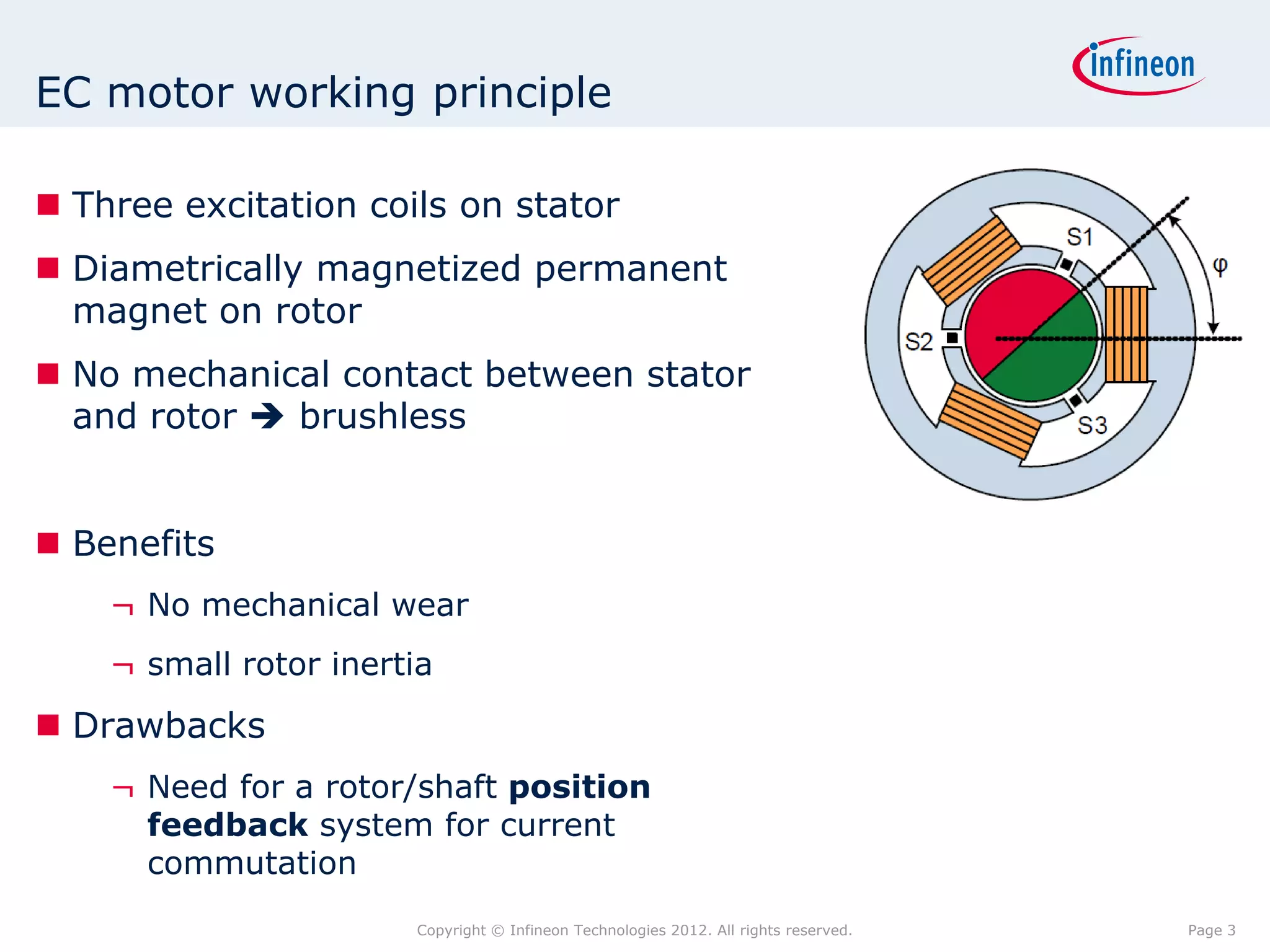
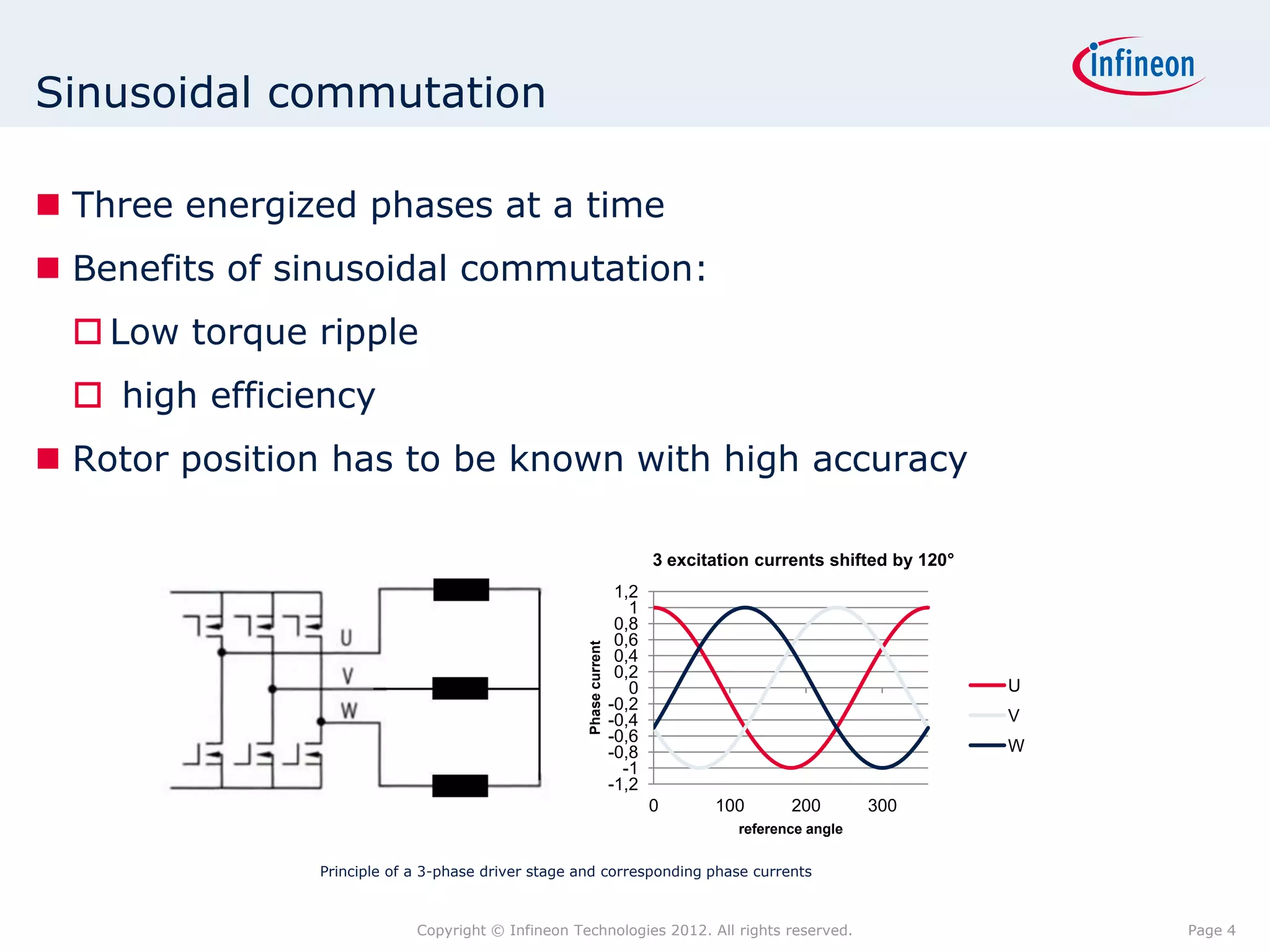
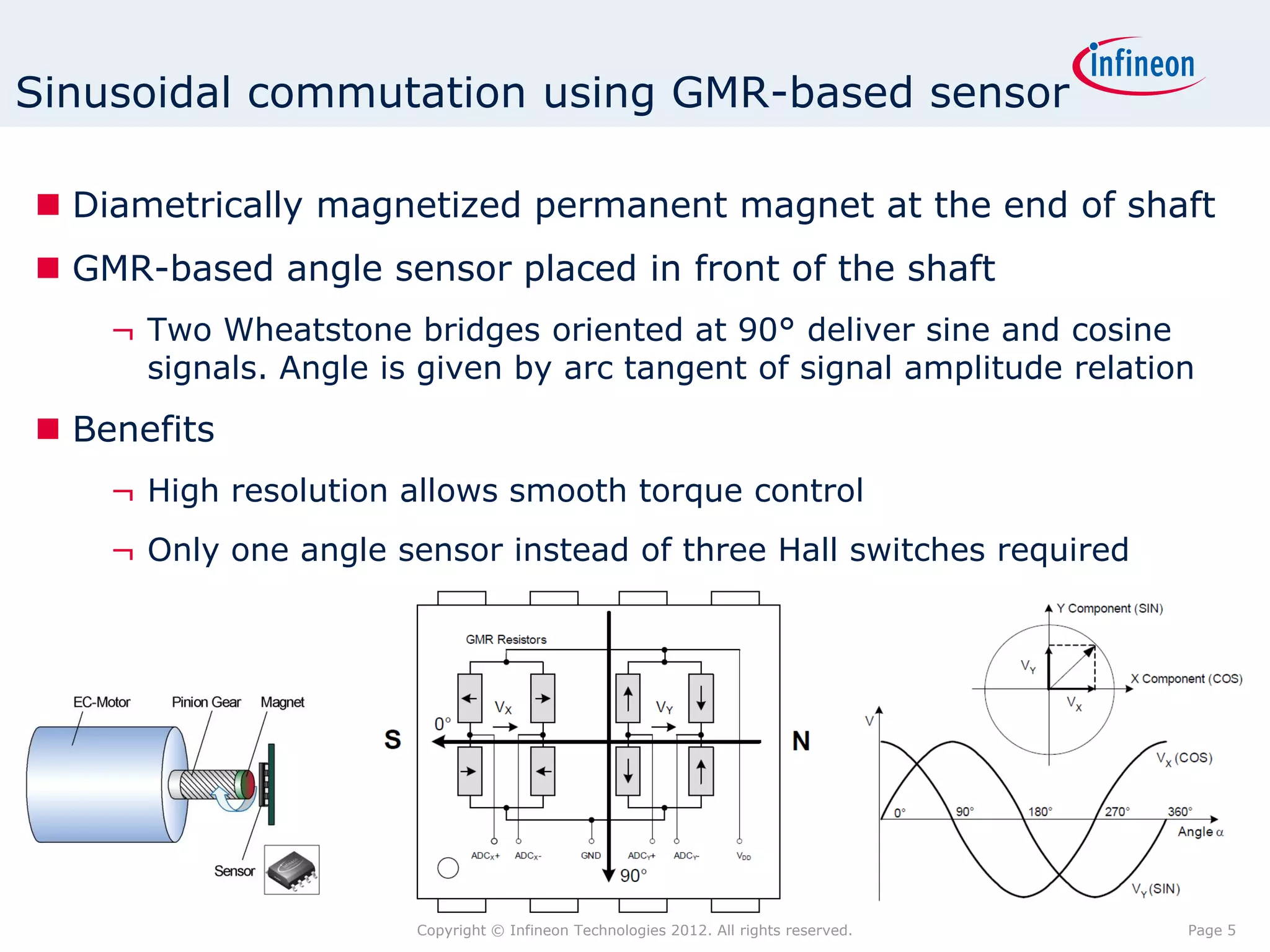
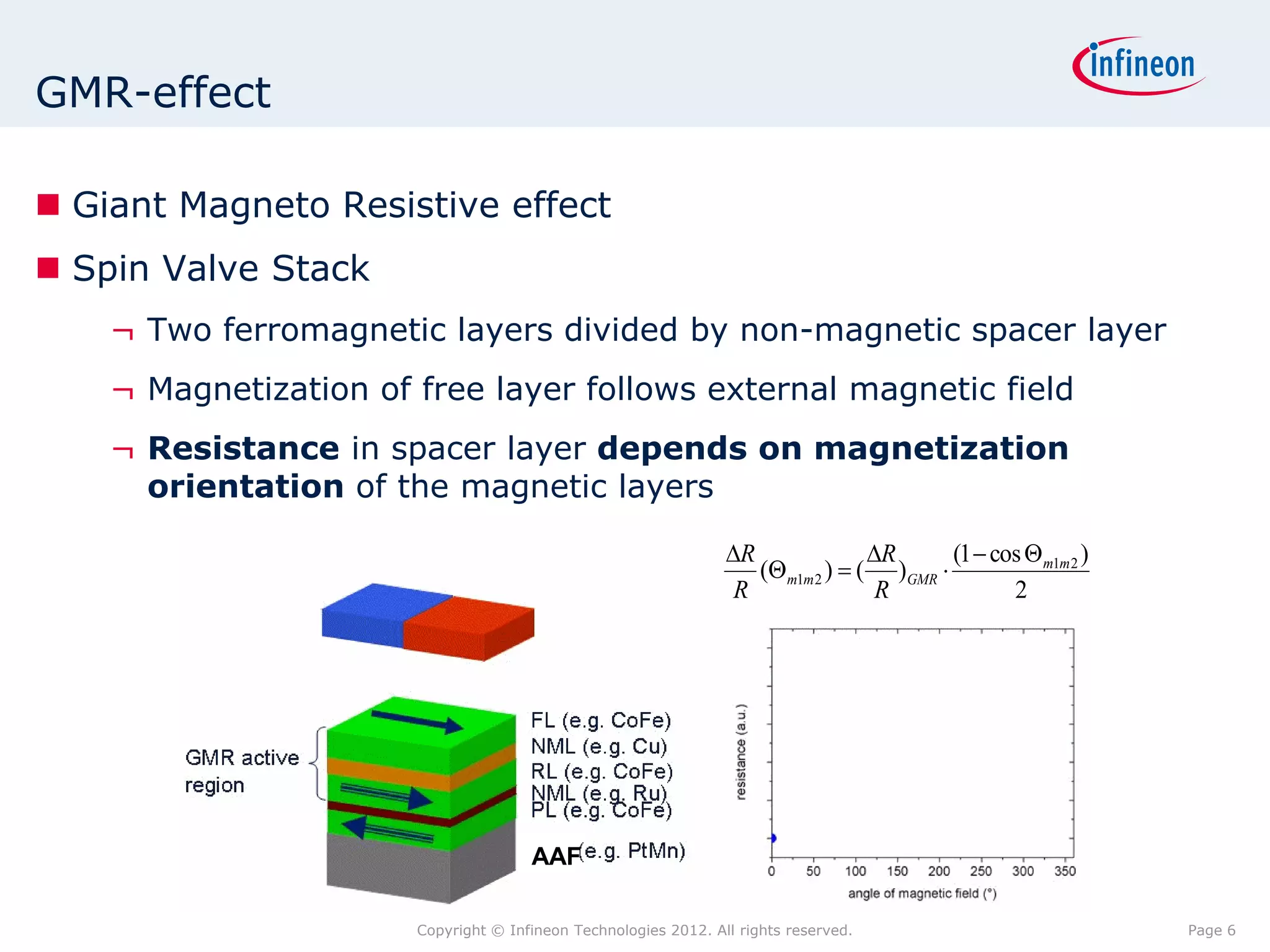
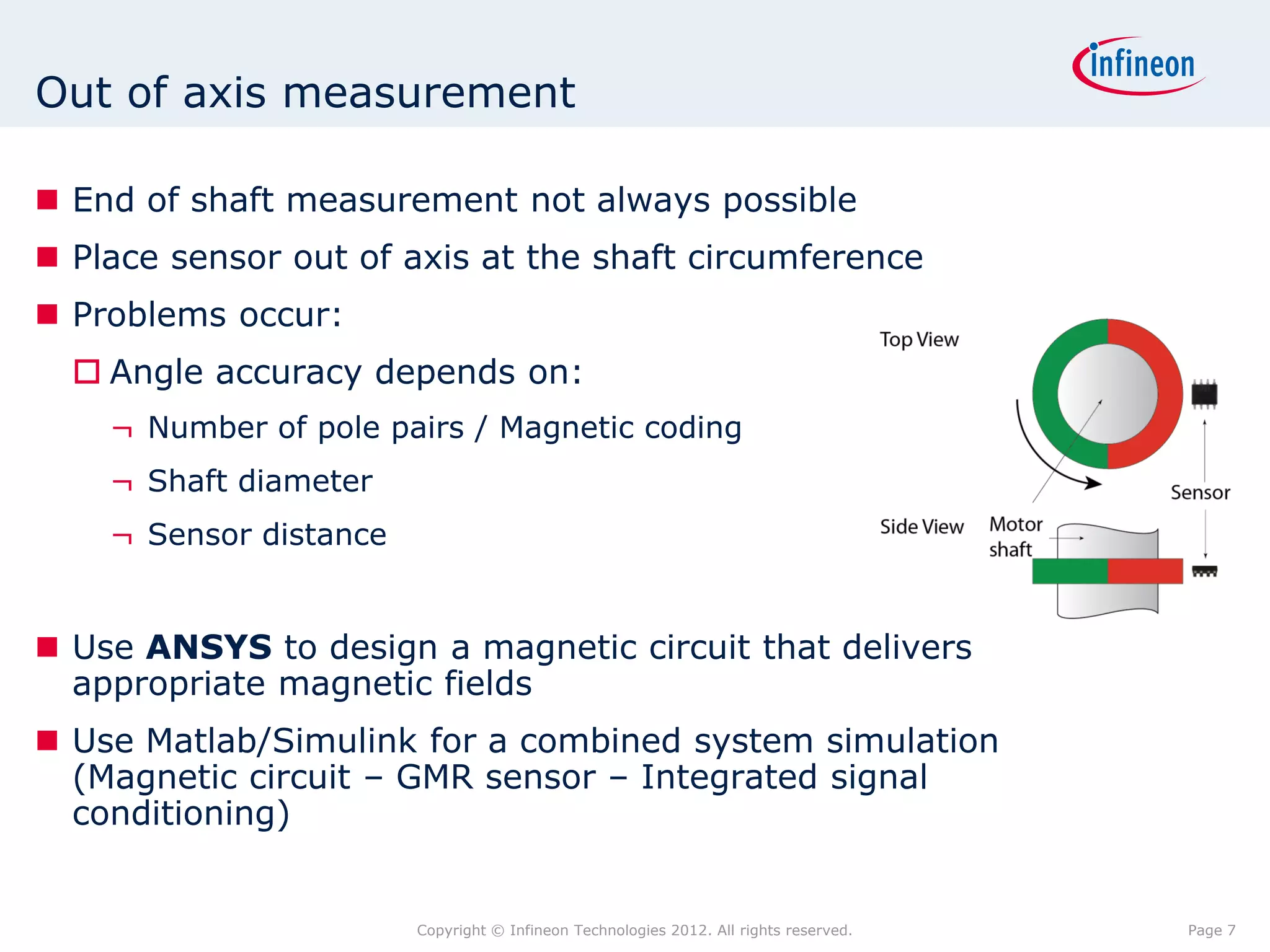
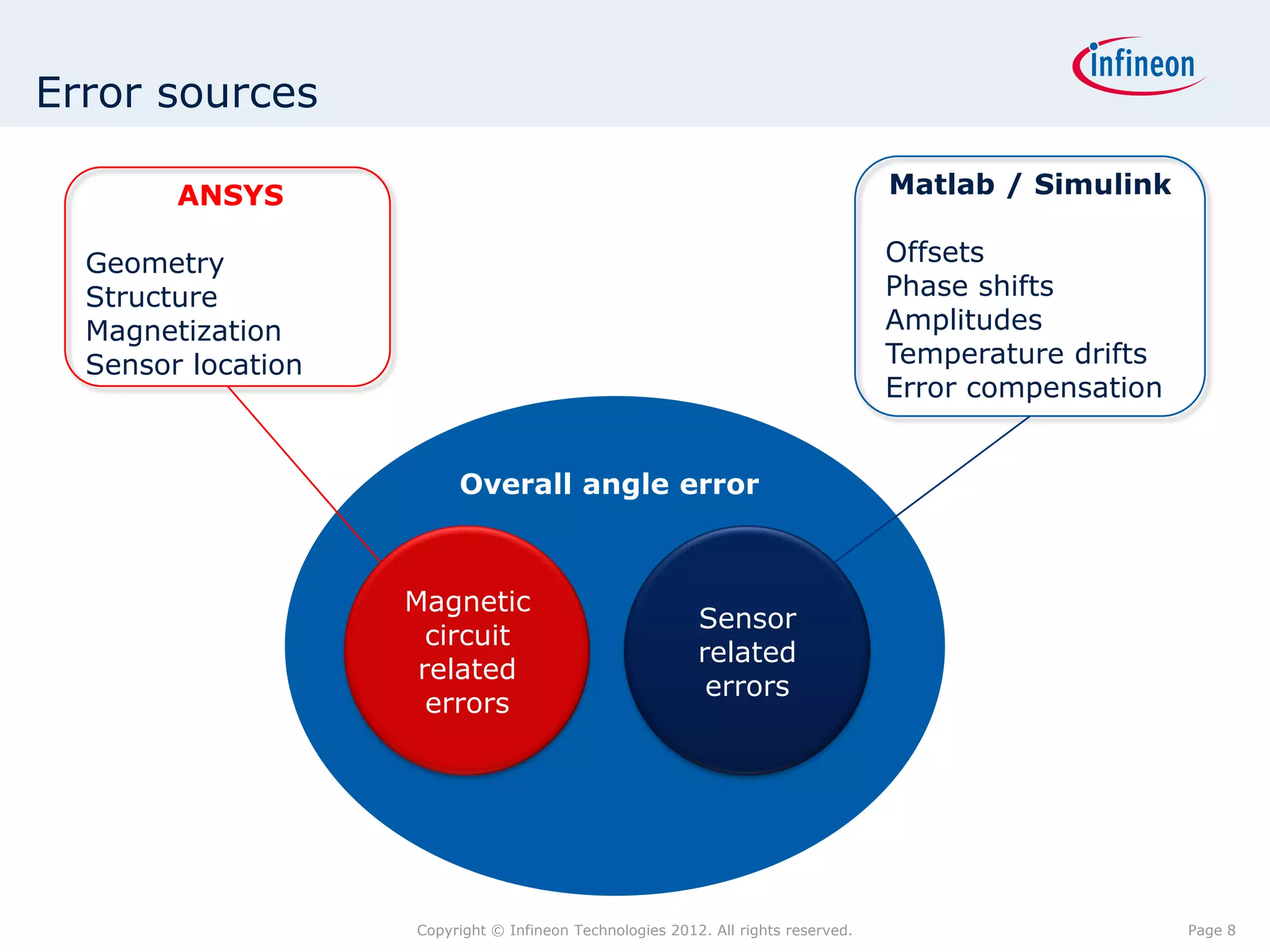
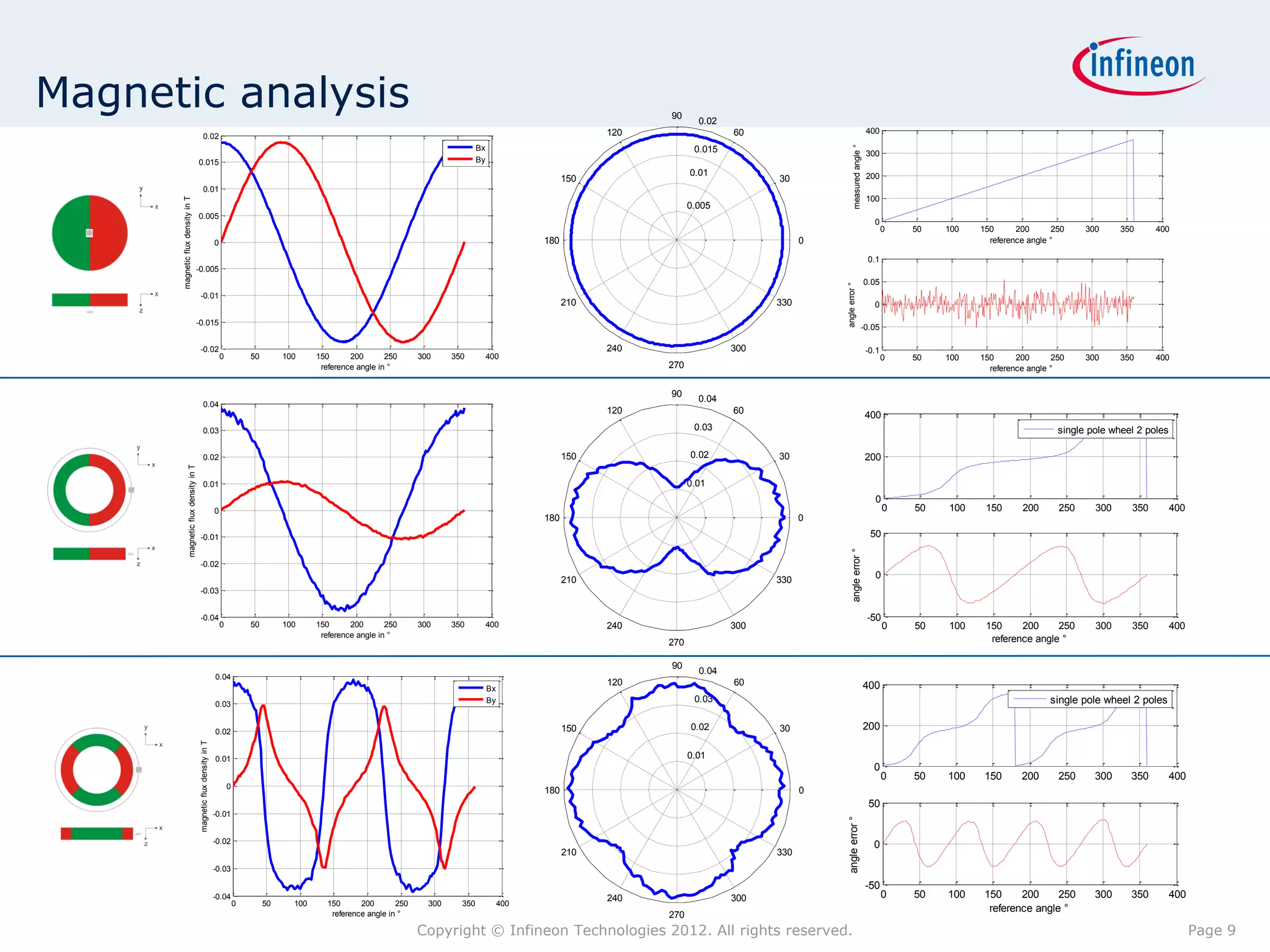
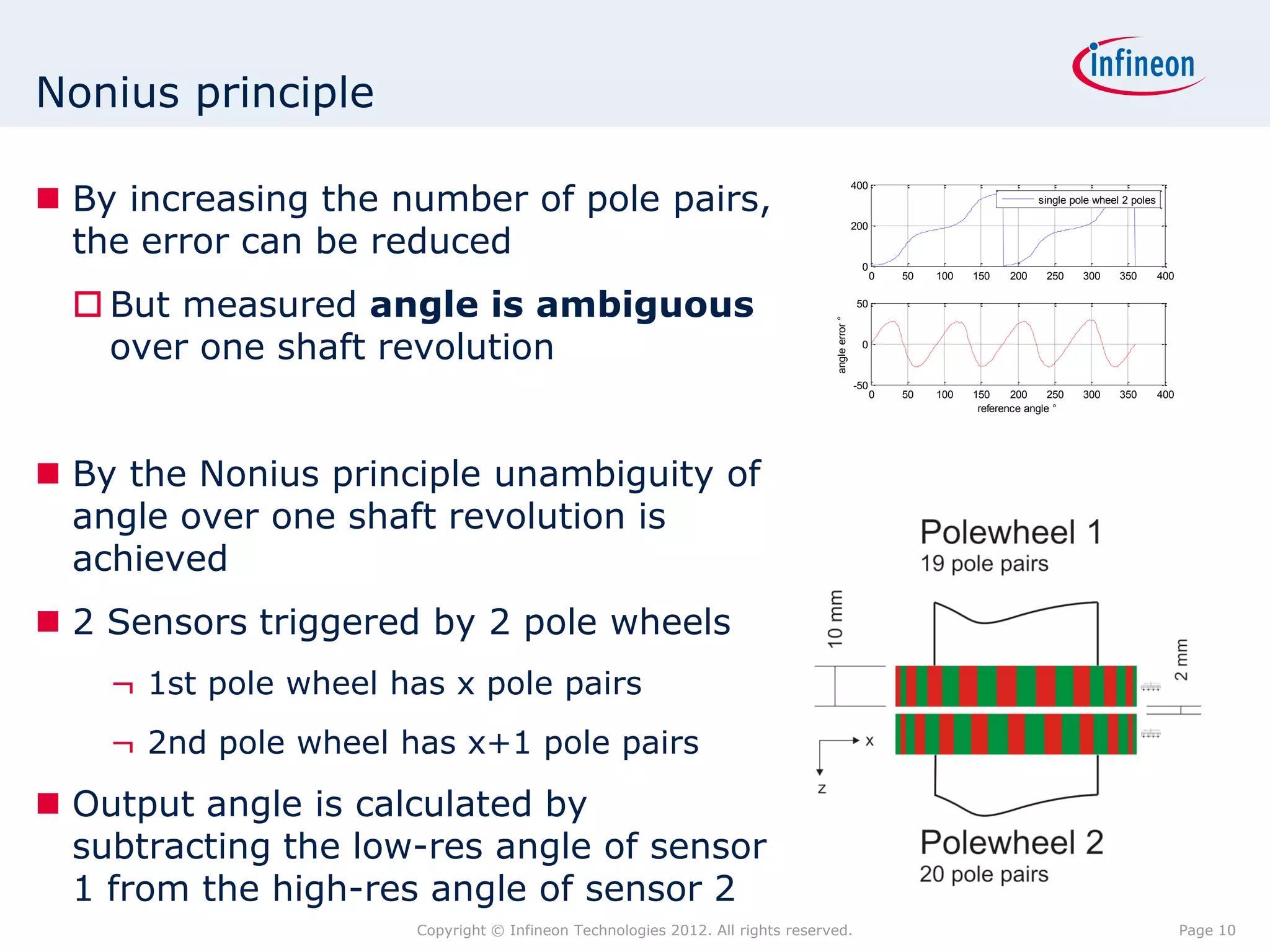
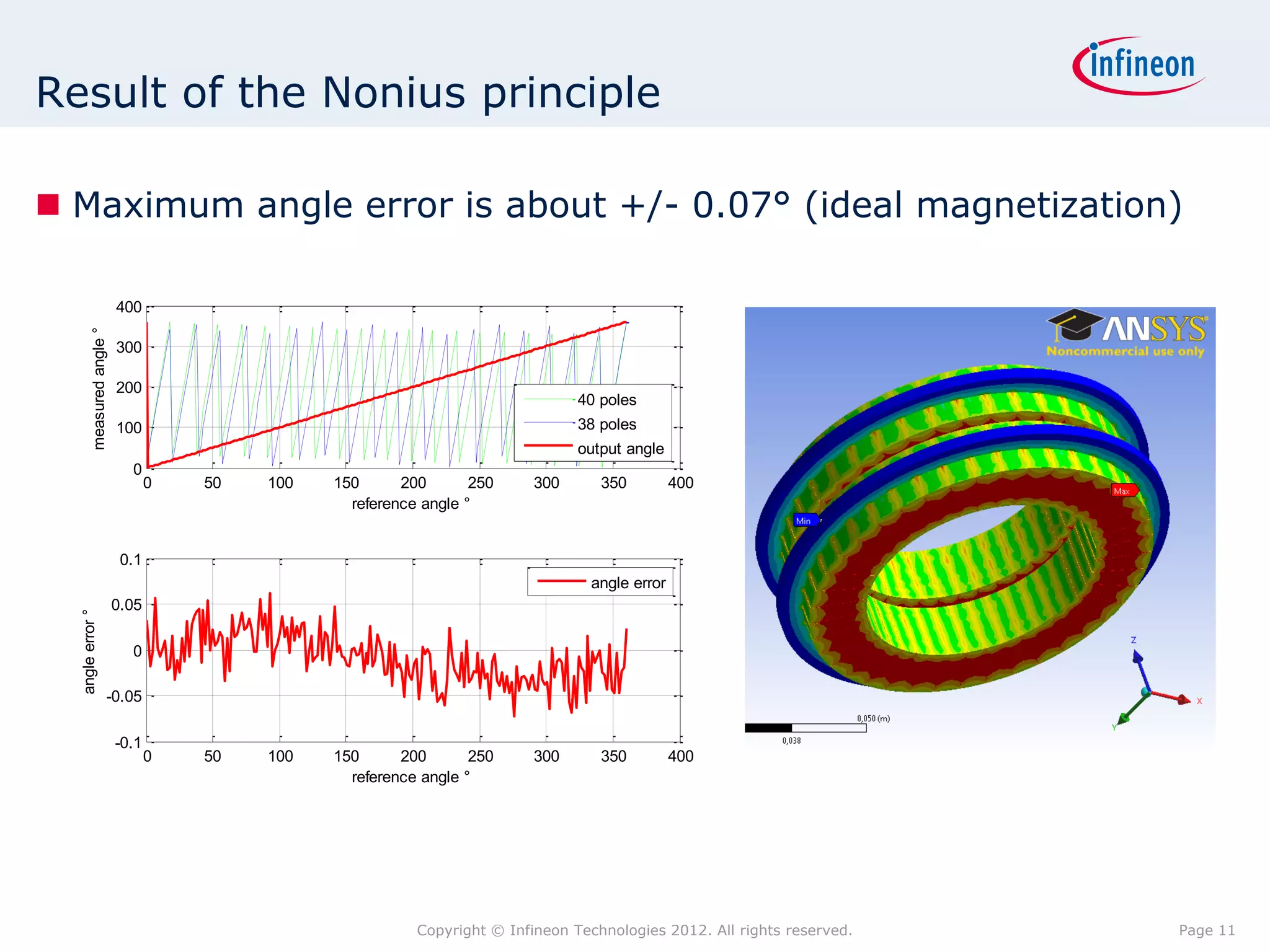
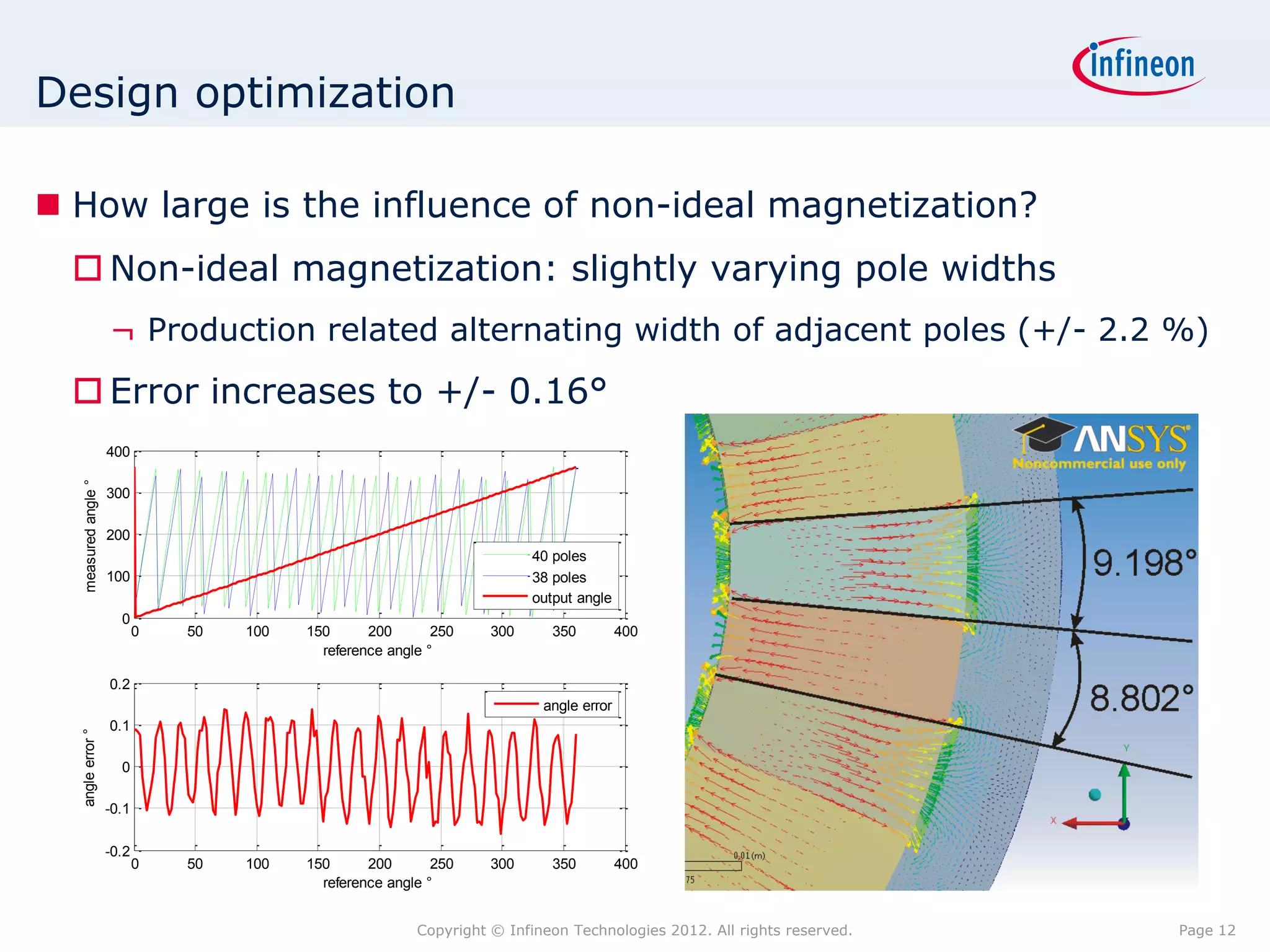
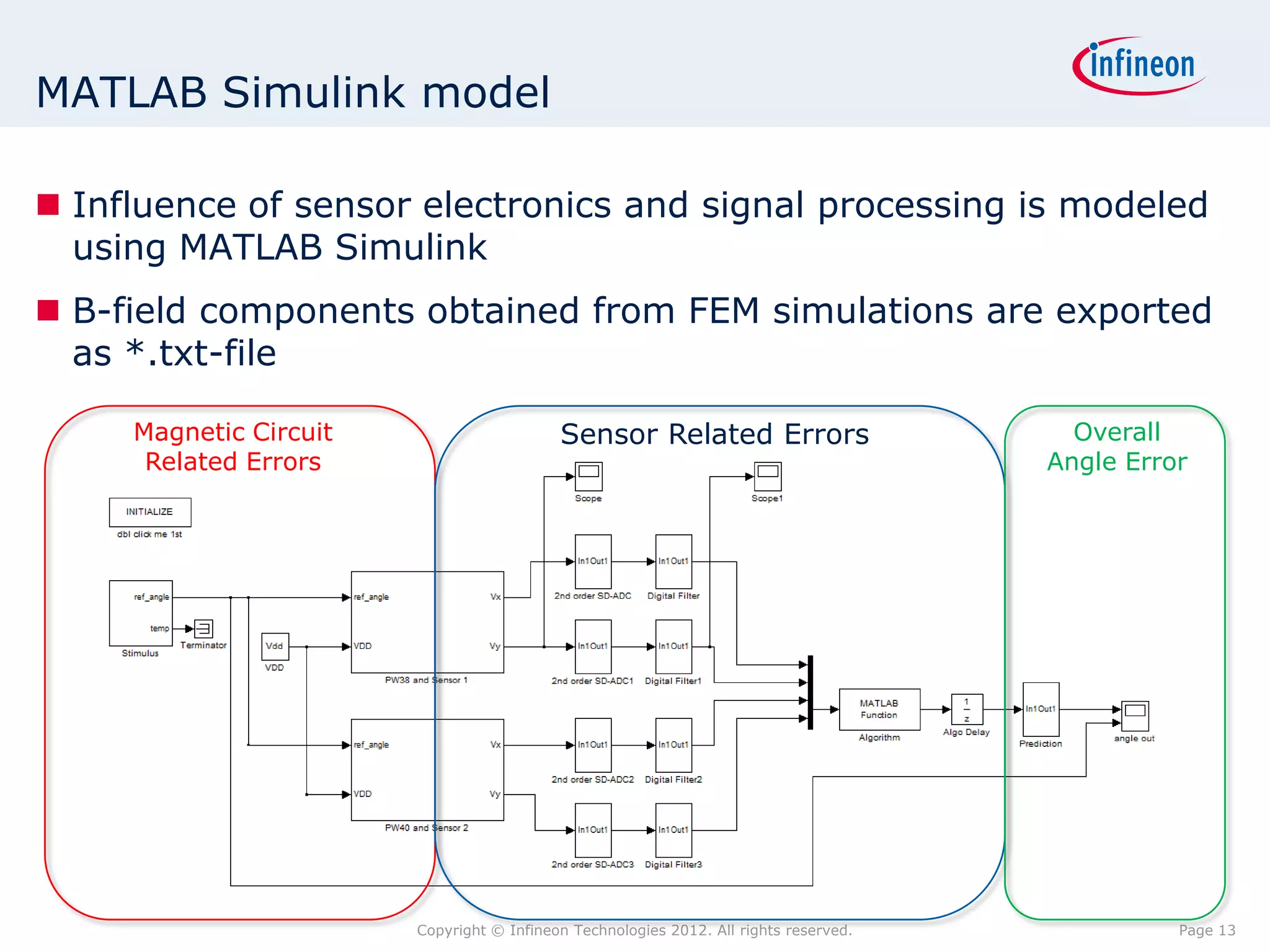
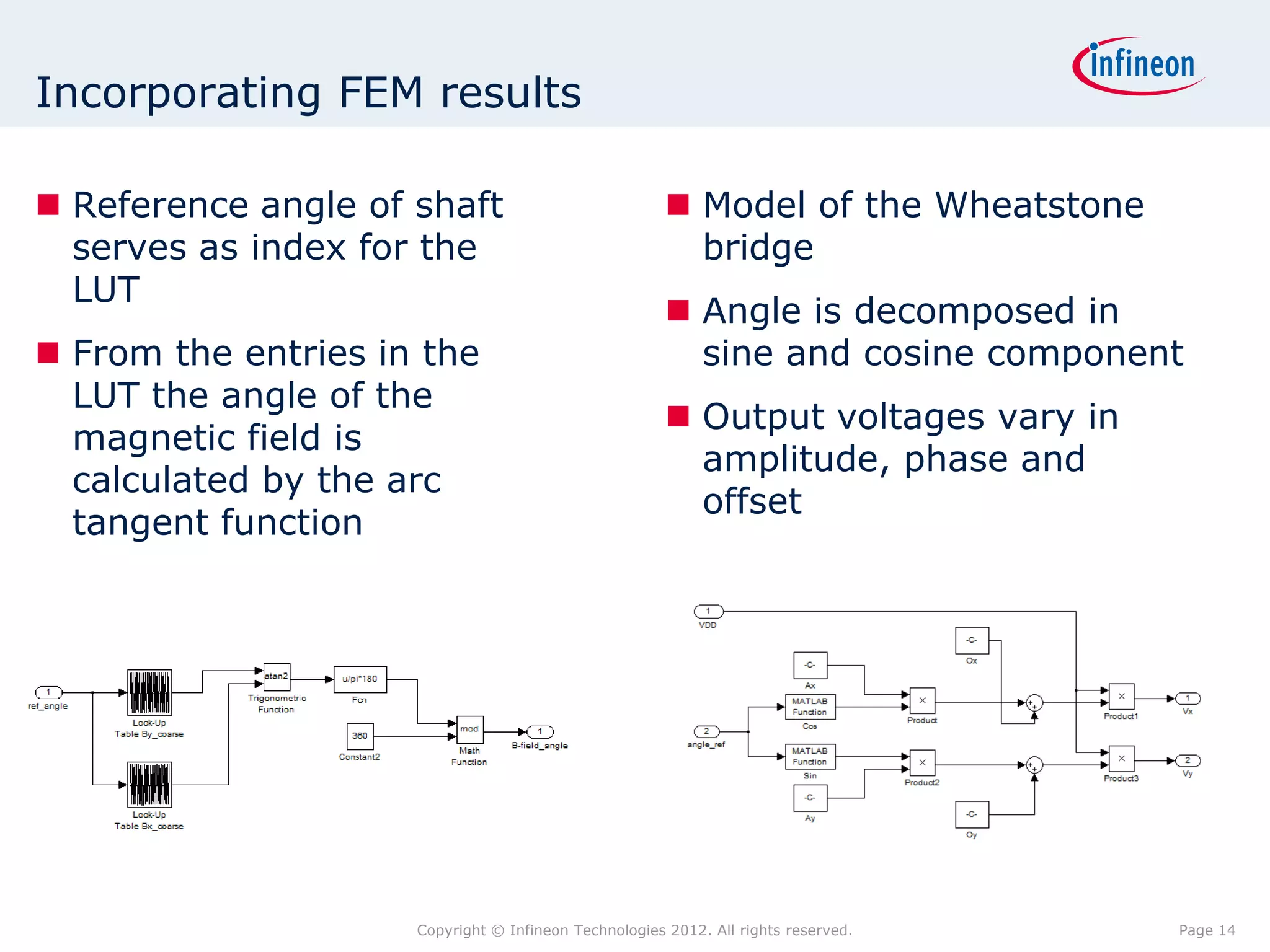
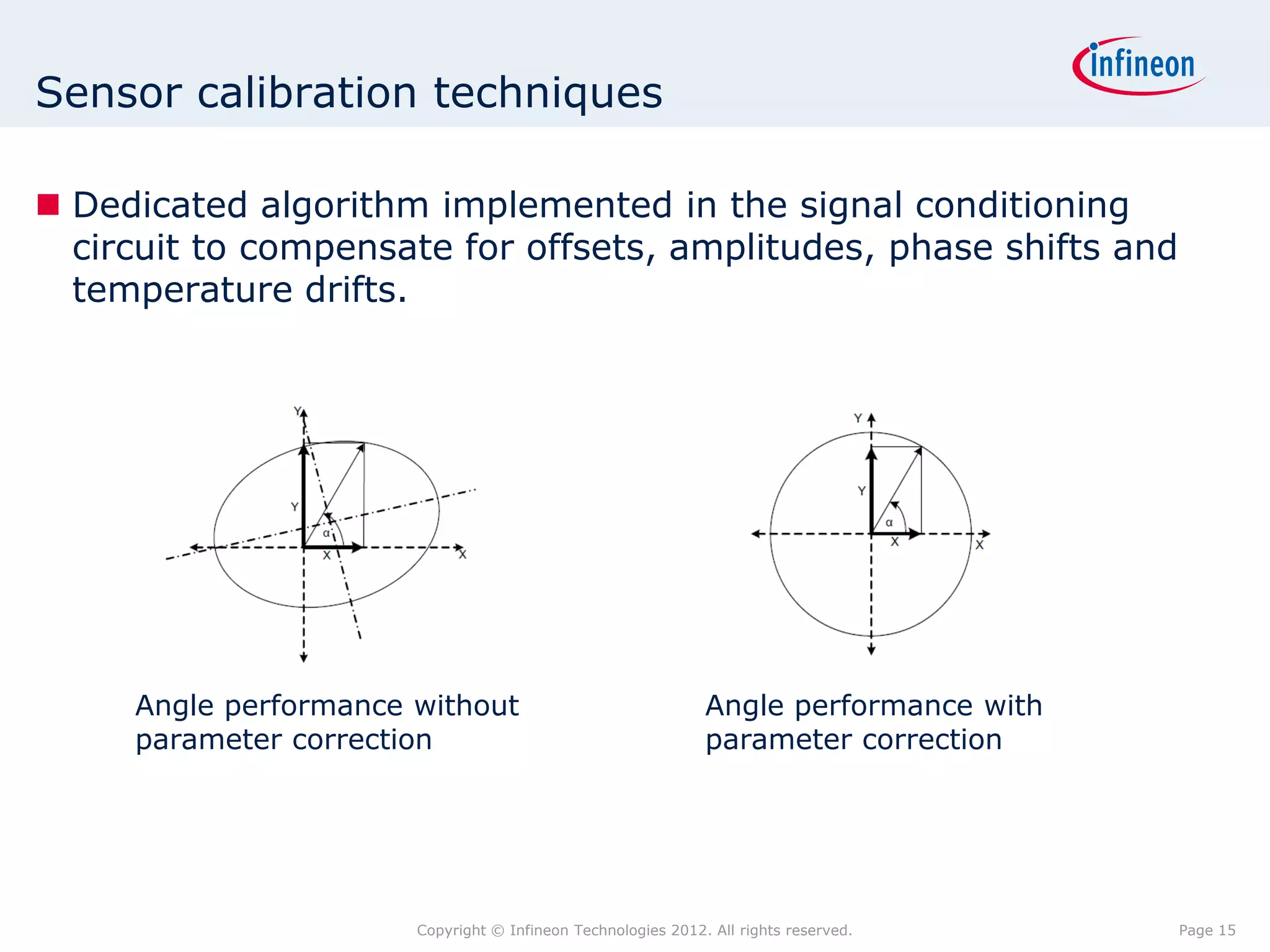
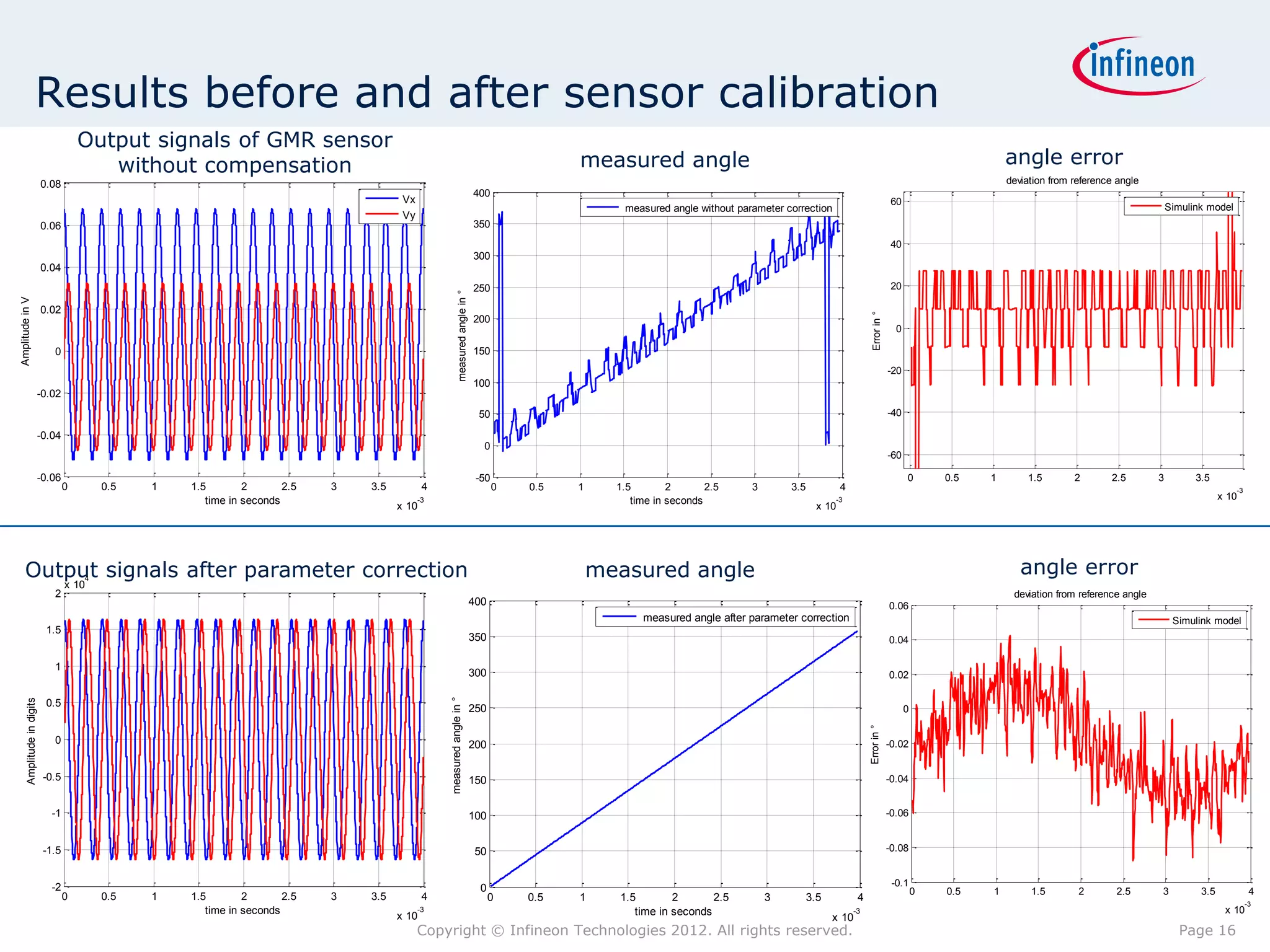
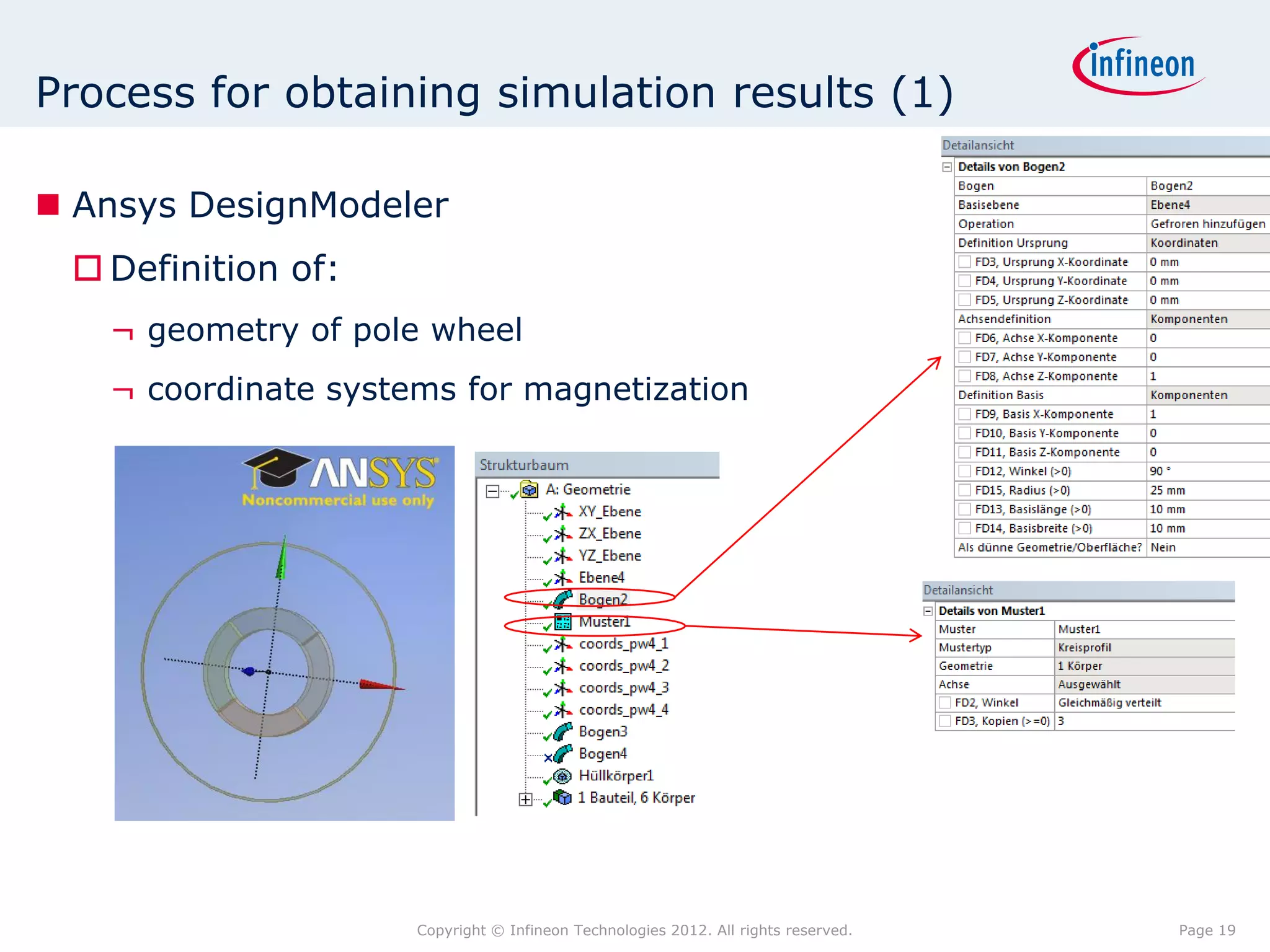
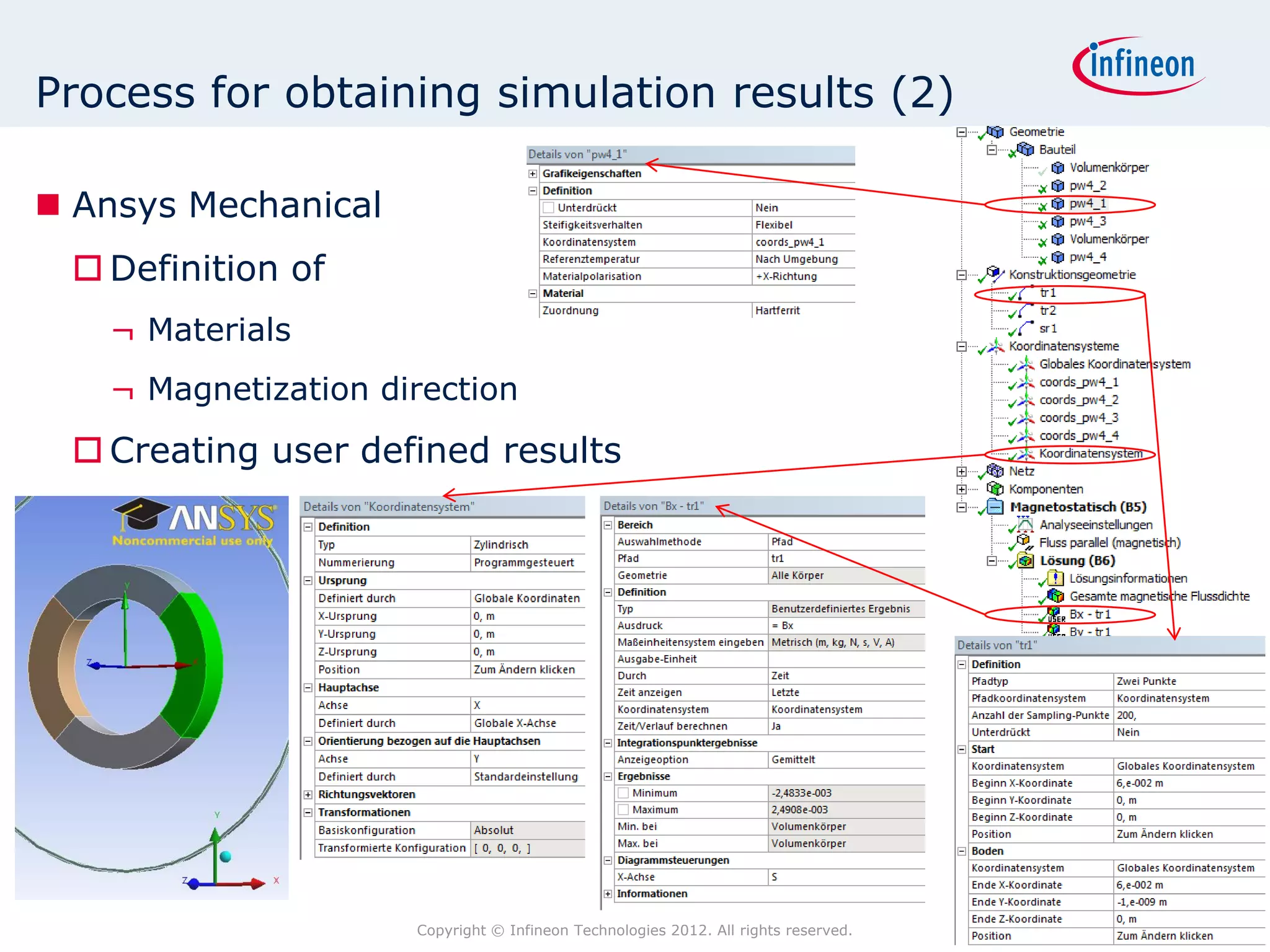
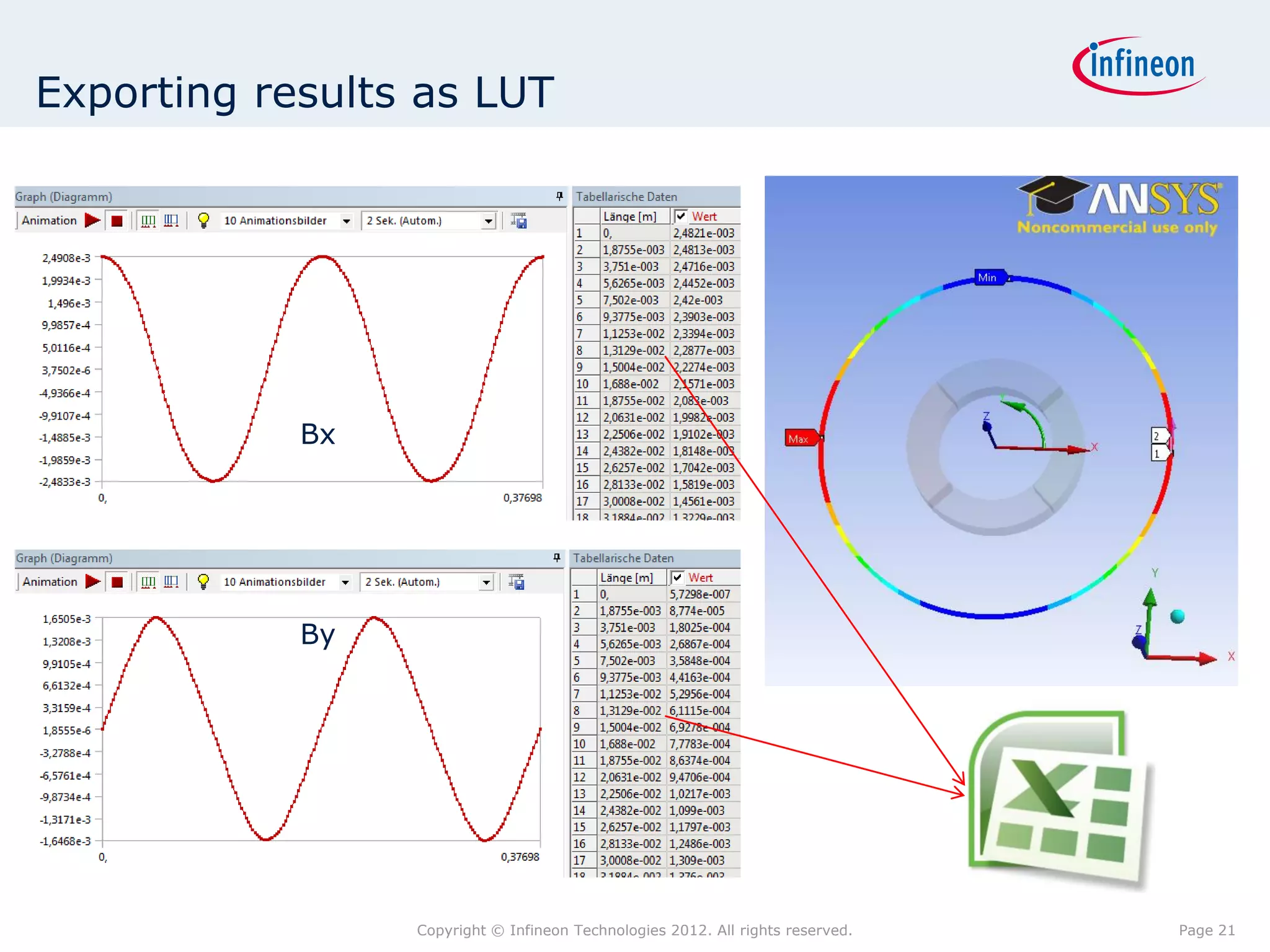
The document discusses simulating a magnetic angle measurement system using ANSYS and MATLAB/Simulink. It describes modeling the magnetic circuit of a permanent magnet and pole wheels using ANSYS, exporting the flux density results, and incorporating them into a Simulink model of a GMR sensor and signal conditioning circuit. The goals are to analyze error sources, optimize the design, and test sensor calibration techniques.