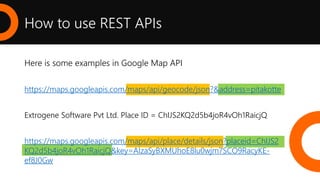
This document provides an overview of REST APIs, including:
1. What is an API and how it connects different platforms and applications.
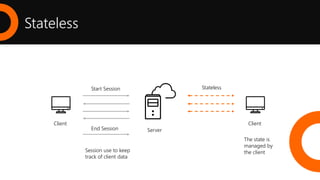
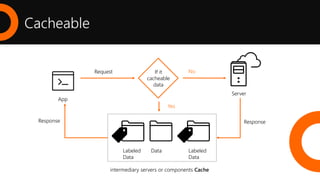
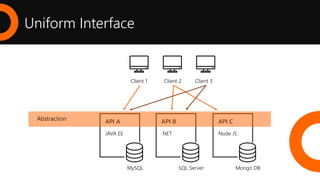
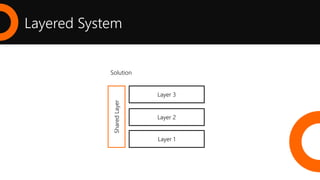
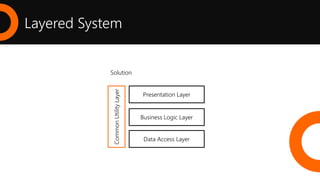
2. What is a REST API and the key architectural constraints it follows including being stateless, cacheable, having a uniform interface, and using a layered system.
3. An overview of HTTP as the most popular protocol for REST APIs and how it uses verbs like GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE to make requests.





![Message Formats
REST is not tied to a specific
message format.
• XML - Extensible Markup
Language
• JSON - JavaScript Object
Notation
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<Person>
<Name>Matt</Name>
<Surname>Van Der Westhuizen</Surname>
<Hobbies>
<Hobby>Boardgames</Hobby>
<Hobby>GameDev</Hobby>
<Hobby>Reading</Hobby>
</Hobbies>
<PhoneNumbers>
<PhoneNumber>
<Type>home</Type>
<Number>1234567890</Number>
</PhoneNumber>
<PhoneNumber>
<Type>cell</Type>
<Number>0821234567</Number>
</PhoneNumber>
</PhoneNumbers>
</Person>
{
"name": "Matt",
"surname": "Van Der Westhuizen",
"hobbies": [
"Boardgames",
"GameDev",
"Reading"
],
"phoneNumbers": [
{"type": "home", "number": "1234567890"},
{"type": "cell", "number": "0821234567"}
]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/restapis-blkgayan-171103032242/85/REST-API-15-320.jpg)