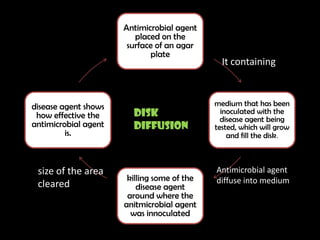
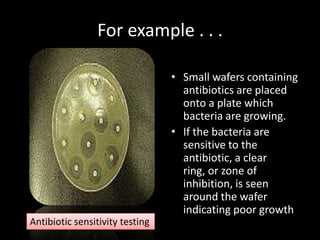
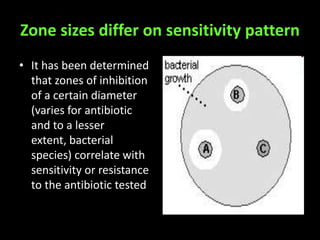
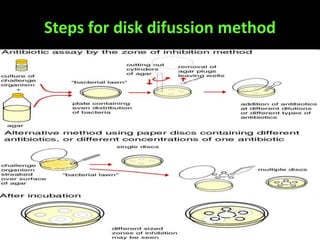
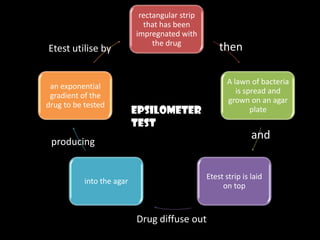
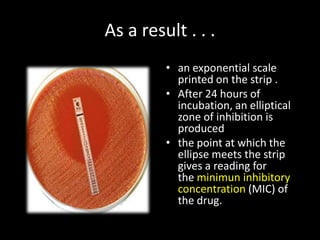
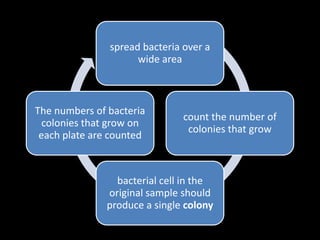
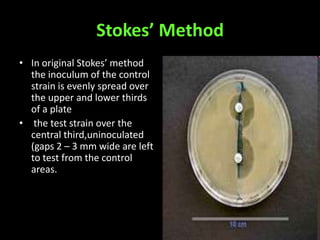
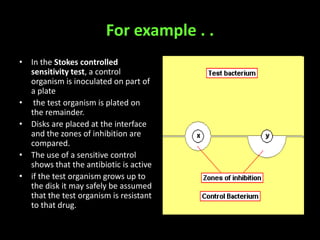
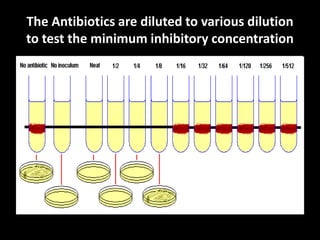
This document discusses various techniques used to test antimicrobial activity, including disk diffusion, Etest, dilution plating, and determining minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC). The disk diffusion technique involves placing disks containing antibiotics on an agar plate inoculated with bacteria, and measuring the zone of inhibition. The Etest uses strips with an exponential gradient of drugs to determine the MIC. Dilution plating reduces bacterial concentration to obtain isolated colonies. MIC testing finds the lowest drug concentration that prevents bacterial growth. These techniques help determine antibiotic effectiveness and resistance.