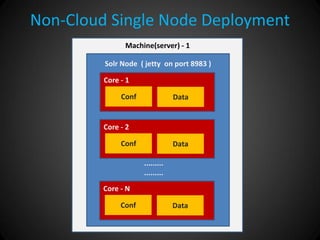
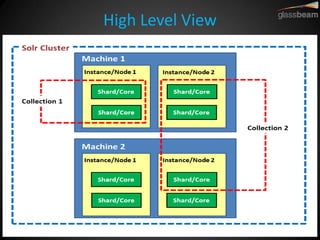
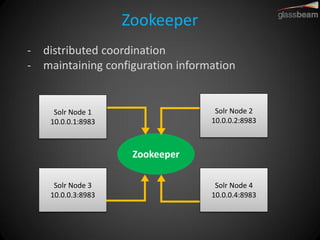
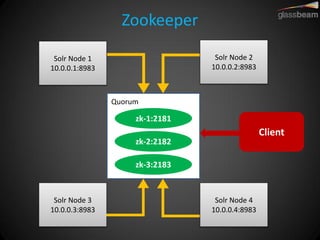
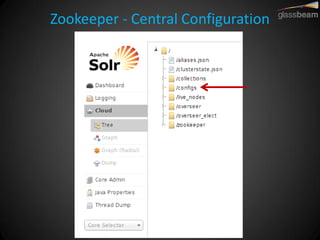
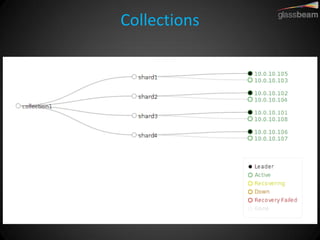
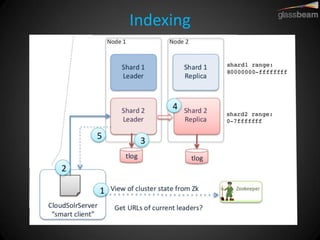
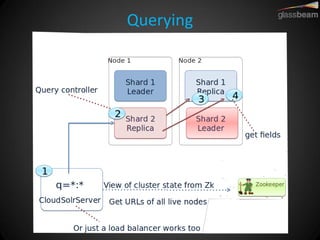
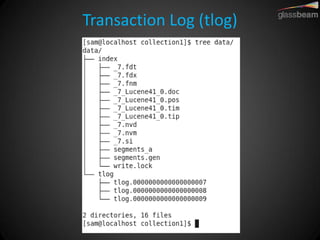
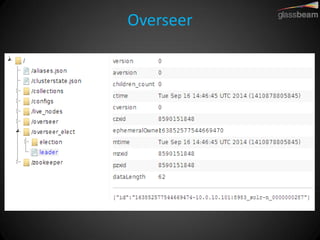
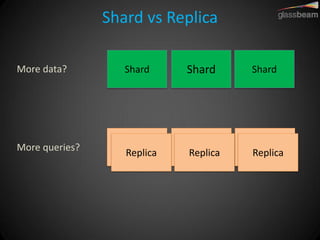
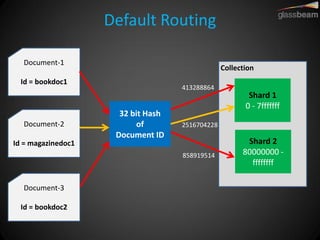
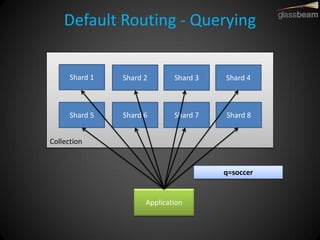
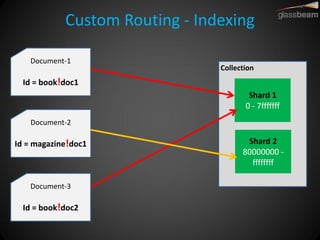
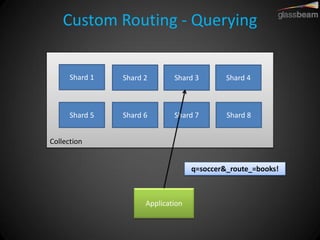
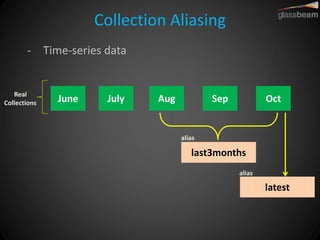
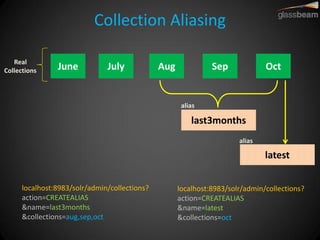
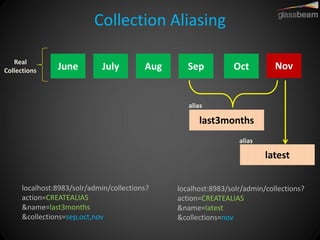
Solr Cloud allows Solr to be distributed and run across multiple servers for increased performance, scalability, availability, and elasticity. It uses Zookeeper for coordination and shares an index across multiple cores and collections. Documents are routed and replicated to shards and replicas based on a hashing function or custom routing rules to partition the data. Queries are distributed and results merged to provide scalable search across an elastic, fault-tolerant cluster.