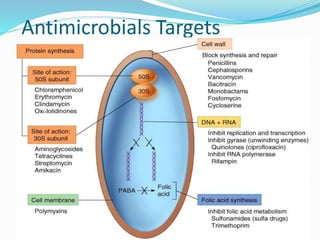
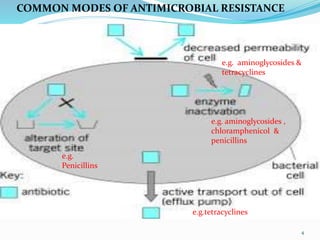
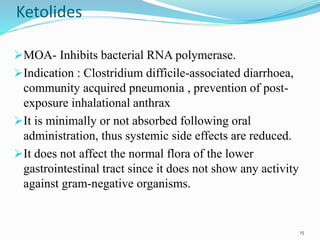
This document discusses various classes of newer antimicrobials that are used to treat resistant bacterial infections. It provides details on the mechanisms of action and modes of resistance for classes such as oxazolidinones, glycopeptides, lipopeptides, ketolides, glycylcyclines, carbapenems, cephalosporins, pleuromutilins, macrocyclic antibiotics, rifamycins, streptogramins, and quinolones. Newer drugs within these classes have improved properties compared to older drugs like having additional mechanisms of action, fewer drug interactions and side effects, and activity against drug-resistant bacteria.