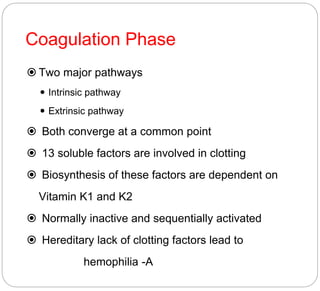
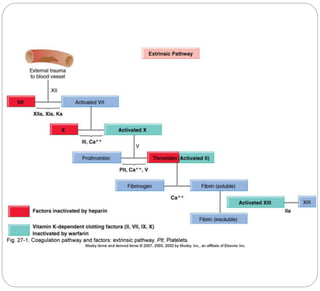
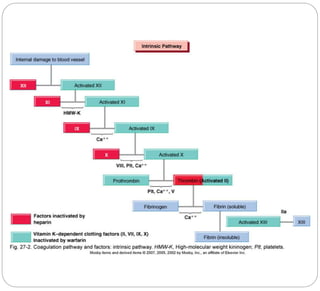
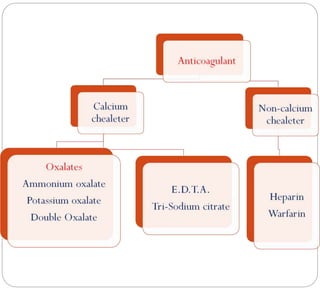
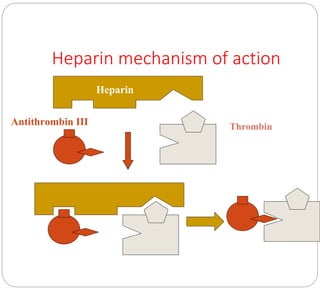
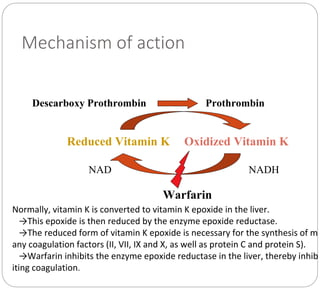
Anticoagulants prevent the clotting of blood when mixed with blood in proper proportion. They are used to study blood components and the coagulation process, and to preserve blood in blood banks. The most commonly used anticoagulant in hematology laboratories is EDTA, which is a powerful calcium chelator. Excess EDTA can affect red blood cells and leukocytes, causing cell shrinkage and changes. Heparin is also used as an anticoagulant but is more expensive and causes a black background in smears. Warfarin is an oral anticoagulant that acts by inhibiting the enzyme that reduces vitamin K, thereby inhibiting coagulation factor synthesis in the liver. Antico