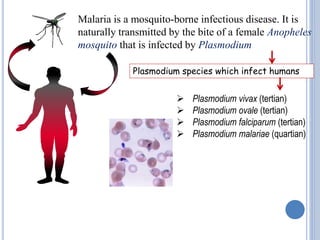
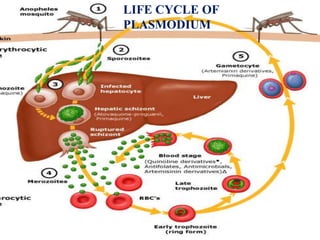
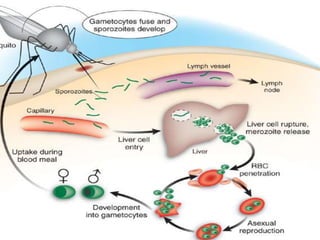
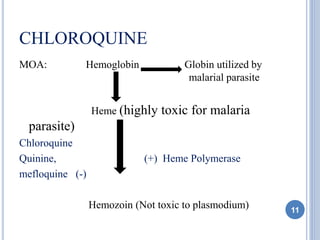
This document discusses various antimalarial drugs, classifying them and describing their mechanisms of action, pharmacokinetics, uses, and side effects. It covers quinoline derivatives like chloroquine and amodiaquine, mefloquine, quinine, proguanil, pyrimethamine, sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine, primaquine, artemisinin and its derivatives, atovaquone, and others. The drugs act against different life stages of the malaria parasite in the liver or blood and are used for prophylaxis, treatment, or radical cure of malaria caused by various Plasmodium species.