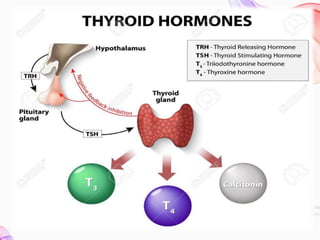
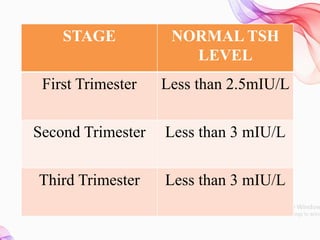
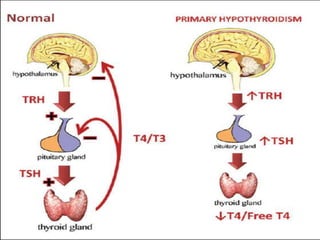
This document discusses thyroid diseases in pregnancy. It notes that normal pregnancy causes physiological changes that alter thyroid function. It then discusses hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism in pregnancy. Hypothyroidism complicates 1-3/1000 pregnancies and can cause maternal risks like infertility and fetal risks like low IQ. It is managed by replacing levothyroxine. Hyperthyroidism affects 2/1000 pregnancies and can cause maternal risks like heart failure. It is managed medically with antithyroid drugs or surgically with thyroidectomy. Nursing management involves monitoring for recurrence of symptoms postpartum. Preconception counseling is also important.