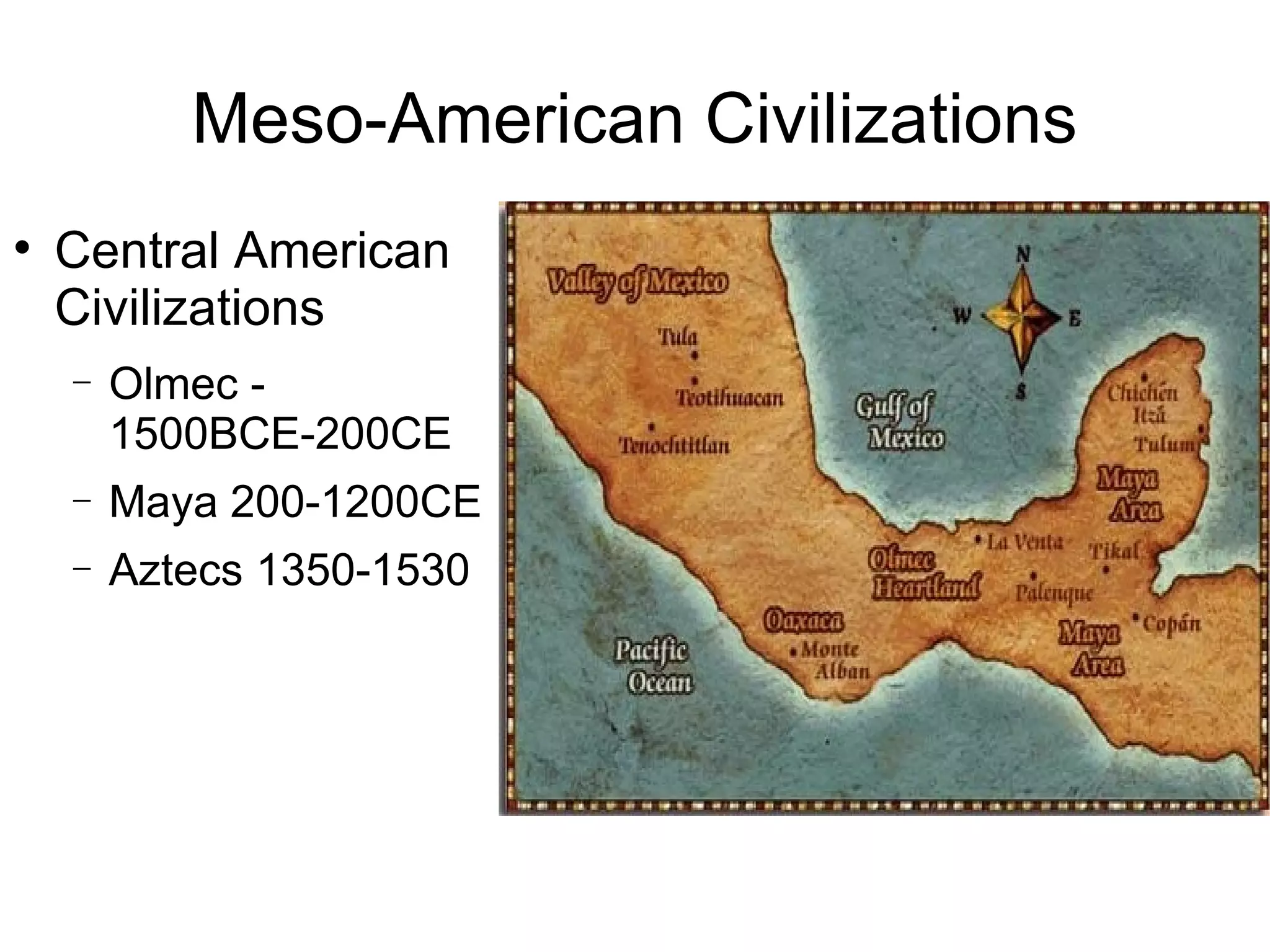
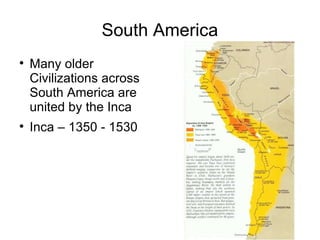
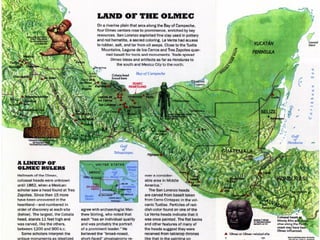
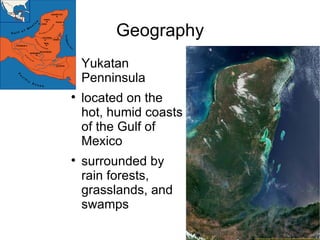
The document summarizes the Olmec civilization of Mesoamerica from 1500 BCE to 200 CE. The Olmec inhabited the coasts of the Gulf of Mexico in what is now Mexico and were among the earliest complex civilizations in Mesoamerica. They built cities and ceremonial centers with earthen pyramids and sculptures. The Olmec were ruled by priest-shamans and had a theocratic form of government. They practiced agriculture, especially of maize, and engaged in trade. The Olmec religion involved shape-shifting shamans and nature worship. Their calendar, ball games, and human sacrifice rituals influenced later Mayan civilization.