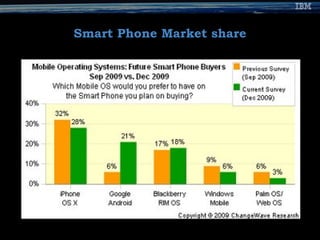
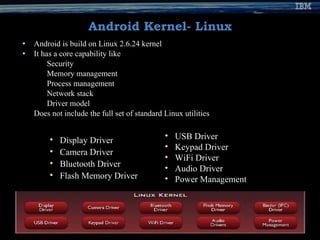
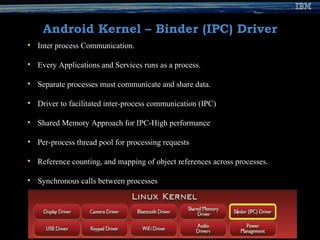
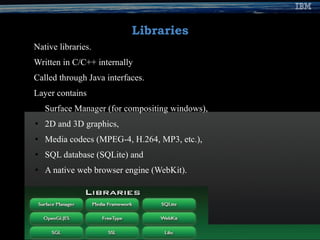
The document provides an overview of the Android mobile platform. It discusses the Android ecosystem and architecture, including the operating system, middleware, key applications, and development tools. The document outlines Android's open source nature, features like the Dalvik VM and app building blocks. It also provides references and contact information for the presenter.

























![IBMer [email_address] Android Evangelist bhavsidd@gmail.com Blogger www.bhavyavoice.blogspot.com Tweeter www.twitter.com/bhavis LinkedIn www.linkedin.com/in/bhavis Thank You !](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/androidanatomy-100306135547-phpapp02/85/Android-Anatomy-33-320.jpg)