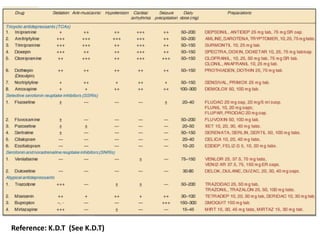
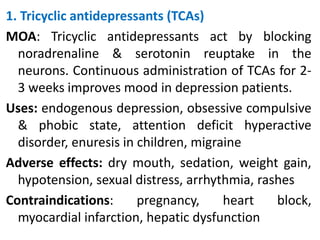
This document provides information on various classes of antipsychotic and antidepressant medications. It discusses the mechanisms and uses of tricyclic antidepressants, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors, and monoamine oxidase inhibitors for treating conditions like depression. It also covers typical and atypical antipsychotics used to treat schizophrenia and other psychoses, describing their dopamine receptor blocking effects. Mood stabilizing drugs like lithium are mentioned for managing manic-depressive disorder.