This document contains a series of questions and answers about project risk management processes and techniques:
1) It describes using decision tree analysis to evaluate options and determine which decision yields the greatest expected value when considering uncertainties.
2) Identify Risks is the process used to determine which risks may affect a project and document their characteristics.
3) Residual risks are risks that remain after risk responses have been implemented and deliberately accepted risks.
4) Contingency plans are planned in advance while workarounds are responses to unplanned risks that have occurred.
5) Establishing a contingency reserve for unplanned risks is an example of active risk acceptance.



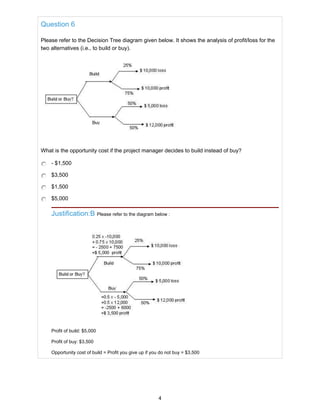
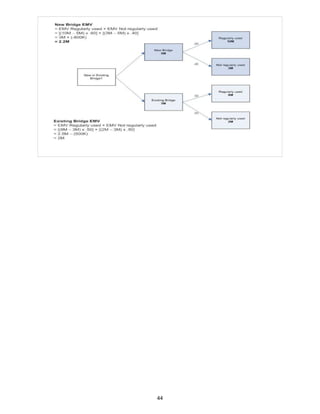
![Question 7
As part of the risk management process, you have just created an overall risk ranking of the
project and a list of prioritized identified risks which need additional analysis and determined
trends in risk analysis results. What should you do next?
Analyze the effect of identified risks on overall project objectives
Create a list of identified risks
Maintain a risk register
Make a list of potential responses to the risks
Justification:A Tasks like creating an overall risk ranking of the project, which includes a list of
prioritized risks, identifying which risks need additional analysis and determining trends in risk analysis
results are all outputs of Perform Qualitative Risk Analysis (PMBOK®
Guide - Fifth Edition, page 333). So, the
next step is Perform Quantitative Risk Analysis (i.e. analyze the effect of identified risks on overall project
objectives) -PMBOK®
Guide - Fifth Edition, page 333. Please note that options 2, 3, and 4 refer to outputs
from Identify Risks process which has already been completed - PMBOK®
Guide - Fifth Edition, page 327.
Question 8
In your project, probabilities are estimated and the alternatives are expected to be as follows:
25% probability for $ 25,000 profit
50% probability for $ 40,000 profit
25% probability for $ 100,000 profit
What is the expected profit in your project?
$ 40,000
$ 50,000
$ 51,250
$ 53,750
Justification:C Expected Profit = Sum of the products of Probability and Profit for all alternatives i.e.
[Sum of (Probability X Profit)] for all the three alternatives
=(0.25 x $ 25,000) + (0.50 x $ 40,000) + (0.25 x $ 100,000)
= $ 6250 + $ 20,000 + $ 25,000
= $ 51,250
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pmstudyprojectriskmanagementtest-160416195349/85/Pm-study-project-risk-management-test-5-320.jpg)










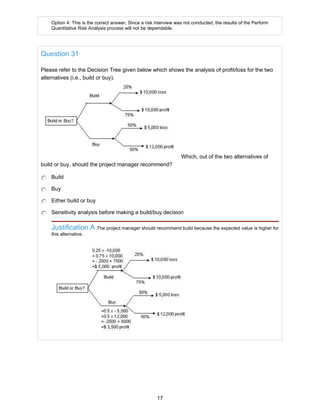


![Question 36
In your new project the objective is to develop a new drug. After doing financial analysis, your
finance manager provided you with these statistics:
30% probability of success with benefits of $700,000
70% probability of failure with loss of $300,000
Based on this information, you:
Suggest that the project should proceed.
Suggest that the project should be stopped.
Communicate to your senior management that you cannot take a decision whether to
proceed with the project or not.
Start working on the project and ask your finance manager for additional information.
Justification:C Expected Value of the project
= Expected Value of success (0.30 x $700,000) + Expected value of Failure [0.70 x (- $300,000)]
= $210,000 - $210,000
= 0
Since the Expected Value is "0", you cannot take a decision whether to continue with the project or not.
Question 37
In your project, you have just conducted a risk data quality assessment to evaluate the degree to
which the data about risks is useful for risk management. What is your next step?
Perform a structured review of project plans and assumptions, both at the total project and
detailed scope levels.
Develop checklists to identify risks based on historical information and knowledge that has
been accumulated from previous similar projects.
Conduct planning meetings to develop the risk management plan.
Conduct interviews to quantify the probability and impact of risks on project activities.
Justification: D Risk data quality assessment is a tool for Perform Qualitative Risk Analysis.
Option 4: This is the correct answer. It refers to "Interviewing" which is a tool and technique for Perform
Quantitative Risk Analysis. Perform Quantitative Risk Analysis is conducted after Perform Qualitative Risk
Analysis.
Option 1: This refers to Documentation Reviews which is a tool for Identify Risks. Identify Risks is conducted
before Perform Qualitative Risk Analysis.
Option 2: This refers to Checklist Analysis which is a tool for Identify Risks. Identify Risks is conducted before
Perform Qualitative Risk Analysis.
Option 3: This refers to "Meetings" which is a tool for Plan Risk Management process. Plan Risk
Management process is conducted before Perform Qualitative Risk Analysis process.
20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pmstudyprojectriskmanagementtest-160416195349/85/Pm-study-project-risk-management-test-20-320.jpg)