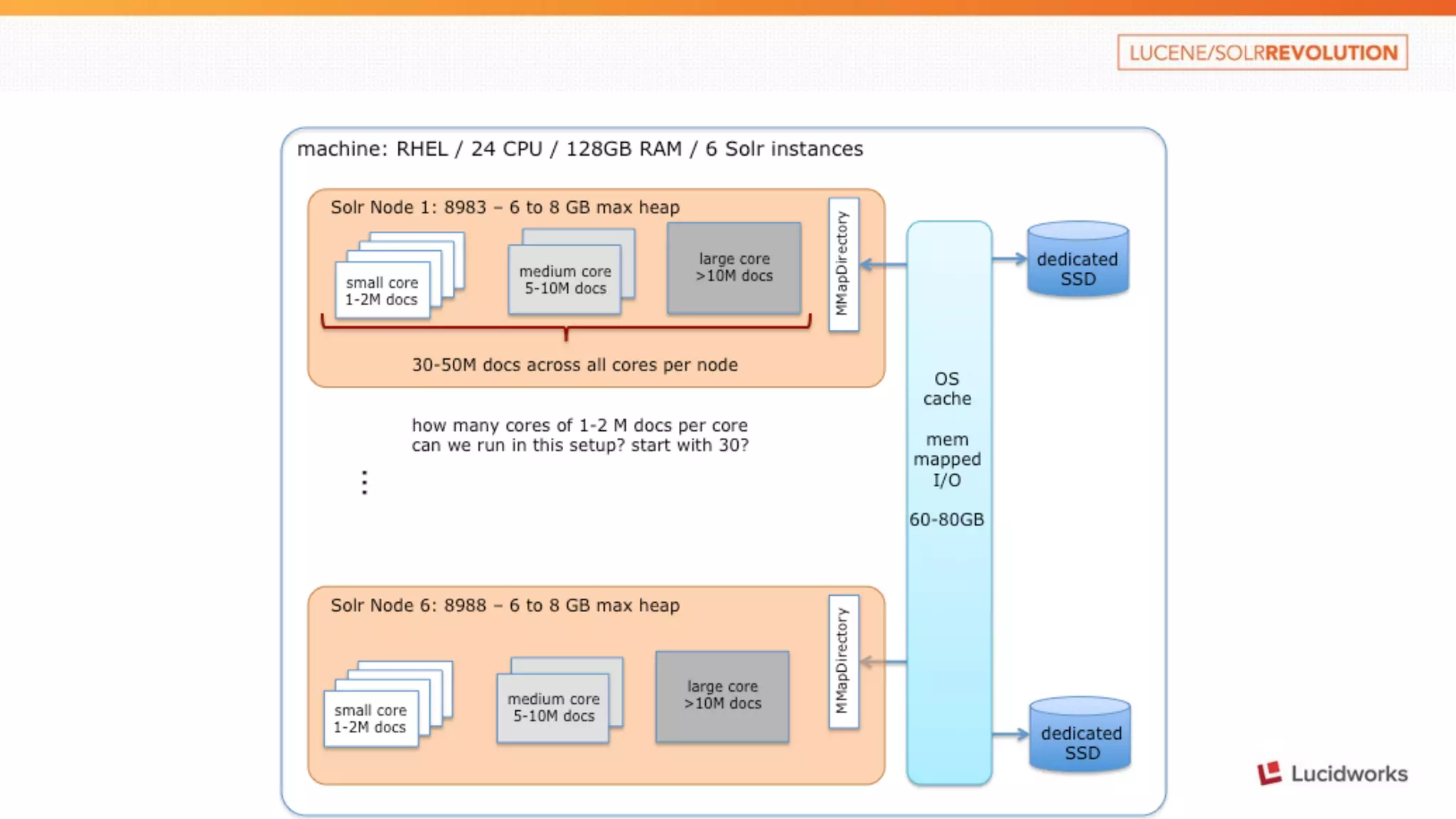
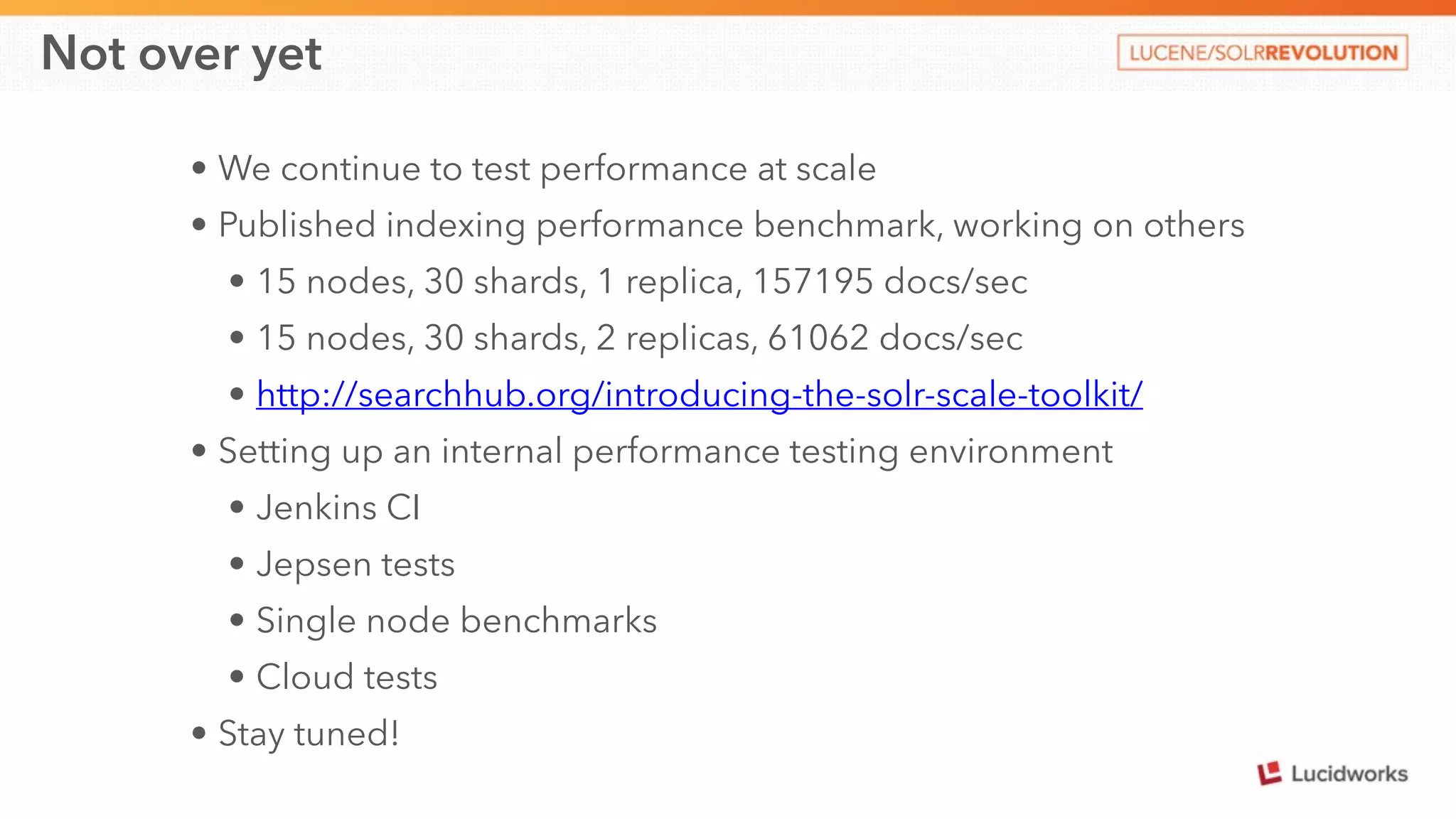
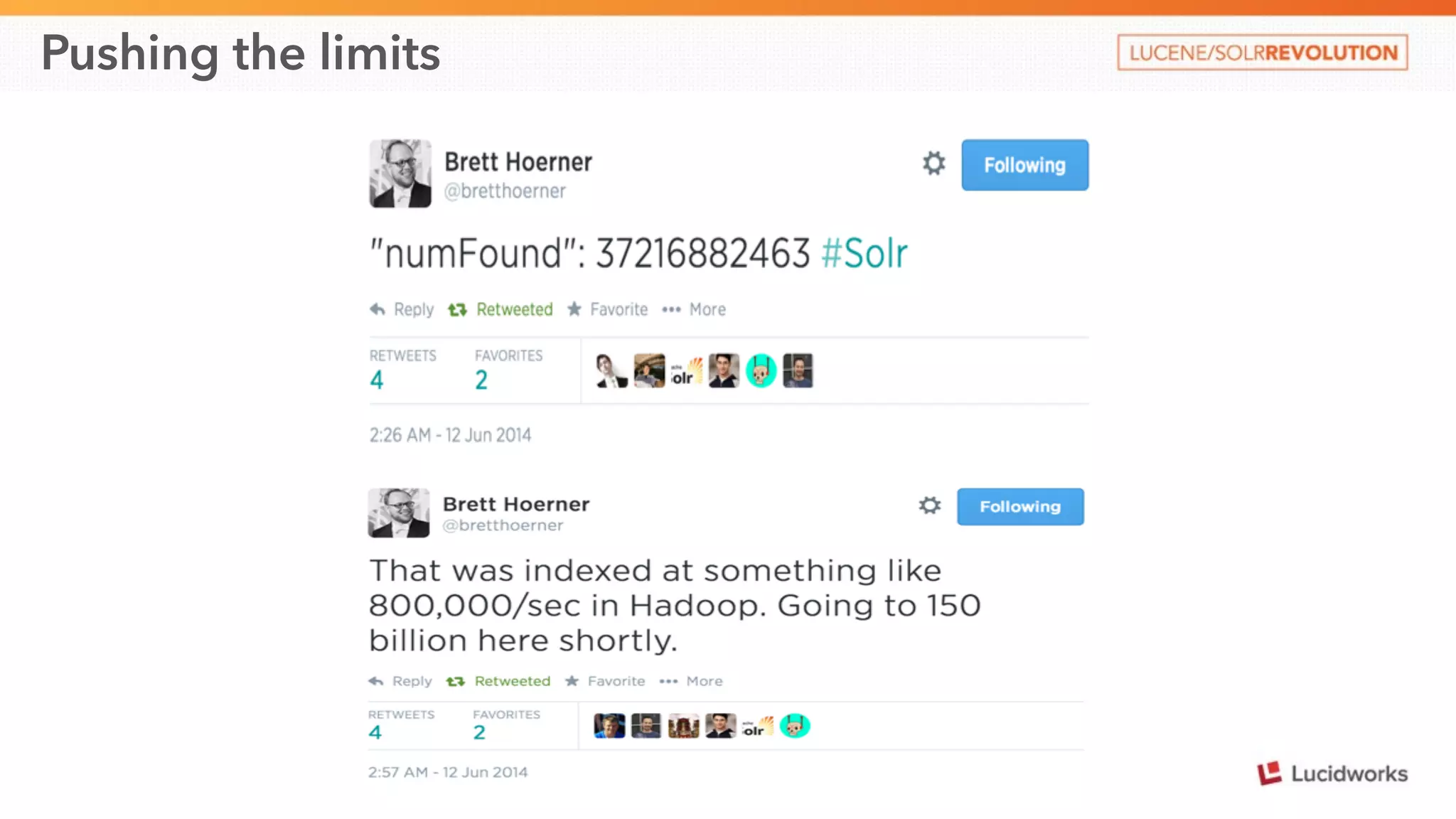
This document discusses scaling SolrCloud to support a large number of collections. It identifies four main problems in scaling: 1) large cluster state size, 2) overseer performance issues with thousands of collections, 3) difficulty moving data between collections, and 4) limitations in exporting full result sets. The document outlines solutions implemented to each problem, including splitting the cluster state, optimizing the overseer, improving data management between collections, and enabling distributed deep paging to export full result sets. Testing showed the ability to support 30 hosts, 120 nodes, 1000 collections, over 6 billion documents, and sustained performance targets.