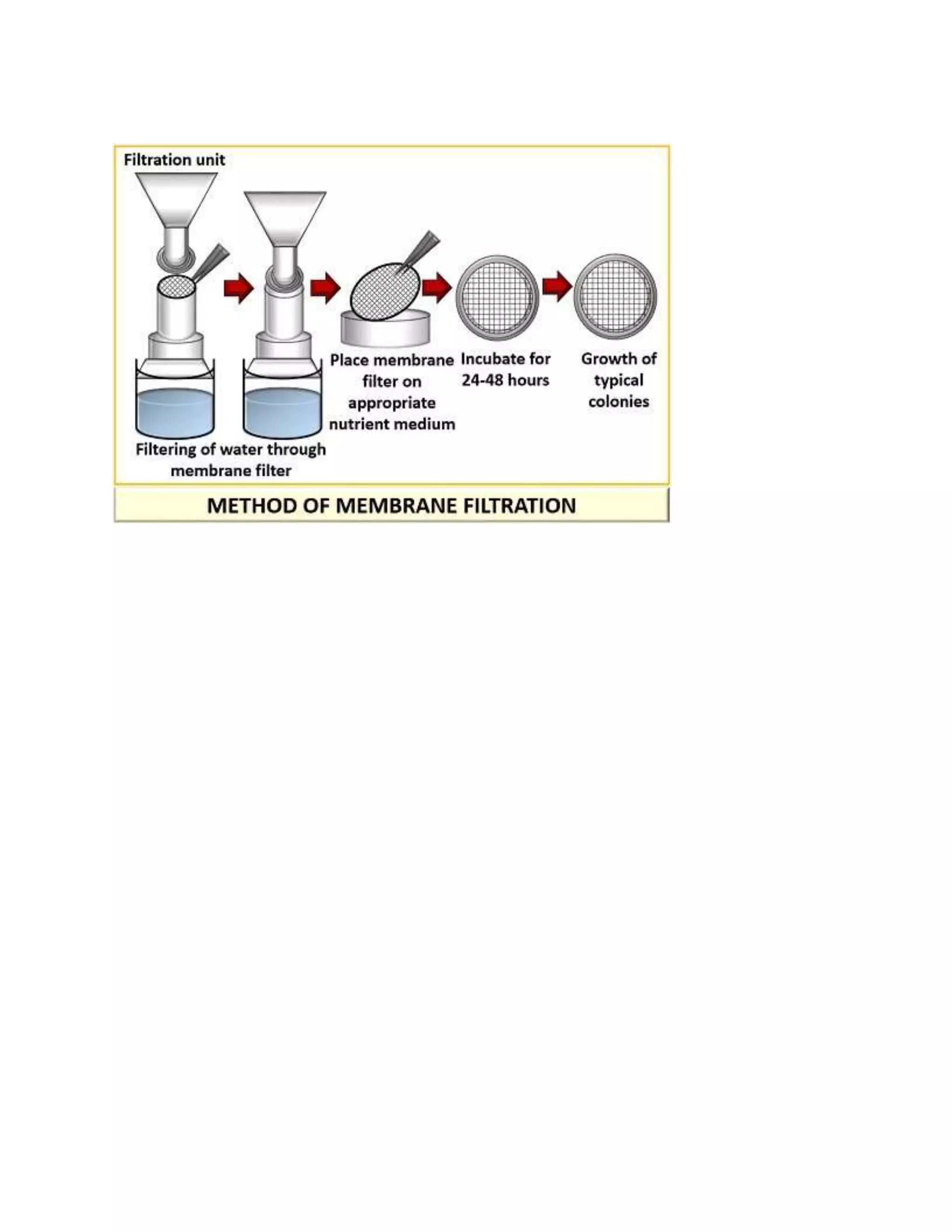
The document discusses techniques for determining viable bacterial counts, including the pour plate method, spread plate method, and membrane filtration technique. It explains that viable bacterial counts determine the number of living bacteria by counting colonies formed after incubation. For the pour and spread plate methods, serial dilutions of a sample are plated and incubated to allow colony formation, then colonies are counted and multiplied by the dilution factor to obtain the bacterial concentration in the original sample. The membrane filtration technique traps bacteria from aquatic samples on a membrane, which is then placed on a nutrient medium and incubated to allow colonies to grow and be counted.