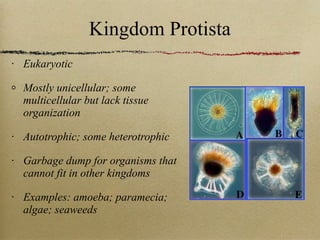
The document describes the six kingdoms of life - Eubacteria, Archaebacteria, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia. It provides key details about each kingdom, including whether they are prokaryotic or eukaryotic, unicellular or multicellular, and how they obtain nutrients (autotrophic or heterotrophic). Examples are given for common organisms from each kingdom.