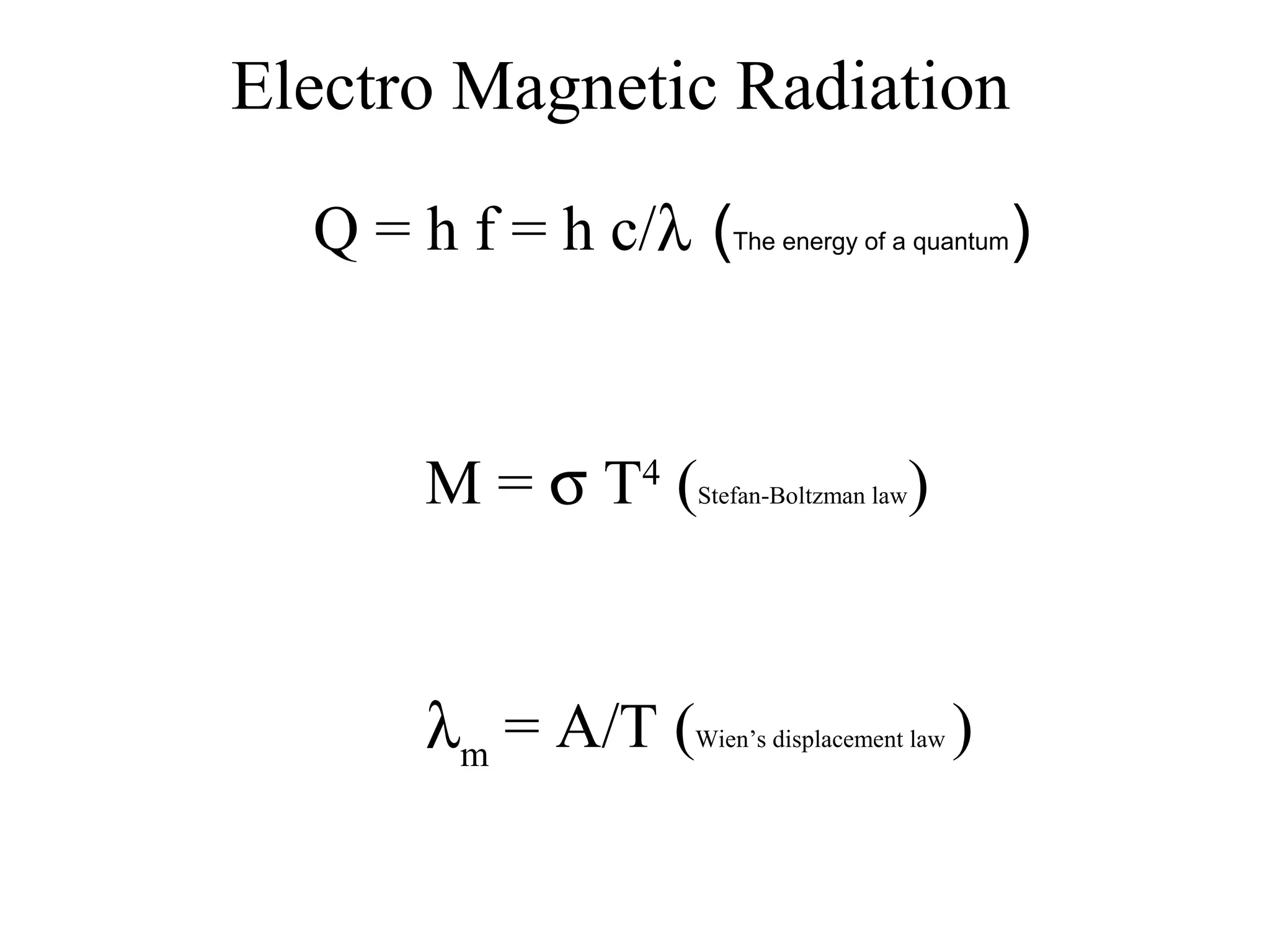
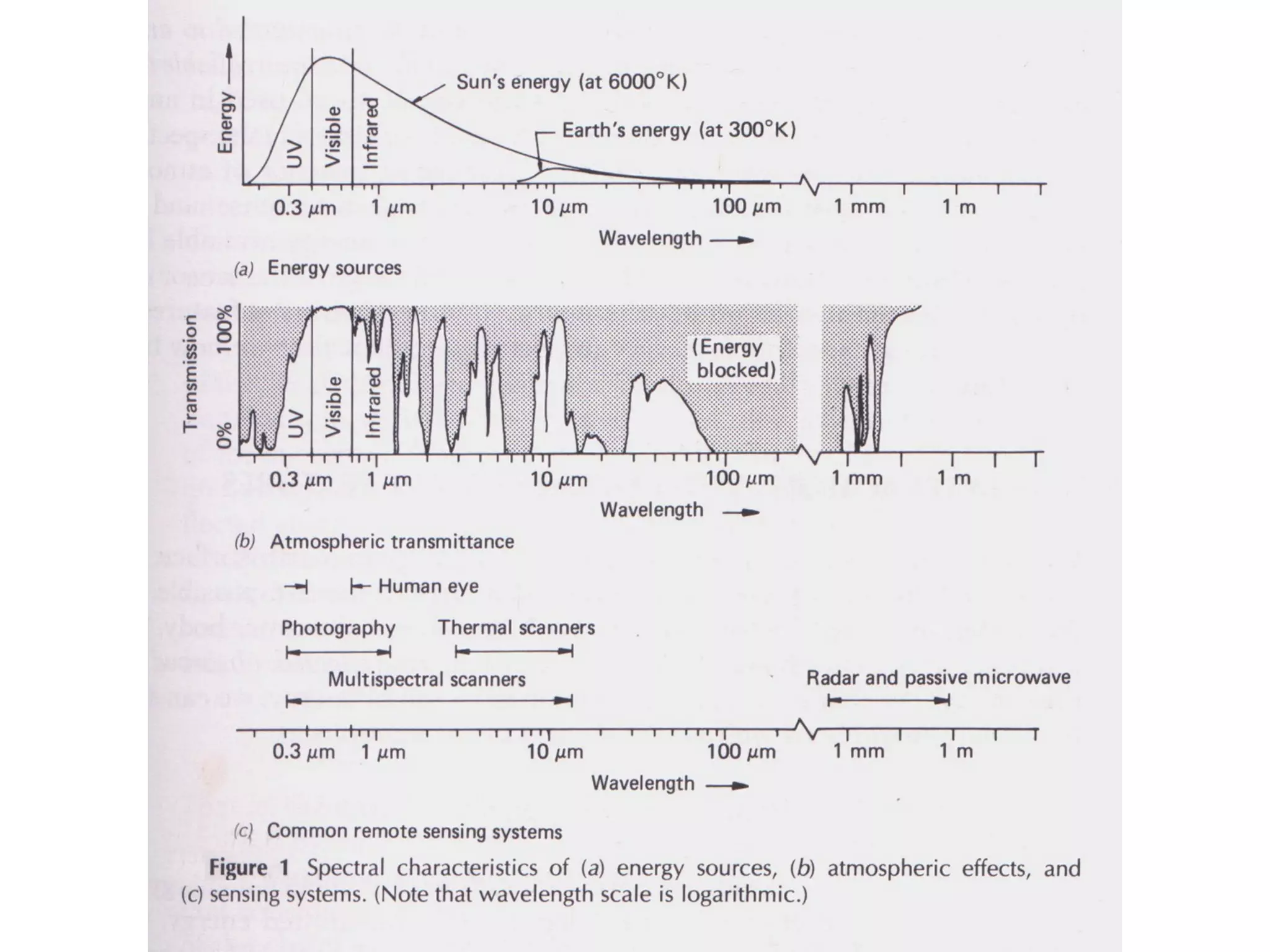
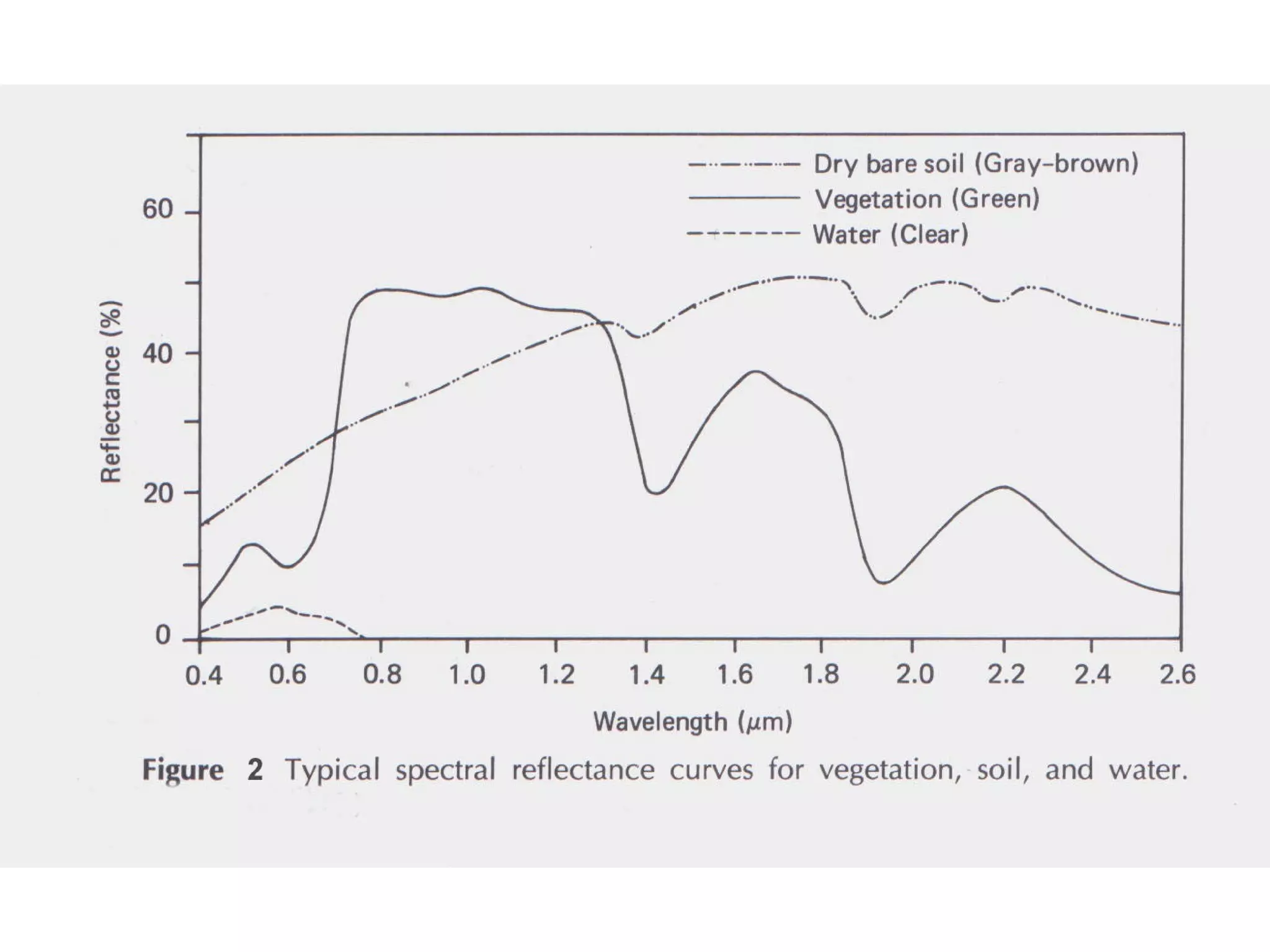
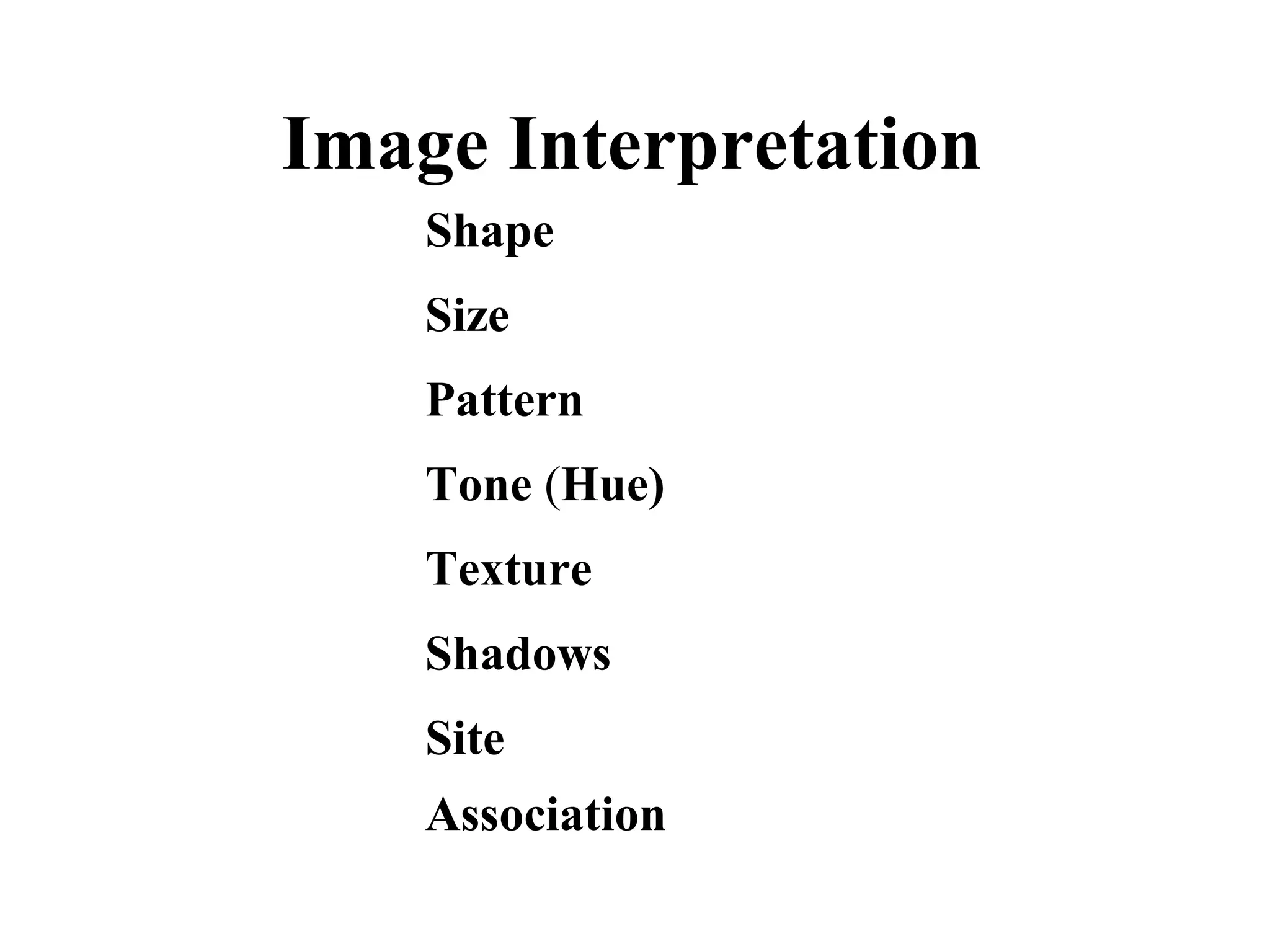
Remote sensing involves obtaining information about an object or area through analysis of data from a device not in direct contact. It uses electromagnetic radiation and various sensors to capture images. Atmospheric factors like absorption and scattering can influence images. Images have spatial, spectral, and radiometric resolution as well as temporal resolution. Interpretation examines shape, size, patterns, tones, textures, and shadows. Applications include land use mapping, geology, agriculture, forestry, wetlands, archaeology, and more. Remote sensing provides improved perspectives, permanent records, and access to inaccessible areas to assess natural resources.