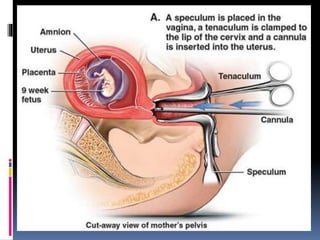
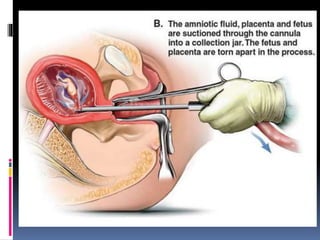
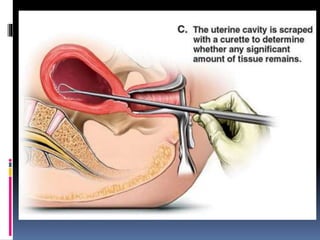
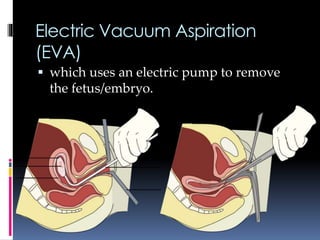
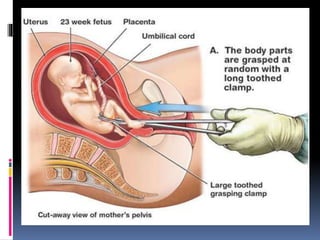
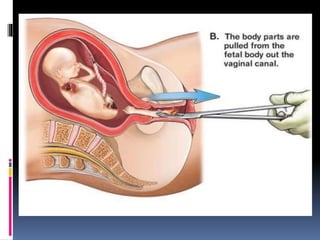
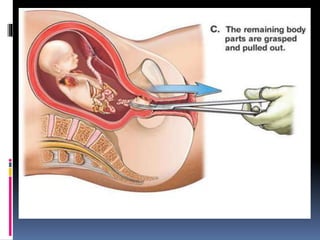
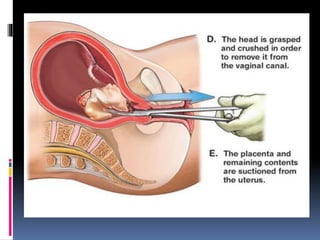
The document discusses abortion, including what it is, different types (induced and spontaneous), methods (medical and surgical), risks, and perspectives on the issue. Abortion is a procedure to end a pregnancy using medicine or surgery. There are two main types - induced abortions are intentionally terminated, while spontaneous abortions occur unintentionally. The two methods are medical, using abortion pills, or surgical vacuum aspiration or dilation and evacuation. Risks include infection, hemorrhaging, and damage to the uterus. Views on abortion consider both pros of access and health, and cons regarding moral and social impacts.