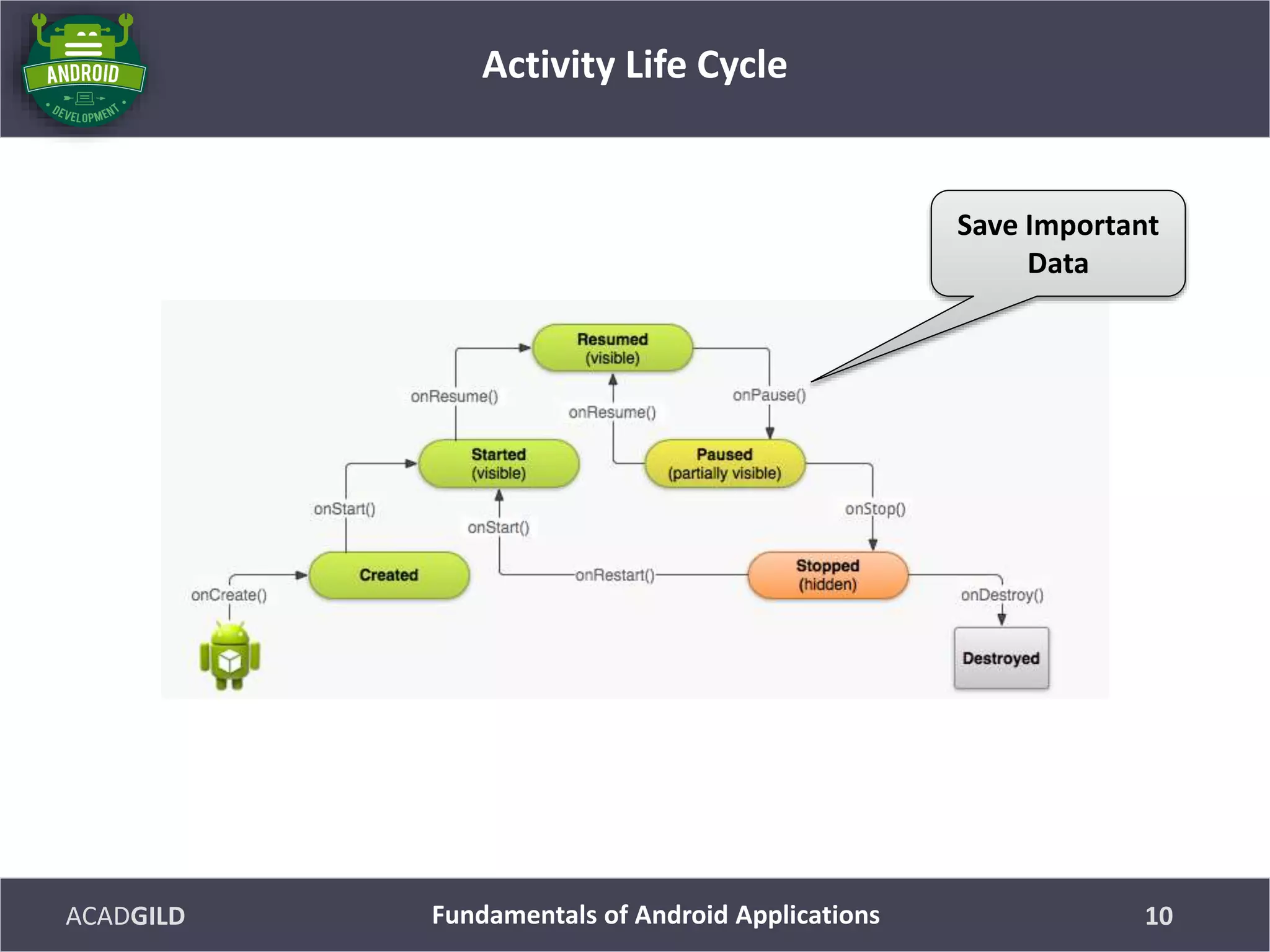
The document discusses the fundamentals of Android applications, including project structure, the Android manifest file, resources, activities and the activity lifecycle. It explains that the project structure includes folders for code, resources, Gradle files and libraries. The manifest declares application components and properties. Resources include files for images, strings, layouts and more. Activities represent screens with user interfaces and have a lifecycle that involves starting, resuming, pausing and stopping.


![ACADGILD
1. Some attributes have values that can be displayed to users — for example, a label and
an icon for an activity.
• The values of these attributes should be localized and therefore set from a resource
or theme.
• Resource values are expressed in the following format : @[package:]type:name
2. The package name can be omitted if the resource is in the same package as the
application, type is a type of resource — such as "string" or "drawable" — and name is
the name that identifies the specific resource.
• For example: <activity android:icon="@drawable/smallPic" . . . >
3. Values from a theme are expressed in a similar manner, but with an initial '?' rather
than '@‘.
• For Example: ?[package:]type:name
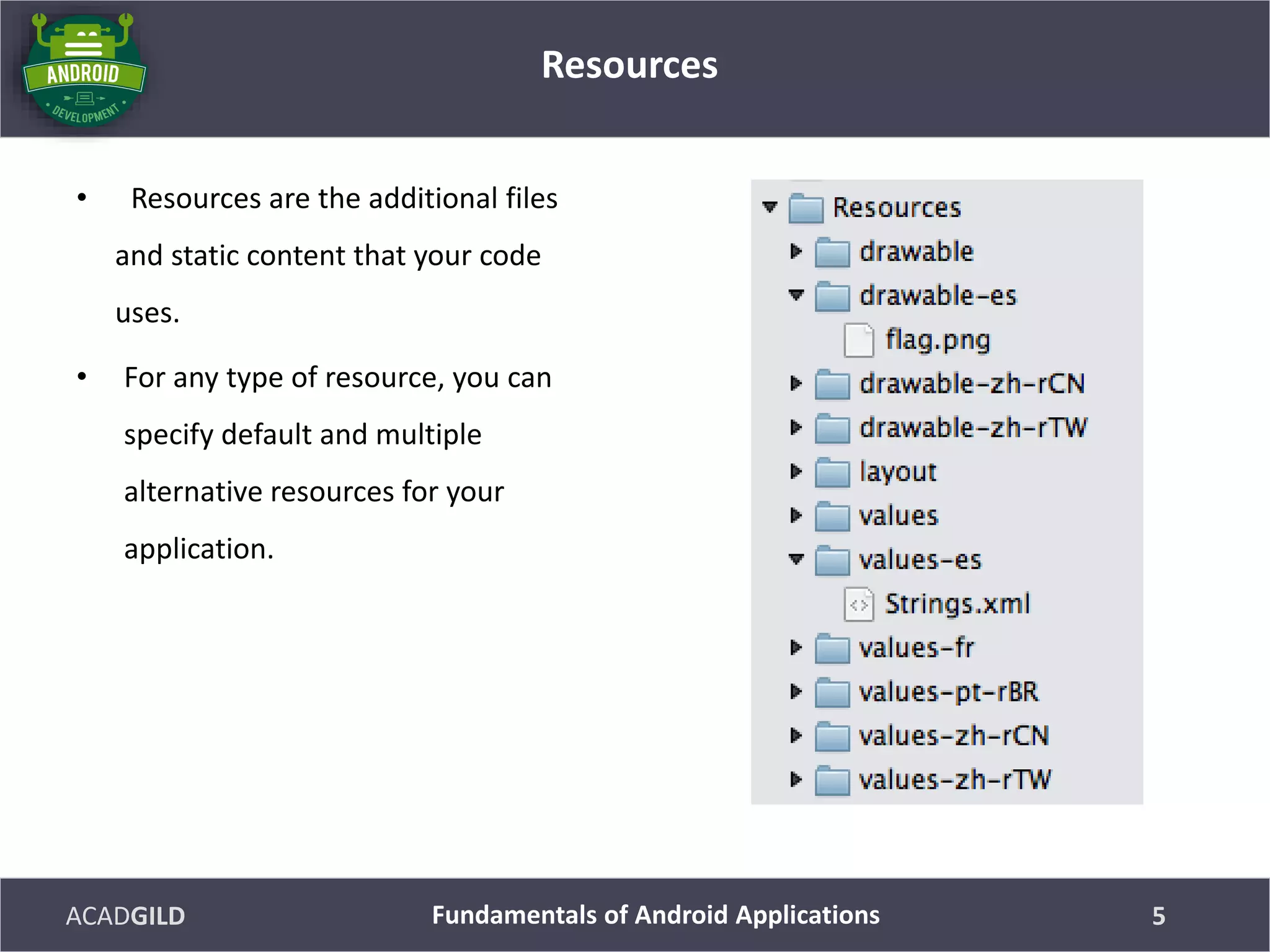
Resources
6Fundamentals of Android Applications](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/androidapplicationfundamentalsv1-160308074413/75/Android-Application-Fundamentals-6-2048.jpg)