Translation of Proteins.ppt
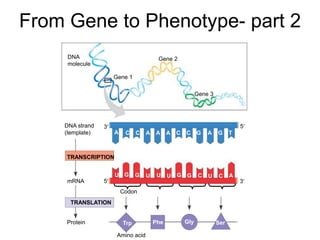
- 1. From Gene to Phenotype- part 2 DNA molecule Gene 1 Gene 2 Gene 3 DNA strand (template) TRANSCRIPTION mRNA Protein TRANSLATION Amino acid A C C A A A C C G A G T U G G U U U G G C U C A Trp Phe Gly Ser Codon 3 5 3 5
- 2. Lecture Outline 11/7/05 • The central dogma: – DNA->RNA->protein • Various types of RNA • The genetic code • Mechanisms of translation – Initiation, Elongation,Termination Exam 3 is next Monday. It will cover mitosis and meiosis, DNA synthesis, transcription, translation, genetics of viruses. (chapters 12, 13, 16, 17, part of 18)
- 3. Four types of RNA • mRNA – Messenger RNA, encodes the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide • rRNA – Ribosomal RNA, forms complexes with protein called ribosomes, which translate mRNA to protein • tRNA – Transfer RNA, transports amino acids to ribosomes during protein synthesis • snRNA – Small nuclear RNA, forms complexes with proteins used in eukaryotic RNA processing
- 4. 3 A C C A C G C U U A A G A C A C C U G C * GUGU C U GAG G U A A A G U C A G A C C CGAG AG G G G A C U C A U U U A G G C G 5 Hydrogen bonds Anticodon * * * * * * * * * * * RNA will fold to specific shapes • Because RNA is single-stranded, parts of the molecule can base pair with other parts of the same molecule, causing it to fold into defined shapes. • Some RNA molecules can even act as enzymes (ribozymes)
- 5. Correspondence between exons and protein domains Gene DNA Exon 1 Intron Exon 2 Intron Exon 3 Transcription RNA processing Translation Domain 3 Domain 1 Domain 2 Polypeptide
- 6. The genetic code Second mRNA base U C A G U C A G UUU UUC UUA UUG CUU CUC CUA CUG AUU AUC AUA AUG GUU GUC GUA GUG Met or start Phe Leu Leu lle Val UCU UCC UCA UCG CCU CCC CCA CCG ACU ACC ACA ACG GCU GCC GCA GCG Ser Pro Thr Ala UAU UAC UGU UGC Tyr Cys CAU CAC CAA CAG CGU CGC CGA CGG AAU AAC AAA AAG AGU AGC AGA AGG GAU GAC GAA GAG GGU GGC GGA GGG UGG UAA UAG Stop Stop UGA Stop Trp His Gln Asn Lys Asp Arg Ser Arg Gly U C A G U C A G U C A G U C A G First mRNA base (5 end) Third mRNA base (3 end) Glu
- 7. The code is a triplet code – the new boy saw the big cat eat the hot dog • The first evidence for triplet code came from deletion experiments – the new boy saw the big cat eat the hot dog – the neb oys awt heb igc ate att heh otd og • Function could be restored by an insertion nearby – the new boy saw the big cat eat the hot dog – the neb oys aaw the big cat eat the hot dog
- 8. The code is a triplet code • . . . or by two more deletions to get it back into the correct “reading frame” – the new boy saw the big cat eat the hot dog – the neb oys awt heb igc ate att heh otd og – the neb osa wte big cat eat the hot dog
- 9. Deciphering the Code • Your book tells how people used synthetic mRNAs and in vitro translation to determine decipher the codons. • E.g. UUUUUUUU -> phenylalanine only – UCUCUCUCUCU -> mix of leucine and serine • Why is it a mixture?
- 10. The code is redundant • Several different codons encode the same amino acid Second mRNA base U C A G U C A G UUU UUC UUA UUG CUU CUC CUA CUG AUU AUC AUA AUG GUU GUC GUA GUG Met or start Phe Leu Leu lle Val UCU UCC UCA UCG CCU CCC CCA CCG ACU ACC ACA ACG GCU GCC GCA GCG Ser Pro Thr Ala UAU UAC UGU UGC Tyr Cys CAU CAC CAA CAG CGU CGC CGA CGG AAU AAC AAA AAG AGU AGC AGA AGG GAU GAC GAA GAG GGU GGC GGA GGG UGG UAA UAG Stop Stop UGA Stop Trp His Gln Asn Lys Asp Arg Ser Arg Gly U C A G U C A G U C A G U C A G First mRNA base (5 end) Third mRNA base (3 end)
- 11. The code is comma free • No punctuation between words. – Therefore deletions cause frameshifts • It does have start and stop signals, however. – Start: AUG – Stop: UAG, UAA, UGA
- 12. Translation: the basic concept TRANSCRIPTION TRANSLATION DNA mRNA Ribosome Polypeptide Polypeptide Amino acids tRNA with amino acid attached Ribosome tRNA Anticodon mRNA Gly A A A U G G U U U G G C Codons 5 3
- 13. The structure of transfer RNA (tRNA) 3 A C C A C G C U U A A G A C A C C U G C * G U G U C U GAG G U A A A G U C A G A C C C G A G A G G G G A C U C A U U U A G G C G 5 Amino acid attachment site Hydrogen bonds Anticodon * * * * * * * * * * *
- 14. tRNA Amino acid attachment site Hydrogen bonds Anticodon Anticodon (b) Three-dimensional structure A A G 5 3 3 5 Symbol used in this book (c)
- 15. TRANSCRIPTION TRANSLATION DNA mRNA Ribosome Polypeptide E P A mRNA 5 3 Ribosomes Growing polypeptide tRNA molecules Large subunit Small subunit RNA + protein. We now think that RNA catalyzes the reactions.
- 16. P site (Peptide site) E site (Exit site) mRNA binding site Large subunit Small subunit E P A A site (Acceptor site) EPA model of a ribosome
- 17. Amino end Growing polypeptide Next amino acid to be added to polypeptide chain tRNA mRNA Codons 3 5 New amino acids are added to the carboxyl end of the polypeptide
- 18. The initiation of translation 2 Initiator tRNA mRNA mRNA binding site Small ribosomal subunit Large ribosomal subunit Translation initiation complex P site GDP GTP Start codon 1 U A C A U G E A 3 5 5 3 3 5 3 5 Small subunit binds just upstream of start Special initiator methionine binds to the start codon (AUG) The large subunit can now bind to make the active ribosome
- 19. Elongation Amino end of polypeptide mRNA tRNA with appropriate anticodon binds at A site Ribosome ready for next aminoacyl tRNA Translocaton. Everything moves left one notch. Polypeptide is now at P. Empty tRNA leaves the E site. E P A E P A E P A E P A GDP GTP GTP GDP 2 2 site site 5 3 3 2 1 TRANSCRIPTION TRANSLATION DNA mRNA Ribosome Polypeptide Peptide bond formed. Growing chain is now at A
- 20. Termination Release factor Free polypeptide Stop codon (UAG, UAA, or UGA) 1 2 3 5 3 5 3 5 3 Stop codon has no matching tRNA Release factor binds and separates the polypeptide from the tRNA The ribosome separates from mRNA
- 21. 4 An aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase joins a specific amino acid to a tRNA Amino acid ATP Adenosine Pyrophosphate Adenosine Adenosine tRNA P P P P P Pi Pi Pi P AMP Appropriate tRNA bonds to amino Acid, displacing AMP. Active site binds the amino acid and ATP. 1 3 Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase (enzyme) Activated amino acid is released by the enzyme.
- 22. See the Animation • www.dnai.org
- 23. Inhibition of protein synthesis Toxin Mode of action Target Puromycin forms peptidyl-puromycin, prevents translocation Procaryotes Tetracycline blocks the A-site, prevents binding of aminoacyl tRNAs Procaryotes Chloramphenicol blocks peptidyl transfer Procaryotes Cycloheximide blocks peptidyl transferase Eucaryotes Streptomycin inhibits initiation at high concentrations Procaryotes Diphtheria toxin catalyzes ADP-ribosylation of residue in eEF2 Eucaryotes Erythromycin binds to 50S subunit, inhibits translocation Procaryotes Ricin inactivates 60S subunit, depurinates an adenosine in 23S rRNA Eucaryotes NOTE: Prokaryotes (this generally includes protein synthesis in mitochondria and chloroplasts)
- 24. Summary of transcription and translation in a eukaryotic cell TRANSCRIPTION RNA is transcribed from a DNA template. DNA RNA polymerase RNA transcript RNA PROCESSING In eukaryotes, the RNA transcript (pre- mRNA) is spliced and modified to produce mRNA, which moves from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. Exon RNA transcript (pre-mRNA) Intron NUCLEUS FORMATION OF INITIATION COMPLEX After leaving the nucleus, mRNA attaches to the ribosome. CYTOPLASM mRNA Growing polypeptide Ribosomal subunits Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase Amino acid tRNA AMINO ACID ACTIVATION Each amino acid attaches to its proper tRNA with the help of a specific enzyme and ATP. Activated amino acid TRANSLATION A succession of tRNAs add their amino acids to the polypeptide chain as the mRNA is moved through the ribosome one codon at a time. (When completed, the polypeptide is released from the ribosome.) Anticodon A A A UG GUU UA U G E A Ribosome 1 5 5 3 Codon 2 3 4 5