Embed presentation
Downloaded 29 times



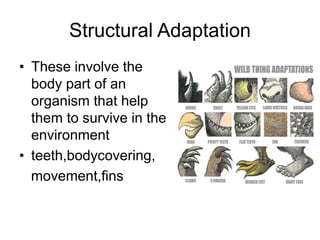




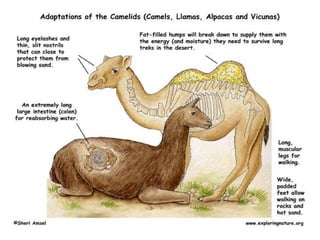
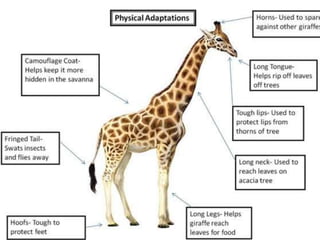
Animal adaptation refers to the biological process by which animals adjust to new environments or changes through structural, behavioral, camouflage, or physiological adaptations. Structural adaptations involve body parts like teeth or fins that help animals survive. Camouflage allows animals to blend in for protection. Behavioral adaptations include migration or hibernation. Physiological adaptations are internal processes like temperature regulation that help maintain homeostasis.









