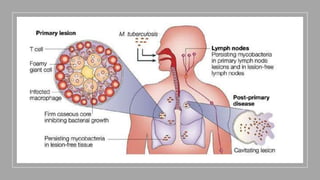
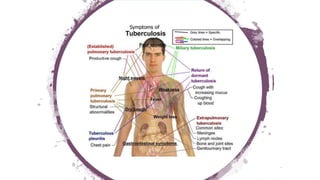
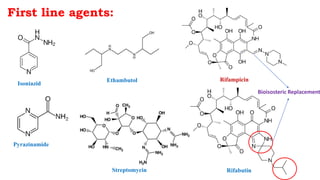
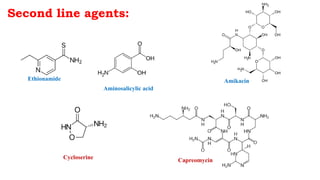
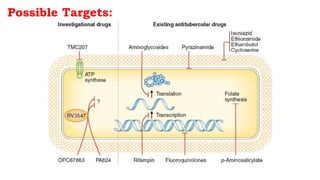
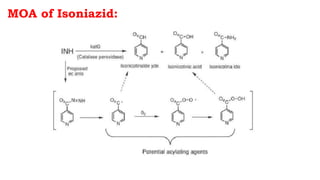
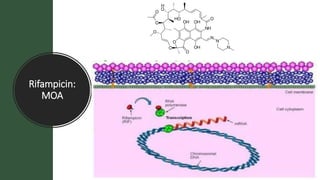
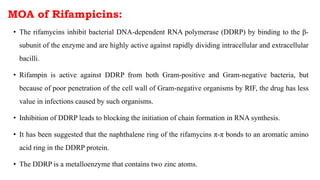
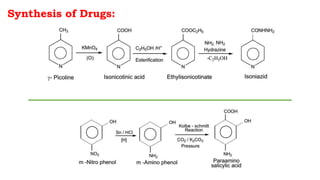
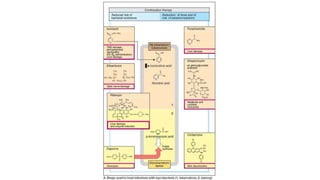
The document discusses antitubercular agents used to treat tuberculosis (TB). TB is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis and spreads through the respiratory system. It can spread through the bloodstream to other organs. Treatment has been hampered by multidrug-resistant TB strains. First-line agents include isoniazid, rifampin, and ethambutol. Second-line agents are used if resistance develops or for patient factors. Isoniazid works by inhibiting fatty acid synthesis, while rifampin inhibits bacterial DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. New antitubercular agents are needed due to increasing drug resistance.