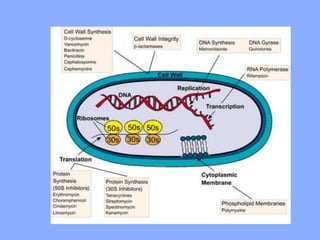
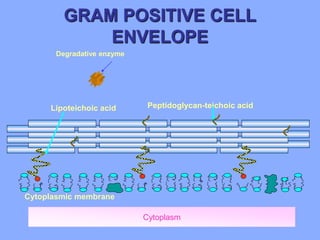
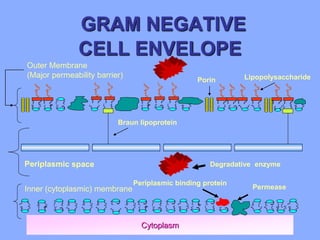
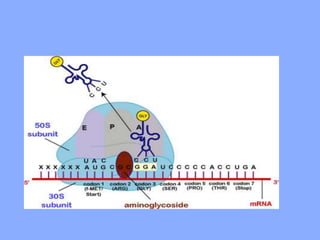
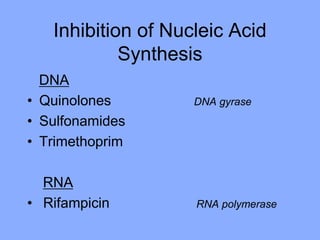
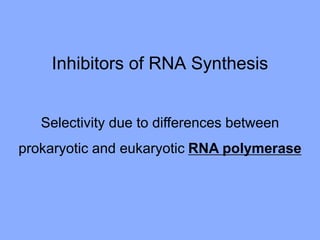
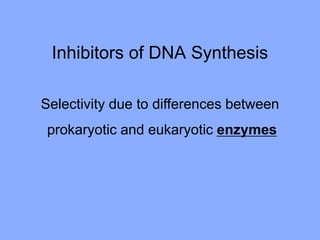
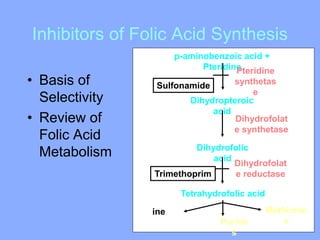
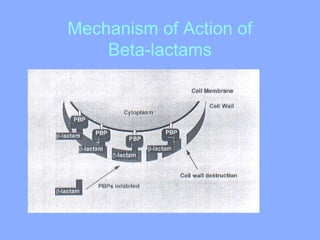
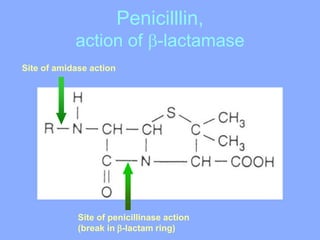
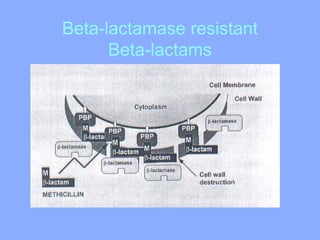
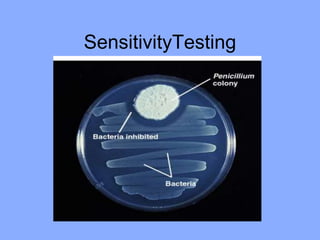
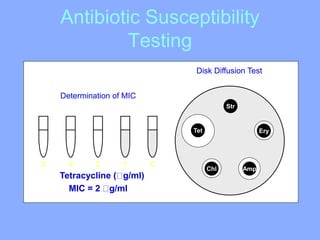
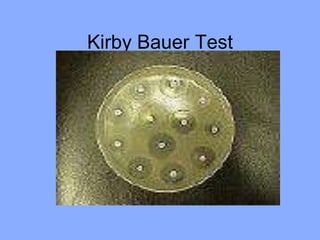
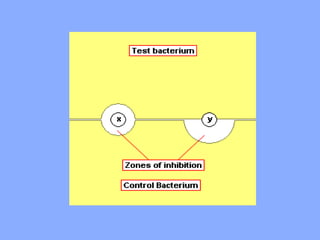
This document discusses antibiotics and their mechanisms of action. It describes how antibiotics target bacterial cell structures like the cell wall and membrane, as well as intracellular components like protein and nucleic acid synthesis. The major groups of antibiotics are outlined, including how they inhibit cell wall synthesis, membrane function, protein production, and nucleic acid replication. Mechanisms of antibiotic resistance in bacteria are also reviewed. The document concludes by explaining methods for determining antibiotic susceptibility, including minimum inhibitory concentration and disk diffusion tests.