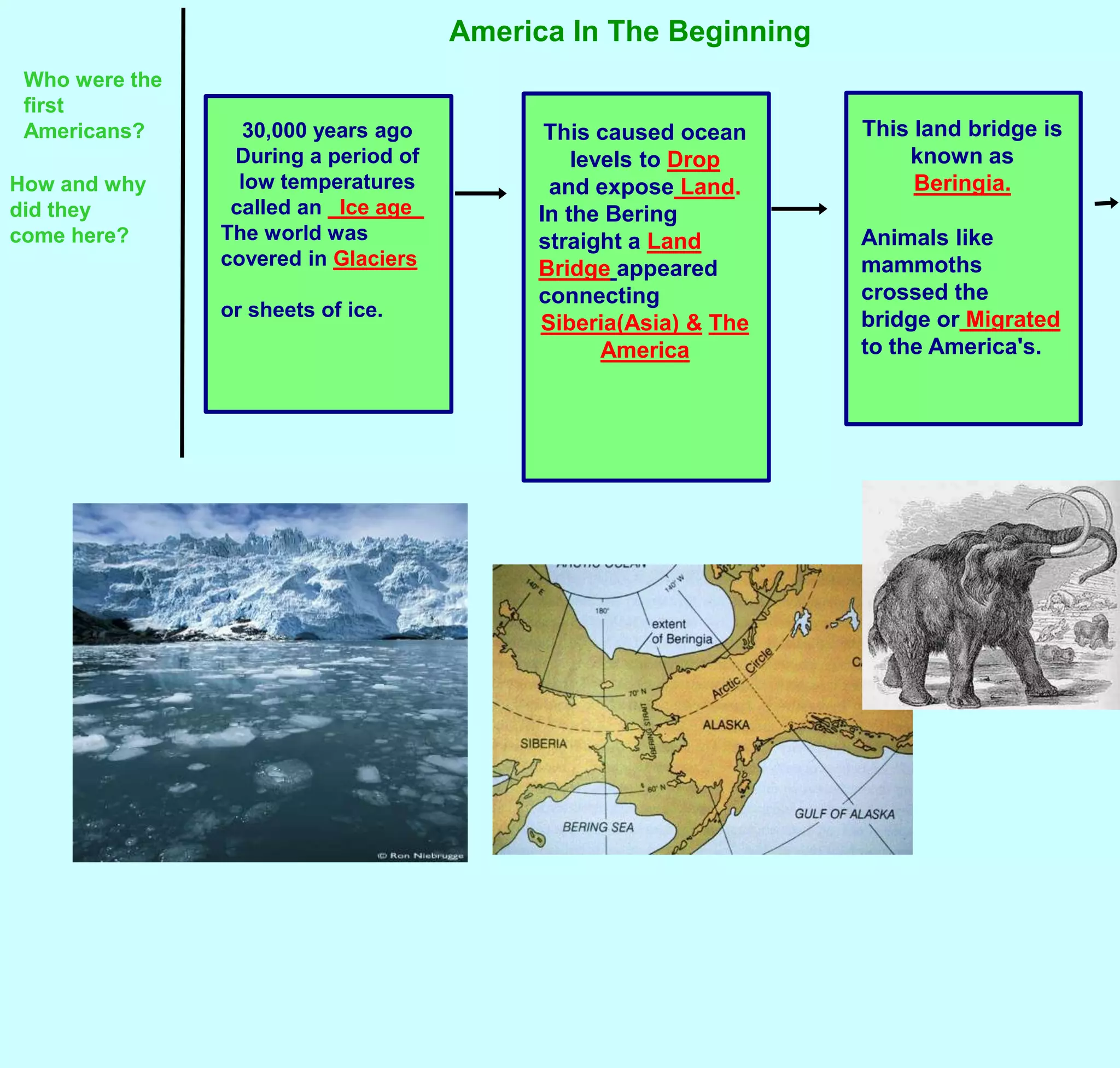
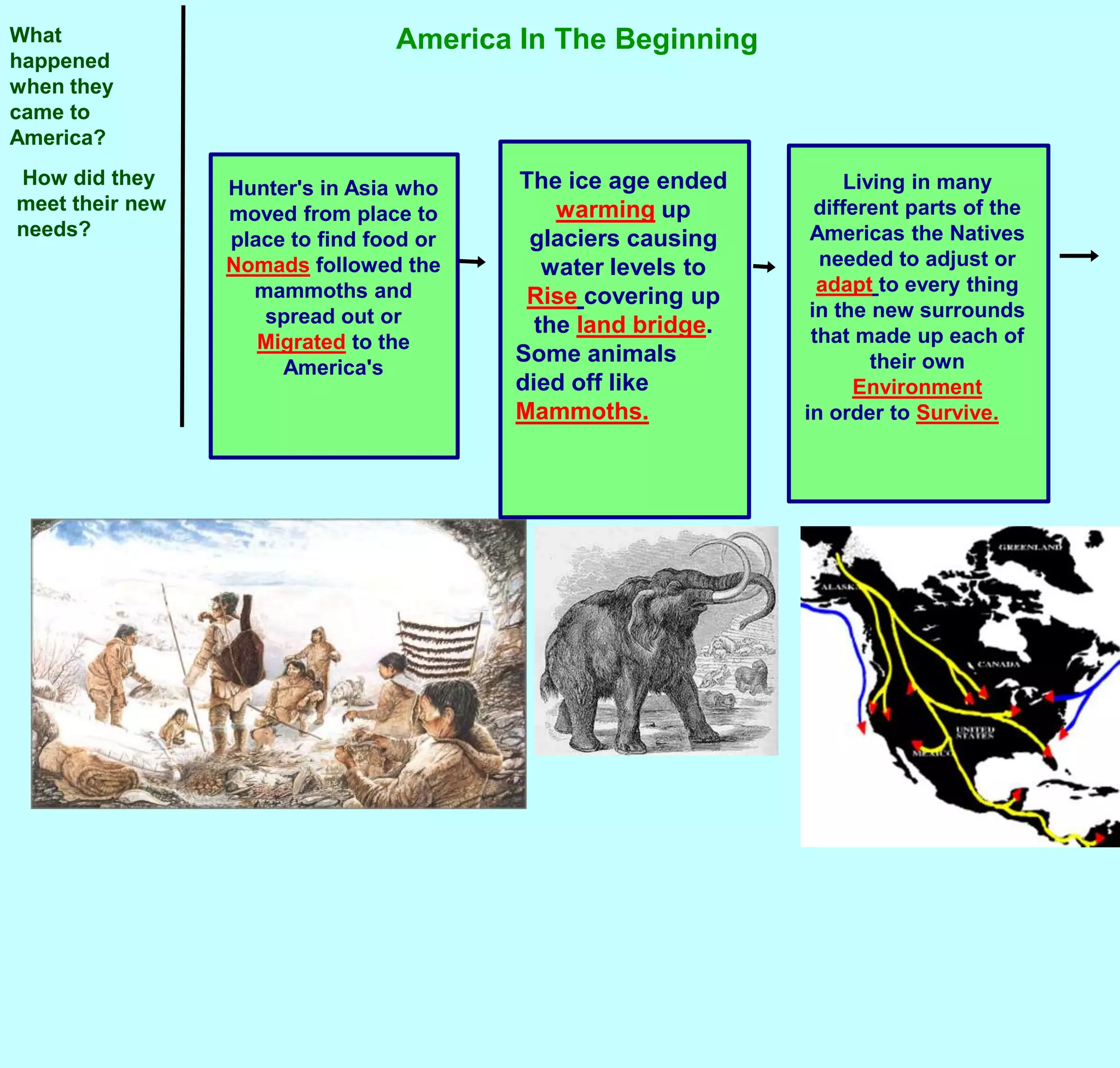
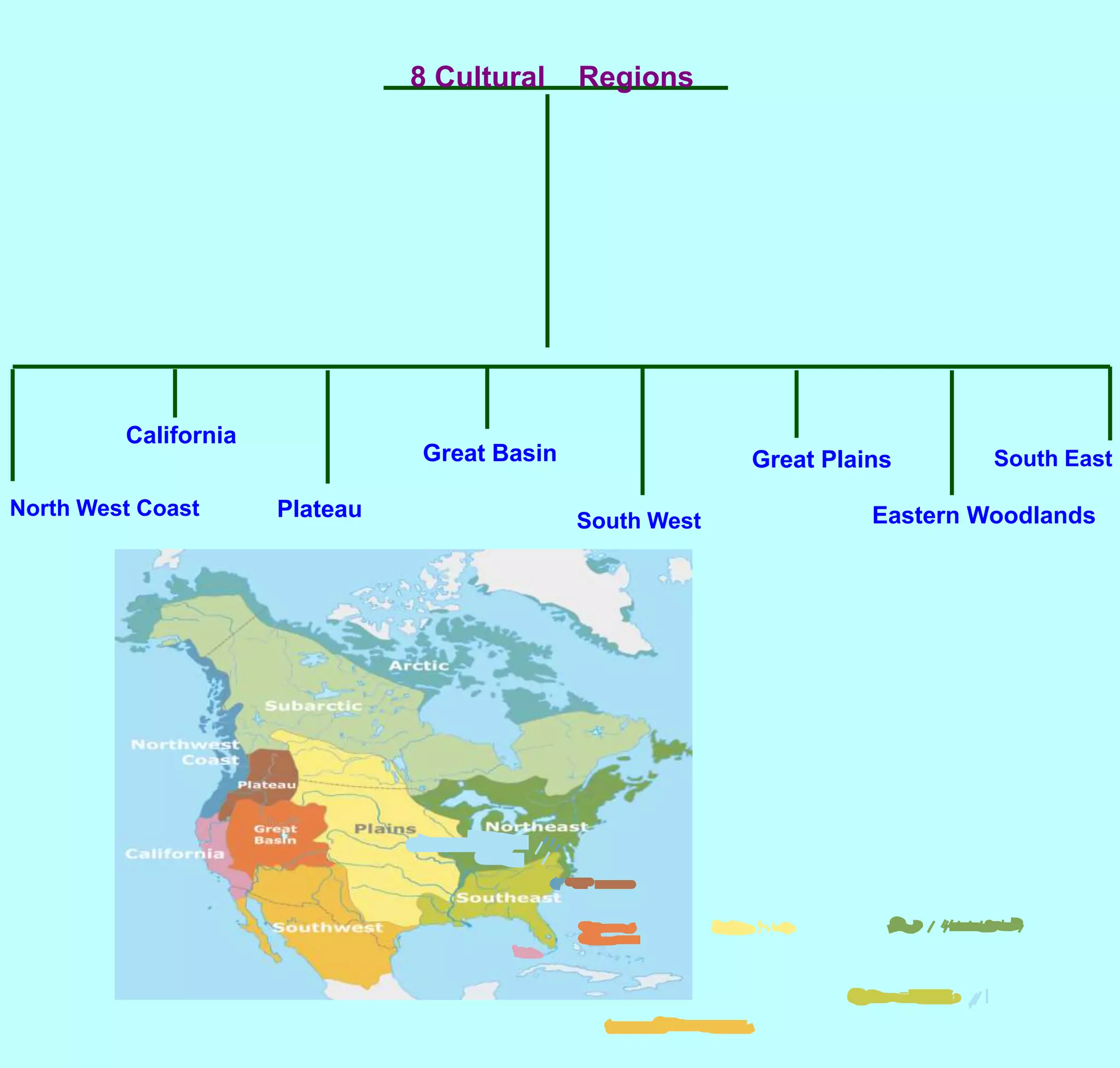
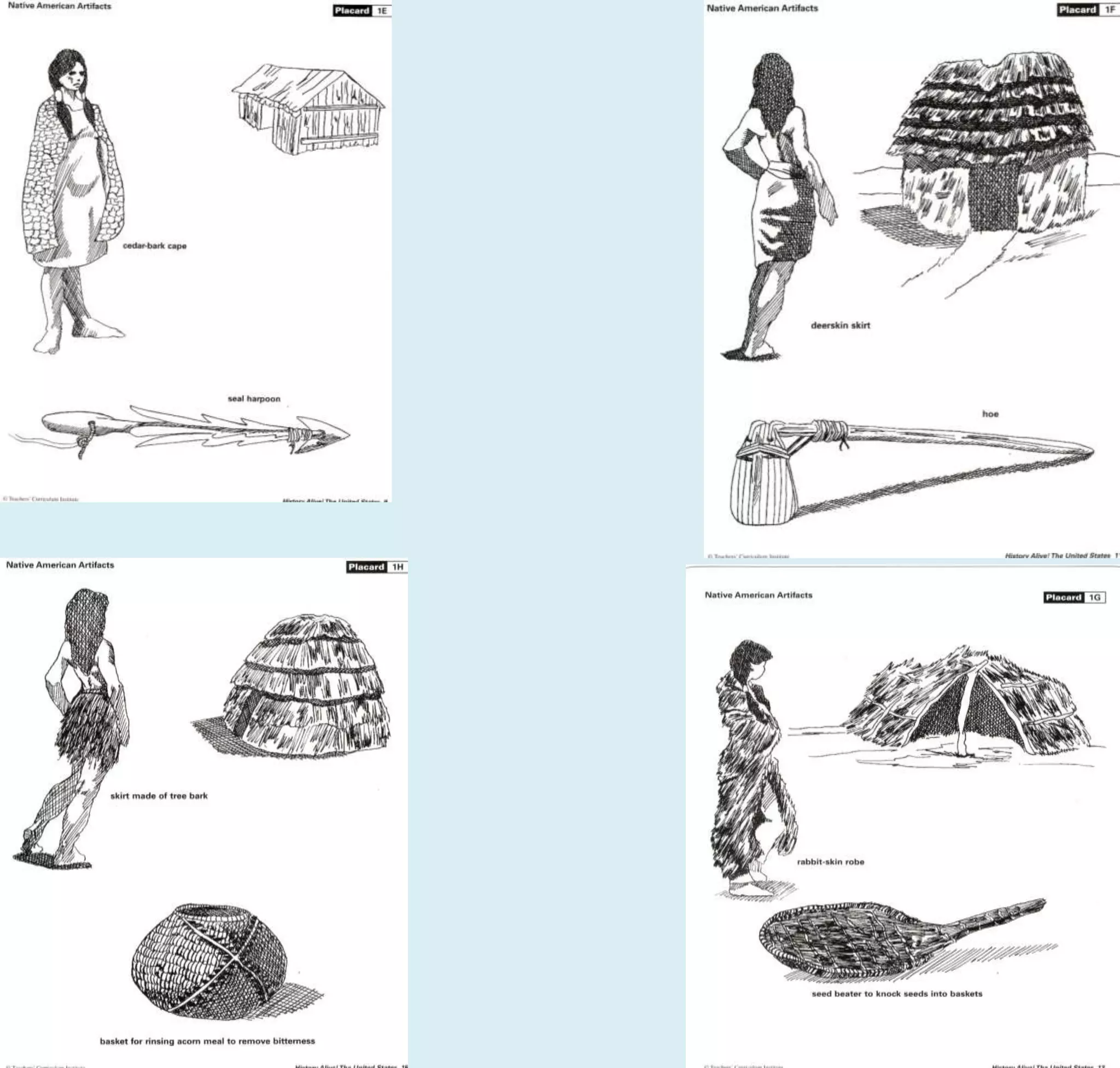
The first Americans crossed into North America from Asia over a land bridge between Siberia and Alaska around 30,000 years ago during an ice age. As the climate warmed, sea levels rose and the land bridge disappeared. These early peoples adapted to different environments across North America, developing distinct cultural regions. They utilized local natural resources for food, clothing, shelter and tools. While practices varied by region, most Native American cultures shared beliefs about respecting nature and only taking what was needed.