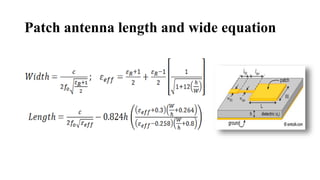
An antenna converts electric power to radio waves and vice versa. It is usually used with a radio transmitter or receiver. There are several types of antennas including wire antennas, traveling wave antennas, reflector antennas, microstrip antennas, log-periodic antennas, and aperture antennas. A patch antenna is a type of radio antenna that is low profile and can be mounted on a flat surface. It consists of a flat metal patch mounted over a larger ground plane. Patch antennas are widely used today in applications like satellite communication, GPS, and mobile devices due to their compact size and light weight.