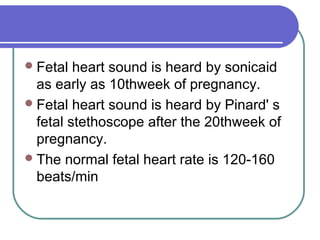
Antenatal care involves comprehensive health supervision and guidance for pregnant women from conception through delivery. It aims to reduce maternal and infant mortality and morbidity. Key aspects of antenatal care include detecting and treating complications, educating mothers, and preparing for labor, lactation, and infant care. Pregnant women should have regular checkups including medical history, exams, and tests to monitor health. Care also involves addressing common discomforts of pregnancy through lifestyle and dietary adjustments.